Automatic Container Handling Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 434673 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 246 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Automatic Container Handling Market Size
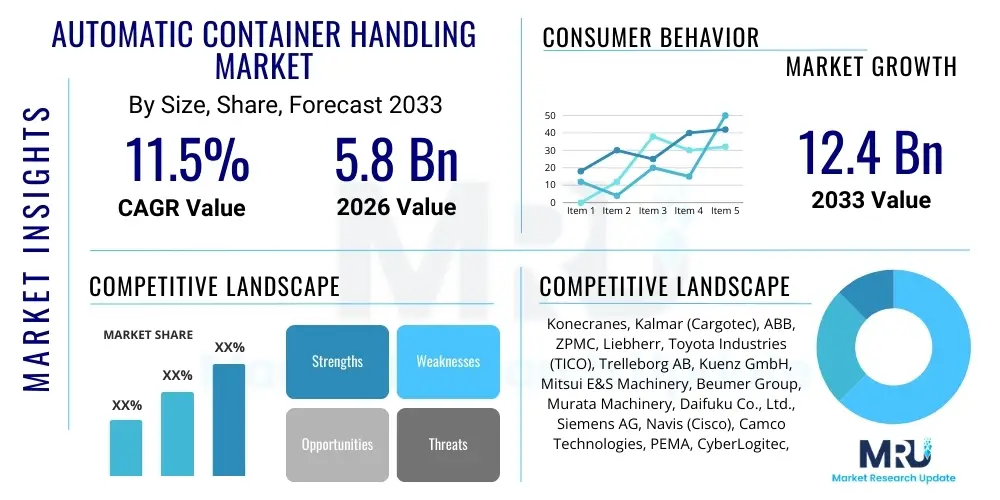
The Automatic Container Handling Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 5.8 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 12.4 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Automatic Container Handling Market introduction
The Automatic Container Handling Market encompasses the advanced technology, equipment, and integrated software solutions designed to facilitate the autonomous movement, stacking, loading, and unloading of standardized shipping containers within logistics hubs, primarily large seaports, intermodal terminals, and rail yards. This domain includes sophisticated machinery such as Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Automated Stacking Cranes (ASCs), and Rail Mounted Gantry (RMG) cranes, all centrally managed by Terminal Operating Systems (TOS). The core purpose of these automated systems is to significantly enhance operational throughput, mitigate human error, and ensure high levels of safety and predictability in high-volume environments, thereby modernizing global trade infrastructure to meet increasing demand.
Product descriptions within this market span hardware components like sensor arrays, control modules, power transmission systems, and heavy-duty vehicles, alongside mission-critical software. The software suite includes optimization algorithms for yard management, real-time data analytics, and integrated machine vision systems crucial for precise container identification and placement. Major applications are predominantly found in greenfield port development projects and large-scale brownfield retrofits where minimizing operational disruption and maximizing land utilization are paramount strategic objectives. Automation is seen not just as a labor substitute but as an essential enabler for 24/7 continuous operations, insensitive to typical shift limitations or fatigue factors.
The primary benefits driving market expansion include substantial reduction in long-term operational costs (OPEX), improved terminal security, and accelerated processing times for vessels and cargo. Key driving factors involve the exponential growth of global seaborne trade, the pervasive trend toward larger container vessels (Ultra Large Container Vessels or ULCVs) requiring faster turnaround times, and persistent challenges related to labor shortages and escalating wage costs in developed economies. Furthermore, governmental initiatives pushing for smarter, more sustainable, and digitally integrated transportation networks are providing crucial policy support, fostering accelerated adoption rates across major global shipping routes.
Automatic Container Handling Market Executive Summary
The Automatic Container Handling Market is characterized by a foundational shift from semi-automated processes to fully integrated, lights-out terminal operations, driven by competitive pressures among global port authorities to achieve peak efficiency metrics. Business trends indicate strong capital expenditure (CAPEX) allocations toward the integration of AI-driven optimization software, focusing heavily on predictive logistics and real-time resource allocation rather than mere machine replacement. The market structure remains moderately concentrated, with key players investing heavily in robotics and standardized modular automation kits that simplify deployment and reduce time-to-market for smaller-scale terminals. The prevailing sentiment is that early adopters, particularly those implementing holistic automation strategies encompassing both yard and quay side operations, will secure a decisive competitive advantage in the coming decade.
Regionally, Asia Pacific (APAC) stands as the undisputed leader, fueled by vast industrial growth, massive infrastructure investments in China and Southeast Asia, and the requirement to handle the world's largest volume of container throughput. European terminals are focusing on sophisticated system upgrades and eco-friendly automation solutions, utilizing existing infrastructure more intelligently. Meanwhile, North America is seeing steady adoption, primarily responding to acute labor union negotiations and the need to standardize processes across diverse geographic locations. Emerging markets in Latin America and the Middle East & Africa (MEA) are showing increasing potential, often adopting full automation in newly constructed port facilities as a leapfrogging strategy.
Segment trends reveal that the Hardware segment (especially AGVs and ASCs) commands the largest market share in terms of revenue, attributed to the high initial investment required for heavy machinery. However, the Software and Services segment is projected to exhibit the highest Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). This accelerating growth is driven by the necessity for sophisticated Terminal Operating Systems (TOS), advanced simulation software, and long-term maintenance contracts, which ensure operational reliability and continuous performance enhancement. The fully automated operation mode segment, while smaller in volume today, is expected to absorb a significant portion of future growth capital as technologies mature and integration risks decrease, becoming the benchmark for new terminal constructions globally.
AI Impact Analysis on Automatic Container Handling Market
User queries regarding AI's influence on automatic container handling frequently center on the tangible return on investment (ROI) derived from algorithmic optimization, the reliability of autonomous decision-making systems, and the implications for terminal cybersecurity and human workforce requirements. Common themes revolve around the ability of Artificial Intelligence to optimize container stacking patterns (yard allocation puzzles) beyond conventional heuristics, thereby minimizing unnecessary re-handles and maximizing yard density. Users are also keenly interested in how machine learning models enhance the predictability of equipment maintenance, shifting from scheduled maintenance to predictive and prescriptive protocols, thereby dramatically reducing unexpected downtime which is highly costly in port operations. A significant underlying concern is the integration complexity and the security vulnerabilities introduced by highly networked, intelligent systems.
AI's fundamental impact is redefining operational efficiency benchmarks, moving beyond simple automation to intelligent automation. Deep learning models are being deployed to analyze massive datasets generated by sensors across the terminal—weather conditions, traffic flow, crane movements, and power consumption—to create dynamic operational schedules. This dynamic scheduling capability allows the Terminal Operating System (TOS) to adapt in real time to unexpected events, such as delayed vessel arrivals or equipment failures, allocating resources optimally without human intervention. Furthermore, AI-powered computer vision systems are revolutionizing the accuracy of container tracking and damage assessment, ensuring higher fidelity in cargo handling processes and mitigating liability risks associated with misidentification or damage.
The integration of advanced reinforcement learning techniques is also being explored to train automated equipment, such as AGVs and ASCs, to navigate complex environments and handle variable loads more efficiently than static programming allows. This creates opportunities for more energy-efficient operations and smoother acceleration/deceleration profiles, leading to extended equipment lifespan. However, the reliance on high-quality data for training these models necessitates rigorous data governance and robust sensor infrastructure, representing a new set of technological challenges for port operators. The ethical implications surrounding autonomous decision-making in safety-critical scenarios also remains a key area of industry discussion and regulatory scrutiny, particularly concerning collision avoidance systems in shared operational zones.
- AI optimizes complex stacking algorithms, reducing re-handles by up to 15-20%.
- Predictive maintenance models decrease critical equipment downtime by forecasting failure points.
- Real-time autonomous resource allocation adapts terminal schedules to dynamic operational changes.
- Machine vision and deep learning enhance container identification accuracy and damage detection.
- Reinforcement learning improves the energy efficiency and path planning of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
- AI-driven cybersecurity monitoring is essential for protecting highly networked operational technology (OT) systems.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Automatic Container Handling Market
The Automatic Container Handling Market is significantly shaped by a powerful confluence of Driving forces, inherent Restraints, and transformative Opportunities, collectively defining the Impact Forces that dictate market direction and growth velocity. The overarching driving force is the imperative for efficiency gains mandated by the global logistics industry’s continuous expansion and the resultant pressure on infrastructure capacity. Simultaneously, high initial capital expenditure (CAPEX) requirements for system installation and complex integration challenges serve as primary restraints, often making full automation prohibitive for smaller or less financially robust port operations. Strategic opportunities, particularly in integrating next-generation technologies like 5G and hyper-automation, promise to overcome these restraints by lowering deployment costs and improving system communication reliability. These factors combine to create a fiercely competitive environment where technological adoption is not optional but essential for long-term viability.
Drivers include the accelerating adoption of standardized shipping protocols and the persistent global shortage of skilled labor willing to work in traditional port environments. The drive towards sustainability and decarbonization also acts as a potent driver; automated systems, particularly electrified AGVs and ASCs, typically offer superior energy efficiency compared to diesel-powered manual equipment. Furthermore, the advent of Ultra Large Container Vessels (ULCVs) necessitates parallel, high-speed handling operations that manual systems struggle to achieve reliably, compelling major ports to invest in automation simply to remain attractive destinations for mega-carriers. Regulatory changes supporting infrastructural digitization and smart port development further bolster these trends, providing governmental incentives and easing bureaucratic hurdles for modernization projects.
Conversely, significant restraints hinder widespread adoption. The primary restraint is the massive financial outlay and the extended payback period associated with automating existing brownfield sites, which often require fundamental civil engineering changes. Integration complexity, specifically the seamless interfacing of new automated machinery with legacy Terminal Operating Systems (TOS) and proprietary software from various vendors, presents another major technical hurdle. Labor resistance and union negotiations in highly industrialized ports also pose political and operational challenges, often delaying or complicating the implementation timelines. Opportunities, however, abound in the development of modular and scalable automation solutions tailored for mid-sized ports and inland terminals. The maturation of technologies like 5G private networks is providing reliable, low-latency connectivity, addressing historical communication bottlenecks, while advancements in digital twin technology allow for comprehensive simulation and de-risking of complex automation projects before physical deployment, thereby tackling the integration restraint head-on.
Segmentation Analysis
The Automatic Container Handling Market is comprehensively segmented based on its technological composition, the mode of operation utilized, and the specific application areas where these systems are deployed. This multi-dimensional segmentation allows for granular analysis of market demand drivers, investment patterns, and technological maturity across various sub-sectors. The market's complexity stems from the interplay between high-capital hardware components and sophisticated, high-value software that manages the entire operational ecosystem. Analyzing these segments provides strategic insights into where growth capital is most effectively utilized, identifying areas ripe for innovation, particularly in the integration of specialized services and next-generation control systems.
The segmentation by Component is critical, as it differentiates between the tangible, high-cost machinery (Hardware), the intellectual property driving efficiency (Software), and the ongoing support structures necessary for sustained performance (Services). Hardware, which includes cranes and vehicles, remains the foundation, but software, encompassing the Terminal Operating System (TOS) and proprietary optimization algorithms, increasingly determines competitive success. By Operation Mode, the distinction between Remote Operation (where human oversight is retained but conducted from a control room) and Fully Automated (requiring minimal to no human intervention in routine tasks) reflects the maturity and ambition of port authorities regarding automation levels. This maturity level directly influences the technological requirements and the CAPEX scale required for implementation.
Finally, the Application segment clarifies the end-user profile, predominantly dividing the market into Seaports and Intermodal/Rail Yards. Seaports, handling the vast majority of global cargo volume, represent the largest demand source, driven by the ULCV trend. Intermodal and Rail Yards, while smaller, are crucial growth segments due to the expansion of inland logistics hubs and the necessity for efficient transfer points between sea and land transportation modes. Successful market penetration requires vendors to tailor their systems—including specific crane types and vehicle guidance technologies—to the unique environmental and spatial constraints inherent in each application area, ensuring operational relevance and maximizing functional utility across the entire logistics chain.
- Component:
- Hardware (Automated Stacking Cranes (ASCs), Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Automated Rail Mounted Gantry (ARMG) Cranes, Sensors, Infrastructure)
- Software (Terminal Operating Systems (TOS), Simulation and Modeling Software, Optimization Algorithms, Maintenance and Diagnostics Software)
- Services (Integration and Implementation, Maintenance and Support, Consulting and Training)
- Operation Mode:
- Remote Operation
- Semi-Automated Operation
- Fully Automated Operation
- Application:
- Seaports and Maritime Terminals
- Intermodal and Rail Yards
- Inland Container Depots (ICDs)
Value Chain Analysis For Automatic Container Handling Market
The value chain for the Automatic Container Handling Market is complex, involving multiple specialized tiers from raw material sourcing and precision manufacturing to sophisticated software integration and long-term service provision. The upstream segment is dominated by heavy machinery manufacturers and specialized component suppliers responsible for producing steel structures, power transmission systems, high-precision sensors, and industrial automation control units. Quality control and supply chain reliability at this stage are paramount, as the durability and performance of the terminal equipment directly depend on these core components. Specialized engineering firms play a crucial role in the design and customization of gantry structures and vehicle chassis to meet specific port layout and weight requirements, ensuring compliance with stringent marine and industrial standards.
Midstream activities involve system integration, which is arguably the most critical stage. This phase includes the development and customization of proprietary Terminal Operating Systems (TOS), the installation of complex communication infrastructure (e.g., WLAN, 5G private networks), and the intricate process of integrating all hardware and software components into a seamless operational flow. System integrators must possess deep domain expertise in logistics, robotics, and IT to manage the immense technical risk associated with deploying these large-scale automation projects. The distribution channel predominantly follows a direct sales model, utilizing a consultative approach where vendors engage directly with port authorities and terminal operators throughout the planning, commissioning, and optimization phases, reflecting the high-value and customized nature of the solutions.
The downstream analysis focuses on the end-users—the port operators and logistics providers—who rely on post-implementation services for operational success. This includes comprehensive training for control room staff, long-term maintenance contracts, and continuous software upgrades to incorporate new optimization algorithms and security patches. Indirect influences on the value chain include financial institutions providing project financing, classification societies ensuring safety and standardization compliance, and academic institutions contributing research into optimization heuristics and robotics. The inherent longevity of port assets means the service and support segment retains high value over the product lifecycle, often generating sustained revenue streams that outweigh the initial machinery sale.
Automatic Container Handling Market Potential Customers
The primary consumers and buyers in the Automatic Container Handling Market are entities responsible for the ownership, management, and operation of large-scale logistics hubs globally, requiring substantial capital investment and long-term strategic planning. These entities typically fall into categories based on their financial backing and operational scope. Category one includes major governmental or semi-governmental port authorities (e.g., Port of Rotterdam, Shanghai International Port Group) that invest in automation as a national infrastructure priority to maintain or enhance their competitiveness in global trade flows. These customers generally target full automation for maximum long-term efficiency and are capable of absorbing the high initial capital outlay, viewing it as an essential strategic investment necessary to handle the burgeoning volume of ULCV traffic.
Category two comprises Global Terminal Operators (GTOs) such as Hutchison Ports, DP World, and APM Terminals. These private multinational corporations operate numerous ports globally and leverage automation to standardize operational processes across their diverse portfolio, maximizing economies of scale and knowledge transfer. GTOs often prefer modular and scalable solutions that can be rapidly deployed in both greenfield and brownfield environments, seeking technologies that demonstrate a clear, measurable return on investment (ROI) within a defined commercial timeframe. Their purchasing decisions are highly influenced by total cost of ownership (TCO) and proven reliability, favoring vendors with a strong global support network capable of servicing equipment across multiple continents and regulatory landscapes.
The third segment, increasingly important for market growth, consists of Inland Container Depots (ICDs), large rail operators, and specialized intermodal logistics companies. While their automation needs are typically smaller in scale than massive seaports, they require high-throughput, customized solutions designed for rapid container transfers between rail, road, and storage yards. These customers focus heavily on automated stacking solutions and precise yard management software to maximize limited inland space utilization. Their adoption is driven by the necessity to speed up the land-side leg of the supply chain, often utilizing smaller-scale AGVs and automated reach stackers tailored for internal distribution centers and railheads, ensuring the overall fluidity of end-to-end logistics operations.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 5.8 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 12.4 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 11.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Konecranes, Kalmar (Cargotec), ABB, ZPMC, Liebherr, Toyota Industries (TICO), Trelleborg AB, Kuenz GmbH, Mitsui E&S Machinery, Beumer Group, Murata Machinery, Daifuku Co., Ltd., Siemens AG, Navis (Cisco), Camco Technologies, PEMA, CyberLogitec, ORTS, Phoenix Contact, KION Group |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Automatic Container Handling Market Key Technology Landscape
The technological landscape of the Automatic Container Handling Market is characterized by the convergence of heavy industrial robotics with sophisticated Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) platforms, creating highly interconnected, intelligent systems. At the core are navigation and guidance technologies, which have evolved significantly from reliance on inductive wires and physical markers to advanced Differential GPS (DGPS), Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), and machine vision systems. These technologies enable precise, centimetre-level positioning of heavy machinery like AGVs and ASCs in dynamic environments, crucial for avoiding collisions and ensuring accurate container placement in tight stacking areas. Furthermore, high-bandwidth, low-latency communication networks, increasingly based on 5G or dedicated private LTE, are fundamental, supporting the massive data flow required for real-time control and synchronization of hundreds of automated assets simultaneously across vast terminal expanses.
The control systems architecture relies heavily on Terminal Operating Systems (TOS) that function as the central brain of the automated port, managing everything from vessel scheduling and berth planning to yard stacking optimization and equipment routing. Modern TOS platforms leverage sophisticated optimization algorithms, often incorporating machine learning, to solve the complex combinatorial problems inherent in efficient container logistics, such as minimizing unproductive moves (re-handles). Integration complexity demands the use of standardized communication protocols, such as industrial Ethernet and proprietary APIs, ensuring seamless interoperability between different hardware components from various suppliers, which remains a significant focus area for ongoing technological development and standardization efforts across the industry.
Crucially, the sustainability drive is pushing rapid technological advancements in electrification and energy management. Electrified Automated Rail Mounted Gantry (ARMG) cranes and battery-powered AGVs are replacing traditional diesel hydraulic systems, demanding robust charging infrastructure and intelligent battery management systems (BMS) to maintain 24/7 operational capability without compromising productivity. Simulation and Digital Twin technology have emerged as essential tools, allowing operators to model entire operational scenarios, test optimization algorithms, and validate system changes in a virtual environment before deployment. This reduces commissioning time and minimizes the operational risk associated with introducing new or upgraded automated handling equipment into live port environments.
Regional Highlights
- Asia Pacific (APAC): APAC dominates the global Automatic Container Handling Market, driven by its unparalleled volume of global manufacturing and trade, particularly concentrated in rapidly developing coastal regions of China, South Korea, and Southeast Asia. The region is characterized by large-scale greenfield projects (newly built ports) that implement full automation from inception, aiming for world-record throughput capabilities. Government support for massive port infrastructure modernization, coupled with the necessity to manage high traffic density efficiently, secures APAC’s position as both the largest revenue contributor and the fastest-growing market. Countries like Singapore, Shanghai, and Busan lead in deploying cutting-edge AI and 5G integrated terminal solutions, setting global benchmarks for technological adoption.
- Europe: Europe represents a mature and technologically sophisticated market focusing heavily on optimizing brownfield sites—retrofitting existing terminals with automated solutions to maintain competitive edge and adhere to stringent environmental regulations. European ports, such as Rotterdam and Hamburg, prioritize sustainability, leading to high adoption rates of electric and hybrid automated equipment, and advanced remote operation centers designed to enhance worker safety and terminal efficiency within constrained geographical footprints. Innovation often centers on software optimization, interoperability standards, and the integration of automation into complex intermodal networks connecting sea, rail, and road transport throughout the continent.
- North America: The North American market is experiencing steady growth, motivated primarily by persistent labor challenges, the need for enhanced security, and the necessity to handle larger vessel sizes arriving through expanded waterways like the Panama Canal. Adoption is often cautious and phased (semi-automation transitioning to full automation), driven by individual port authority strategic mandates and often constrained by complex union agreements. The focus is on leveraging automated stacking cranes (ASCs) and utilizing remote operation capabilities to maximize terminal utilization, particularly in densely populated coastal areas like Southern California and the Eastern Seaboard.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): MEA is an emerging, high-potential market, particularly the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations. These regions are investing heavily in new strategic ports (e.g., Jebel Ali, Khalifa Port) as global transshipment hubs, often implementing full automation as a core part of their economic diversification strategies. These projects benefit from ample space and funding, allowing them to install the latest generation of automated equipment and software architecture. Africa, while slower, presents opportunities for smaller, scalable, modular automation solutions tailored for rising regional trade volumes and improving infrastructure quality.
- Latin America (LATAM): LATAM remains a developing market characterized by selective adoption in key trade hubs (e.g., Brazil, Chile, Mexico). Growth is highly dependent on commodity trade stability and foreign direct investment. While facing significant economic hurdles, key strategic ports are incrementally investing in semi-automation (remote operation of existing equipment) and software upgrades to improve gate efficiency and yard productivity, aiming for incremental efficiency gains before committing to the full capital outlay required for complete automation.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Automatic Container Handling Market.- Konecranes
- Kalmar (Cargotec)
- ABB
- ZPMC (Shanghai Zhenhua Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.)
- Liebherr
- Toyota Industries Corporation (TICO)
- Trelleborg AB
- Kuenz GmbH
- Mitsui E&S Machinery Co., Ltd.
- Beumer Group
- Murata Machinery, Ltd.
- Daifuku Co., Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Navis (Cisco Systems, Inc.)
- Camco Technologies
- PEMA
- CyberLogitec
- ORTS
- Phoenix Contact
- KION Group
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Automatic Container Handling market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What are the primary factors contributing to the high initial investment (CAPEX) in automatic container handling systems?
The high initial CAPEX is primarily driven by the cost of specialized, heavy-duty automated machinery (such as Automated Stacking Cranes and AGVs), the sophisticated sensor and guidance technology required for precise operation, and the significant expenses associated with developing, integrating, and customizing the complex Terminal Operating Systems (TOS) necessary to manage the entire automated ecosystem.
How does automation impact the safety and security protocols within modern container terminals?
Automation significantly enhances safety by removing personnel from high-risk operational areas where heavy machinery operates, thereby reducing accidents caused by human error or fatigue. Security is improved through centralized, monitored control systems and enhanced perimeter protection, often leveraging AI-powered surveillance and real-time anomaly detection to prevent unauthorized access or cargo tampering.
What is the typical Return on Investment (ROI) timeframe for a fully automated container terminal?
While highly variable based on terminal throughput and labor costs, the typical ROI timeframe for a fully automated greenfield terminal ranges between 8 to 12 years. This is achieved through substantial savings in operational expenditure (OPEX), particularly reduced energy and labor costs, coupled with enhanced revenue generation from drastically improved vessel turnaround times and higher yard density.
Which technological component offers the highest growth potential in the automatic container handling market?
The Software and Services segment, specifically advanced Terminal Operating Systems (TOS) and AI-driven optimization algorithms, offers the highest growth potential. This is due to the increasing demand for continuous system performance improvement, predictive maintenance solutions, and the necessity for sophisticated software to maximize efficiency derived from existing hardware investments.
What role does 5G technology play in advancing container terminal automation?
5G technology is crucial as it provides the ultra-reliable, high-bandwidth, and low-latency connectivity required for real-time communication between hundreds of autonomous machines and the centralized control system. This ensures instantaneous data transmission necessary for synchronized crane movements, obstacle avoidance, and remote monitoring, enabling truly seamless, fully automated operations across wide geographical terminal areas.
The Automatic Container Handling Market is experiencing a paradigm shift propelled by technological maturity, economic imperatives, and globalization trends. The transition from labor-intensive conventional operations to highly efficient, capital-intensive automated systems defines the competitive landscape of modern logistics. The integration of Artificial Intelligence and advanced robotics is transforming terminal efficiency, moving the industry toward predictive operations and hyper-optimization. This widespread adoption is accelerating in response to the pressure of accommodating larger vessels and meeting rigorous sustainability targets, cementing automation as a prerequisite for future growth in global trade infrastructure. Regional disparities in investment capacity and existing infrastructure necessitate diverse solutions, ranging from full greenfield automation in Asia Pacific and the Middle East to sophisticated brownfield retrofitting in established European ports. The market outlook remains robust, characterized by sustained investment in software, integration services, and electric propulsion technologies, confirming its trajectory toward becoming a fully digitized and interconnected global logistics network. The demand for highly reliable, scalable, and secure automated solutions will continue to drive innovation and consolidation among key market players as they vie to offer comprehensive, end-to-end terminal automation packages essential for navigating the complexities of modern supply chains.
The key challenge remains mitigating the high upfront cost and the complexity associated with integrating varied proprietary systems, which often slows the pace of adoption, particularly in emerging economies and legacy terminals. However, the maturation of modular automation concepts, combined with standardization efforts spearheaded by industry leaders and regulatory bodies, is expected to gradually reduce these barriers. Furthermore, the strategic imperative to achieve higher throughput and faster vessel turnaround times, directly impacting global supply chain resilience, overrides these financial and technical hurdles for major port operators. As labor costs rise globally and the need for 24/7 continuous operation becomes standard, the cost-benefit analysis decisively favors long-term automation investments. The future of container handling is definitively automated, intelligent, and deeply integrated into the overarching digital framework of global logistics.
Technological advancements, particularly in sensor fusion, real-time data analytics, and digital twin simulation, are making automation accessible and reliable across a broader spectrum of operational conditions, including adverse weather and complex yard geometries. The competitive edge in the market is increasingly shifting from who can build the largest cranes to who can provide the most intelligent, resilient, and adaptive Terminal Operating System. This drives continuous research and development into software solutions that can dynamically manage complex resources and prevent bottlenecks before they occur. The Automatic Container Handling Market is therefore positioned not just as an equipment market, but as a critical segment of the industrial IoT and AI application domain, essential for the efficient functioning of the global economy. The forthcoming years are projected to feature strong collaborations between traditional heavy machinery manufacturers and specialized AI/software firms, pooling expertise to deliver next-generation, integrated solutions that redefine operational productivity and safety standards worldwide.
As geopolitical landscapes continue to influence trade flows, the agility and resilience provided by automated terminals become paramount strategic assets. Ports equipped with advanced automated systems are better positioned to handle unexpected volume surges or shifts in shipping routes with minimal operational strain. This strategic advantage further cements the business case for adopting full automation, particularly for ports aiming to serve as crucial transshipment hubs. Moreover, the focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors is increasingly tying investment decisions to the implementation of clean, electric automated machinery, aligning market growth with broader global sustainability objectives. This comprehensive interplay of economics, technology, and environmental responsibility ensures that the Automatic Container Handling Market will remain a dynamic and high-growth sector throughout the forecast period.
The continued evolution of the Automatic Container Handling market will see a strong emphasis on cybersecurity measures, given the reliance on networked OT systems. Protecting these critical infrastructure assets from cyber threats is becoming a major operational and investment priority for port authorities. Solutions involving advanced encryption, network segmentation, and real-time threat detection are being integrated directly into the core automation systems. Furthermore, the development of standardized training programs and certifications for technical staff managing these complex automated environments will be essential to ensure operational readiness and minimize human-caused disruptions, supporting the long-term reliability and performance of automated terminals globally.
The push towards 'port community systems'—integrated platforms that connect various stakeholders, including customs, trucking companies, and terminal operators—is also being accelerated by automation. Automated handling provides the high-fidelity, real-time data necessary for these community systems to function effectively, streamlining the entire cargo journey from vessel to final destination. This level of transparency and integration enhances predictive capabilities across the supply chain, benefiting all participants and further cementing the necessity of intelligent automation at the physical handling layer. Consequently, market participants are increasingly focusing on delivering solutions that are not only efficient within the terminal gates but are also connective and cooperative with the broader digital logistics ecosystem, leveraging the terminal's automated data streams as a strategic asset.
In terms of equipment specialization, the market is witnessing growing demand for smaller, more flexible Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) capable of operating in mixed traffic environments, especially in complex brownfield sites and intermodal yards. This shift balances the necessity for automation with the practical constraints of existing infrastructure, providing scalable entry points for terminal operators hesitant to commit to large-scale infrastructure overhauls. Similarly, the development of automated straddle carriers and automated reach stackers, capable of adapting to varying container stacking heights and density requirements, expands the addressable market beyond traditional yard cranes, offering versatile automation solutions for diverse terminal types and operational profiles globally.
Looking forward, the competitive dynamics will likely involve deeper collaborations and strategic mergers and acquisitions between industrial equipment providers and specialized software/robotics firms. This consolidation aims to offer seamless, single-source solutions that simplify procurement and integration for port operators. The focus on predictive maintenance, achieved through embedded sensors and AI analytics, is set to revolutionize service offerings, guaranteeing higher uptime and lower long-term maintenance costs. These service-centric business models, relying on continuous data feedback loops, will establish strong, recurring revenue streams for market leaders, shifting the value proposition further toward intelligent operational services rather than purely hardware provision.
The impact of rising energy costs globally further reinforces the appeal of automated electric solutions. The precision control offered by automated systems minimizes wasted motion and optimizes energy consumption compared to manual operations, providing a clear economic and environmental benefit. This aligns perfectly with the increasing governmental and public pressure on the shipping and logistics sector to significantly reduce carbon emissions. Consequently, the adoption of electric Automated Stacking Cranes (e-ASCs) and battery-powered AGVs is becoming standard practice in new terminal specifications, driven by both regulatory compliance and compelling long-term operating cost advantages. This dual pressure ensures that energy-efficient automation remains a central technological trend.
Furthermore, standardization efforts regarding the interfaces between various automated equipment (e.g., between cranes and yard vehicles) are becoming crucial for reducing integration risk. Proprietary interfaces have historically complicated multi-vendor environments, but industry initiatives promoting open standards and interoperability are addressing this challenge. Success in this market will increasingly depend on a vendor's ability to offer open, modular platforms that integrate easily with existing infrastructure and are compatible with future technological upgrades, ensuring long-term flexibility and minimizing vendor lock-in for terminal operators navigating rapid technological change.
The long-term vision of the market involves 'lights-out' operation for the majority of core container handling tasks, pushing human involvement entirely to supervision, remote monitoring, and complex exception handling. This shift necessitates significant investment not only in technology but also in retraining the existing workforce to manage complex automated systems and interpret predictive analytics outputs. The market for training, simulation, and digital workforce management tools is therefore experiencing rapid growth, forming an essential services sub-segment necessary to unlock the full potential of automated terminal investments globally and ensure operational continuity.
The regulatory environment is also evolving to accommodate autonomous operations. International maritime organizations and local port authorities are developing new standards and certification processes for automated equipment and operational protocols, particularly concerning safety in shared operational spaces and compliance with environmental mandates. These regulatory frameworks provide necessary guidance and assurance, facilitating wider industry confidence and faster technology deployment. Compliance with these stringent new standards will be a key differentiator for leading solution providers, affirming their commitment to safety and operational excellence in the automated environment.
Finally, the role of Big Data analytics is becoming indispensable. Terminals generate terabytes of data daily on equipment performance, energy use, container movements, and waiting times. Leveraging this data through AI and deep learning enables operators to gain unprecedented visibility into operational bottlenecks and resource inefficiencies. This data-driven approach to continuous improvement is accelerating the optimization lifecycle of automated terminals, turning them into self-learning, highly adaptive logistical hubs capable of responding dynamically to global trade fluctuations and operational challenges. The ability to harness and effectively utilize this operational data is emerging as the ultimate competitive tool in the Automated Container Handling Market.
The market also reflects a growing trend towards customization and specialized automation solutions tailored for niche logistical needs, such as handling refrigerated containers (reefers) or dangerous goods. These specialized requirements necessitate bespoke automated systems and specific software protocols to ensure compliance and safety, driving innovation in areas like automated cold chain management within the terminal environment. This segmentation ensures that automation is not a one-size-fits-all solution but a scalable, adaptable technology capable of meeting the diverse, high-stakes requirements of modern global trade.
Further emphasizing regional nuances, the market in North America continues to see strong investment in integrating rail-side automation, focusing on high-speed transfer capabilities between port terminals and inland rail networks. The goal is to rapidly clear cargo from the quayside, reducing congestion and enhancing the overall fluidity of the intermodal supply chain. This requires automated gantry cranes and transfer systems capable of handling complex loading sequences and varied rail car types, a technological specialization distinct from the high-density yard stacking requirements prevalent in many APAC ports. These varying regional priorities underscore the need for vendors to maintain a flexible and comprehensive product portfolio.
The technological push for remote commissioning and remote acceptance testing is gaining momentum, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with terminal construction and system integration. By using virtual environments and digital twin technology, complex automation systems can be tested and validated off-site, minimizing on-site disruption and accelerating the transition to live operation. This methodology not only improves project delivery timelines but also enhances the safety of the commissioning process, proving crucial for global deployment models where expert engineering teams may be geographically distant from the physical terminal site. This remote capability is set to become a standard offering in the market.
The strategic importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As automated ports are classified as critical national infrastructure, the integrity of their control systems is paramount. The market is increasingly seeking solutions that embed security features directly into the operational technology (OT) hardware and software layers, rather than relying solely on traditional IT-level perimeter defenses. This 'security-by-design' approach ensures that the automated equipment itself is resilient to both internal and external threats, addressing the heightened risk profile associated with highly connected, complex industrial automation systems.
Finally, the market growth is intrinsically linked to macro-economic indicators, particularly global GDP and trade agreements. While automation provides operational stability against short-term market fluctuations, sustained capital expenditure is reliant on a positive long-term outlook for global trade volumes. The market performance is therefore highly sensitive to geopolitical shifts and protectionist policies, which can directly impact container throughput projections and, consequently, the willingness of port authorities to undertake multi-billion dollar automation projects. Despite these external risks, the fundamental requirement for increased efficiency and reduced operational costs continues to drive resilient demand for automated handling solutions worldwide.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
