Binders Excipients Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 438814 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 251 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Binders Excipients Market Size
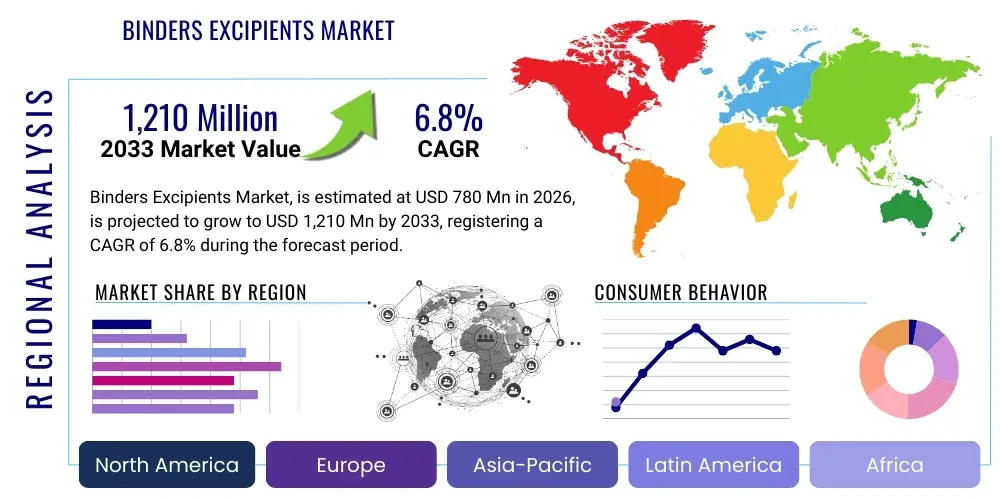
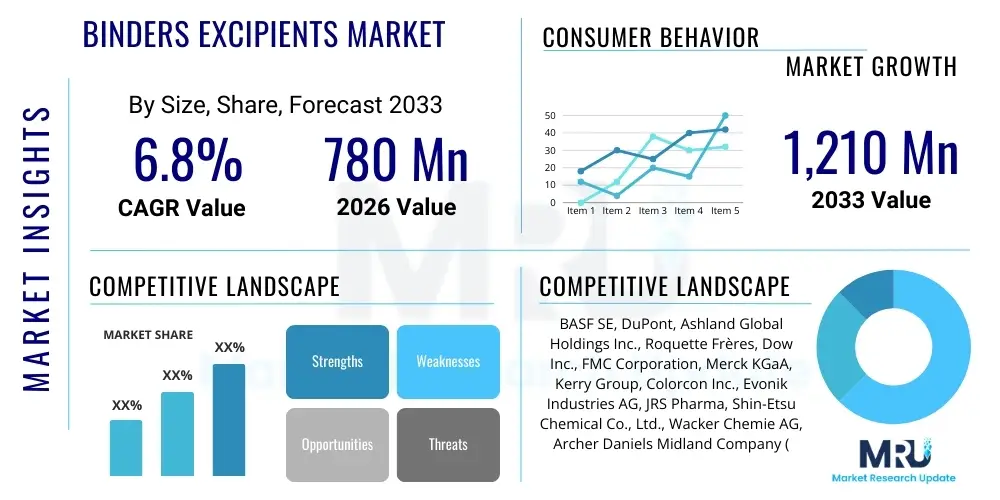
The Binders Excipients Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.8% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at $780 million in 2026 and is projected to reach $1,210 million by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Binders Excipients Market introduction
Binders excipients are essential functional ingredients utilized primarily within the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and food industries. These substances are crucial for ensuring the mechanical integrity of solid dosage forms, such as tablets and granules, by promoting particle adhesion and cohesion. Common examples include cellulose derivatives (like MCC and HPMC), natural gums, starch, and various synthetic polymers (like PVP). The selection of an appropriate binder is critical for the manufacturing process, influencing factors such as tablet hardness, disintegration time, and ultimately, the dissolution profile and bioavailability of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). The increasing complexity of drug formulations, particularly those involving high-dose or poorly soluble APIs, necessitates the use of high-performance binders that can facilitate advanced processing techniques like direct compression.
The primary application of these excipients lies in tablet compression and granulation processes, where they provide the necessary binding force to form robust and stable dosage units. In pharmaceuticals, binders ensure that tablets withstand mechanical stress during handling, packaging, and consumption without premature crumbling. Beyond structural integrity, certain functional binders also play a dual role, aiding in controlling the release kinetics of the drug. The market is characterized by a continuous demand driven by the robust growth of the global generic drug sector and the increasing adoption of continuous manufacturing technologies, which require specialized excipient properties for high-speed processing and consistent quality control. The regulatory environment also plays a significant role, demanding high purity and consistency for all ingredients used in therapeutic products.
Major driving factors fueling this market include the global expansion of the elderly population, which requires increasing volumes of oral solid dosage forms, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases demanding continuous medication. Furthermore, innovation in drug delivery systems, such as mucoadhesive and orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs), is pushing manufacturers to develop novel binder excipients with enhanced functional properties. The benefits associated with high-quality binders—including improved tablet stability, predictable drug release profiles, and efficient manufacturing throughput—make them indispensable components in modern drug formulation. The shift toward specialized excipients that reduce manufacturing steps, such such as those enabling direct compression, further consolidates their market importance.
Binders Excipients Market Executive Summary
The Binders Excipients Market demonstrates robust commercial momentum, principally driven by innovation in pharmaceutical manufacturing techniques and the increasing focus on patient adherence via novel dosage forms. Business trends indicate a strong move toward co-processed and multi-functional excipients, which allow formulators to simplify processes, reduce costs, and enhance the performance of the final product. Key industry players are focusing on expanding production capacity for polymers like MCC and PVP, while also investing in sustainable sourcing and production methods to align with global environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards. Strategic partnerships between excipient manufacturers and pharmaceutical companies are becoming common, facilitating the co-development of customized excipient solutions tailored for specific API characteristics and advanced drug delivery requirements.
Regional trends highlight Asia Pacific (APAC) as the fastest-growing market, primarily fueled by massive expansion in the domestic generic drug manufacturing sectors in China and India, coupled with increasing regulatory harmonization across the region favoring quality excipients. North America and Europe maintain dominance in terms of market value due to the presence of major biopharmaceutical companies and stringent regulatory requirements that mandate high-quality, traceable excipients. Furthermore, demand in developed regions is increasingly concentrated on premium, specialized binders required for complex formulations, including biologics and personalized medicine approaches. Investment in R&D infrastructure across these major regions ensures continued innovation in excipient functionality and processing efficiency.
Segment trends underscore the dominance of natural binders, particularly cellulose derivatives, due to their broad compatibility, established safety profile, and versatility in various formulation technologies. However, the synthetic polymers segment, including Povidone and Crospovidone, is exhibiting rapid growth owing to their superior binding strength and utility in enabling advanced drug release mechanisms. Within applications, the pharmaceutical segment remains the largest consumer, but the nutraceutical industry is rapidly increasing its market share, driven by consumer demand for immune boosters, vitamins, and dietary supplements frequently delivered in tablet form. Formulators are continuously balancing the need for cost-effective bulk binders with the necessity for highly functional specialty excipients to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
AI Impact Analysis on Binders Excipients Market
Common user questions regarding AI's impact on the Binders Excipients Market revolve around how artificial intelligence can accelerate the discovery of novel excipients, optimize formulation processes, and enhance supply chain resilience. Users are particularly concerned with AI's potential to predict excipient-API interactions, thereby reducing time-consuming experimental trials and minimizing the risk of batch failures or unexpected stability issues. There is significant interest in understanding how machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets concerning powder flow characteristics, compressibility, and dissolution kinetics to select the optimal binder type and concentration for a specific drug product, ultimately leading to faster time-to-market for new medicines. Users expect AI to move excipient selection from an empirical process to a highly predictable, data-driven science, lowering R&D costs and increasing the reliability of complex solid dosage forms.
AI's integration into the Binders Excipients domain is primarily focused on predictive modeling and process optimization within continuous manufacturing environments. Machine learning models are being developed to analyze real-time processing data from granulators and tablet presses, allowing manufacturers to dynamically adjust binder concentrations or processing parameters to maintain quality attributes consistently. This capability significantly enhances the efficiency of processes like wet granulation and direct compression, where minor variations in excipient quality or API properties can drastically affect batch quality. By predicting potential deviations before they occur, AI minimizes waste and ensures that the functional performance of the binder, such as its impact on tablet hardness and disintegration, remains within strict regulatory specifications throughout the production run.
Furthermore, AI-driven computational chemistry is starting to influence the molecular design and structural modification of existing excipients to create super-functional versions. This involves simulating molecular interactions between potential new binders and APIs to screen thousands of compounds virtually, drastically reducing the physical synthesis and testing workload. This predictive capability is vital for addressing modern formulation challenges, such as handling highly potent or poorly water-soluble compounds. For excipient suppliers, AI assists in optimizing material sourcing, inventory management, and logistics planning by forecasting demand fluctuations across diverse geographical markets and optimizing production schedules to improve operational efficiency and decrease lead times for crucial binding agents.
- AI facilitates the high-throughput virtual screening of novel binder candidates.
- Machine learning optimizes binder concentration and process parameters for continuous manufacturing.
- Predictive modeling minimizes empirical trials, accelerating formulation development time.
- AI enhances supply chain forecasting and inventory management for excipient manufacturers.
- Data analytics improve quality control by real-time monitoring of binding efficiency during compression.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Binders Excipients Market
The Binders Excipients Market is shaped by powerful dynamics stemming from healthcare expansion, technological necessity, and regulatory stringency. Key drivers include the overwhelming global demand for oral solid dosage forms (OSDFs), particularly generics, which require robust binding agents for mass production efficiency. Opportunities arise from the transition toward continuous manufacturing, which necessitates advanced, high-flowability excipients capable of operating reliably at high speeds. Restraints often center on the high costs associated with developing novel, co-processed excipients and the extremely lengthy regulatory approval processes required before any new functional ingredient can be introduced into therapeutic products. The overall impact forces suggest a market trajectory characterized by stable, mandatory demand counterbalanced by increasing pressures for cost efficiency and enhanced functional specialization.
Drivers: A major impetus is the increasing number of patents expiring, leading to a surge in generic drug production worldwide, primarily centered in high-volume markets like APAC. These generic manufacturers rely heavily on consistent and cost-effective binders to ensure product equivalence and stability. Additionally, the growing popularity of specialized dosage forms such as ODTs, multi-layered tablets, and controlled-release formulations significantly drives the demand for specialty binders that offer unique functional advantages, such as enhanced plasticity or specific water solubility profiles, which cannot be achieved with conventional materials. The need for improved patient compliance also necessitates better tasting and easier-to-swallow solid forms, influencing the demand for specific types of film-forming and binding agents.
Restraints: Significant limitations include the complex and restrictive regulatory landscape, particularly in highly regulated markets such as the US FDA and EMA territories, which demand extensive toxicology data and strict documentation for excipient components. This high barrier to entry slows down the adoption of innovative products. Furthermore, the volatility in raw material pricing, especially for natural sources like cellulose or starch, can impact the profit margins of excipient manufacturers. The challenge of maintaining cost-effectiveness while simultaneously meeting the high purity and consistency standards required by the pharmaceutical industry poses a persistent constraint for manufacturers attempting to scale their binder production.
Opportunities & Impact Forces: The most prominent opportunity lies in the development of co-processed excipients (CPEs) that combine two or more functional properties (e.g., binding and disintegration) into a single ingredient, streamlining the formulation process for drug developers. CPEs are optimized specifically for advanced techniques like direct compression, offering superior flow properties and uniformity. Furthermore, the push towards green chemistry and sustainable excipient sourcing represents a growing niche opportunity, appealing to environmentally conscious pharmaceutical companies. The overall impact forces are high, compelling manufacturers to continuously innovate in material science to provide tailored solutions that address increasingly complex formulation challenges related to poorly soluble APIs and high-speed production environments.
Segmentation Analysis
The Binders Excipients Market is comprehensively segmented based on the type of excipient material, their chemical origin, the formulation technique they support, and the end-use application industry. Analysis reveals that material type and application industry are the most critical factors influencing market dynamics and competitive strategy. Material-based segmentation clearly differentiates between natural and synthetic/semi-synthetic polymers, each catering to distinct formulation requirements regarding binding strength, stability, and regulatory acceptance. The application segmentation, dominated by the pharmaceutical industry, dictates the volume and quality requirements, while the rapidly growing nutraceutical sector influences the demand for natural and clean-label binder options.
- By Type:
- Cellulose Derivatives (Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC), Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC), Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC))
- Starch and Derivatives (Pregelatinized Starch)
- Povidone and Crospovidone
- Co-processed Excipients (CPEs)
- Others (Gelatin, Sugars, Natural Gums)
- By Route of Administration:
- Oral Solid Dosage Forms (Tablets, Capsules)
- Topical Formulations
- Parenteral and Injectable Systems (Less prevalent use of binders)
- By Formulation Type:
- Direct Compression
- Wet Granulation
- Dry Granulation
- By End-Use Industry:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Nutraceuticals (Dietary Supplements)
- Food and Beverages
- Cosmetics and Personal Care
Value Chain Analysis For Binders Excipients Market
The value chain for the Binders Excipients Market initiates with the sourcing and processing of raw materials, largely consisting of agricultural products (cellulose, starch, gelatin) or basic petrochemicals for synthetic polymers. Upstream activities are critical, focusing on purifying and refining these raw materials to meet stringent pharmaceutical-grade standards, a phase that demands high capital investment and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Excipient manufacturers then engage in complex chemical modification processes, such as etherification or polymerization, to transform basic raw materials into functional binders like MCC, HPMC, or PVP, requiring specialized chemical engineering expertise. The purity and consistency achieved in this upstream manufacturing phase directly dictate the quality and price point of the final excipient product, creating a significant barrier to entry for new market participants.
Downstream analysis focuses on the utilization and incorporation of binders into finished products, primarily by pharmaceutical and nutraceutical companies. This phase involves extensive formulation development, where R&D teams select the optimal binder based on the API characteristics, desired dissolution profile, and chosen manufacturing method (e.g., direct compression vs. wet granulation). Formulation expertise becomes a major value driver, as the successful selection and use of the binder determines the efficiency of tablet compression and the stability of the final drug product. The final stages involve packaging, regulatory submission, and distribution of the finished dosage form to hospitals, pharmacies, and consumers, demonstrating a high degree of integration between excipient suppliers and their end-user customers.
Distribution channels for binders excipients are bifurcated into direct sales to large, multinational pharmaceutical companies and indirect sales facilitated by specialized chemical distributors for small-to-mid-sized companies and regional markets. Direct distribution allows for customized technical support, batch consistency agreements, and close collaboration on novel formulation projects, which is typical for high-volume, specialized excipients. Indirect channels provide local inventory management, smaller order fulfillment, and logistical convenience. The complex regulatory requirements necessitate a robust quality assurance system throughout the distribution network, ensuring that the excipient's integrity and certification documentation remain impeccable from the manufacturer's site to the formulator's facility, thus preventing counterfeiting and maintaining product safety.
Binders Excipients Market Potential Customers
Potential customers for binders excipients are broadly categorized based on their manufacturing needs for solid dosage forms, dominated significantly by the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors. Within pharmaceuticals, customers range from large multinational corporations specializing in branded, complex drug development to smaller generic drug manufacturers focused on high-volume, cost-effective production. These customers require binders that offer superior functionality, consistency, and compliance with global pharmacopeial standards (USP, EP, JP). Their purchasing decisions are driven by factors such as the excipient's ability to facilitate specific drug release kinetics (e.g., sustained or immediate release) and its performance in high-speed manufacturing environments, prioritizing suppliers who can offer extensive technical support and regulatory documentation.
The nutraceutical industry represents a rapidly expanding customer base, particularly manufacturers of vitamins, herbal supplements, and dietary minerals. Unlike the highly regulated pharmaceutical sector, nutraceutical buyers often prioritize 'natural' or 'clean-label' binders, such as certain cellulose derivatives or starches, to align with consumer preferences for minimal synthetic ingredients. Their focus is often on high binding strength coupled with acceptable organoleptic properties (taste, texture) to improve consumer acceptance of large supplement tablets. The growth in this segment is driven by increasing health consciousness and the aging population, leading to stable, high-volume demand for common, food-grade certified binding agents.
Secondary but significant customer segments include the food and beverage industry, where excipients function as stabilizers, thickeners, or texture enhancers, and the cosmetics sector, where binders are used in pressed powders and solid formulations. These customers often have different regulatory requirements (e.g., GRAS status) compared to pharmaceuticals, though they still require high purity and stability. Overall, the market for binders is defined by customers seeking functional efficiency, regulatory compliance, and formulation versatility. The increasing complexity of modern formulations means that the most valuable customers are those seeking innovative, co-processed, or tailor-made excipient solutions that address specific production challenges.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | $780 million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | $1,210 million |
| Growth Rate | 6.8% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | BASF SE, DuPont, Ashland Global Holdings Inc., Roquette Frères, Dow Inc., FMC Corporation, Merck KGaA, Kerry Group, Colorcon Inc., Evonik Industries AG, JRS Pharma, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd., Wacker Chemie AG, Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM), Cargill, Innophos Holdings, Inc., SPI Pharma, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, Gelita AG, Pfanstiehl Inc. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Binders Excipients Market Key Technology Landscape
The technology landscape for Binders Excipients is primarily defined by advancements in solid dosage manufacturing techniques, specifically the shift towards more efficient and less resource-intensive processes. The dominant technological driver is the maturation of Direct Compression (DC), a method that bypasses wet or dry granulation steps, significantly reducing energy consumption, processing time, and the overall complexity of tablet manufacturing. Binders specifically engineered for DC, such as specialized grades of Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) and advanced co-processed excipients (CPEs), must exhibit superior flowability, compactibility, and low moisture content to perform effectively. Technological innovation is continuously focused on improving the particle size distribution and morphology of these binders to maximize their performance under high-speed compression.
Another pivotal technological area involves the refinement of Wet Granulation techniques, which still dominate the processing of high-dose or challenging APIs. Here, the technology centers on developing polymer binders, like Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) or Povidone (PVP), that offer optimal binding properties at low concentrations and ensure uniform distribution throughout the granule matrix. Fluidized bed granulation and high-shear granulation technologies demand binders that interact predictably with the solvent and the API. Manufacturers are also increasingly adopting Process Analytical Technology (PAT) tools to monitor binder performance in real-time, allowing for immediate process adjustments and ensuring batch-to-batch consistency, which is crucial for maintaining the quality of the final tablet product.
The emerging technology of Continuous Manufacturing (CM) represents the next frontier, demanding highly robust and consistent binder excipients that can be accurately dosed and processed continuously for hours or days without interruption. CM requires binders with extremely tight specification tolerances regarding density, particle shape, and moisture content, as process variability cannot be easily buffered by large batch holds. Technology development is focusing on creating 'smart' excipients and integrated feeding systems that work seamlessly with CM platforms, utilizing sophisticated techniques like twin-screw granulation and specialized coating methodologies. The overarching technological goal is to enable faster drug development cycles and minimize production costs while strictly adhering to regulatory expectations for product quality.
Regional Highlights
The global distribution of the Binders Excipients Market demonstrates significant geographic variation influenced by pharmaceutical manufacturing density, regulatory environments, and healthcare expenditure. North America, particularly the United States, represents a mature market characterized by high spending on innovative, specialized excipients required for novel drug delivery systems and controlled-release technologies. The region's stringent regulatory landscape necessitates the use of high-quality, fully documented excipients, driving premium pricing and fostering strong relationships between key excipient suppliers and major pharmaceutical and biotech firms. Furthermore, the strong presence of R&D infrastructure supports continuous formulation advancement, often setting global quality standards.
Europe holds a substantial market share, driven by strong growth in the generic drug sector in Western and Central Europe and significant activity in advanced pharmaceutical formulation. Countries such as Germany, Switzerland, and Ireland are key manufacturing hubs demanding robust supply chains for essential binding agents. The implementation of EU regulations, emphasizing safety and traceability, ensures consistent demand for high-grade excipients. European market trends show a particular focus on sustainable and green excipient solutions, pushing manufacturers to invest in environmentally friendly production processes and renewable raw materials, thus influencing procurement decisions across the continent.
Asia Pacific (APAC) is projected to be the fastest-growing region, propelled by massive population size, improving healthcare access, and the dominant presence of pharmaceutical manufacturing centers in India and China. These nations are major global suppliers of generic drugs, creating immense demand for cost-effective, bulk-volume binders like standard grades of MCC and starch derivatives. Market growth in APAC is further supported by governmental initiatives to strengthen local drug production capabilities and harmonize regulatory standards, although quality and price competition remains intense across the region.
- North America: Dominant market value, focus on specialized binders for novel drug delivery systems and adherence to strict regulatory standards (FDA).
- Europe: High demand from established generic manufacturers and a growing emphasis on sustainable, bio-based excipients.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Highest growth rate, driven by mass production of generics in India and China; demand for cost-efficient bulk excipients.
- Latin America (LATAM): Developing market, characterized by increasing foreign investment in local drug production and moderate demand for standard excipients.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): Nascent growth, primarily relying on imports but showing potential due to investments in local pharmaceutical hubs in Saudi Arabia and South Africa.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Binders Excipients Market.- BASF SE
- DuPont
- Ashland Global Holdings Inc.
- Roquette Frères
- Dow Inc.
- FMC Corporation
- Merck KGaA
- Kerry Group
- Colorcon Inc.
- Evonik Industries AG
- JRS Pharma
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Wacker Chemie AG
- Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM)
- Cargill
- Innophos Holdings, Inc.
- SPI Pharma
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- Gelita AG
- Pfanstiehl Inc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Binders Excipients market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What are binders excipients and their primary function in pharmaceuticals?
Binders excipients are inactive ingredients used in pharmaceutical formulations, primarily oral solid dosage forms like tablets, to promote cohesion and adhesion between powder particles. Their primary function is to provide the mechanical strength necessary for the tablet to remain intact during manufacturing, packaging, and handling, ensuring proper stability and controlled disintegration once ingested.
Which type of binder excipient dominates the market?
Cellulose derivatives, specifically Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) and Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC), currently dominate the binders excipients market. MCC is highly favored due to its excellent compressibility, versatility in both wet granulation and direct compression, and its well-established safety and regulatory profile across global markets.
How does the shift towards continuous manufacturing impact binder selection?
The shift to continuous manufacturing (CM) demands binders with extremely consistent quality attributes, including uniform particle size distribution, high flowability, and predictable moisture content. CM technology favors specialized co-processed excipients (CPEs) that reduce formulation steps and ensure stable performance over long, high-speed production runs, minimizing variability.
What role does Direct Compression (DC) play in the market growth?
Direct Compression (DC) is a major growth driver as it eliminates costly and time-consuming granulation steps. DC requires excipients, particularly binders, that are intrinsically flowable and highly compactable. The increasing adoption of DC necessitates continuous innovation and supply of high-functionality, DC-grade binders, thereby expanding the specialized excipients segment.
What are the key regulatory challenges faced by excipient manufacturers?
Excipient manufacturers face stringent regulatory scrutiny, particularly concerning batch-to-batch consistency, impurity profiles, and traceability documentation. Regulatory bodies require extensive data demonstrating quality and safety, including adherence to global pharmacopeial standards (USP, EP). Any change in raw material sourcing or manufacturing process requires comprehensive validation and potential re-submission.
How do binders influence drug bioavailability?
Binders indirectly influence drug bioavailability by affecting the tablet's disintegration time and dissolution rate. If a binder is too strong, it can slow down the tablet’s breakdown, delaying the release of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and potentially reducing the rate or extent of absorption (bioavailability). Therefore, binder selection must balance mechanical strength with effective disintegration kinetics.
What are co-processed excipients (CPEs) and why are they gaining popularity?
Co-processed excipients (CPEs) are physical mixtures of two or more conventional excipients processed together to create a single component with superior functional properties not achievable with the individual components alone. They are gaining popularity because they streamline formulation by combining functions (e.g., binding and lubrication) and offer optimized properties, making them highly suitable for advanced manufacturing techniques like high-speed direct compression.
Which geographic region exhibits the highest demand volume for binders?
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region, driven primarily by the high-volume generic drug manufacturing markets in China and India, exhibits the highest demand volume for binders excipients. While North America commands the highest market value for specialized products, APAC requires large quantities of standard and cost-effective binders to sustain its expansive production capacities.
Are synthetic or natural binders preferred in the nutraceutical industry?
The nutraceutical industry generally exhibits a strong preference for natural and semi-synthetic binders, such as certain grades of Microcrystalline Cellulose (derived from wood pulp) and natural gums or starches. This preference is driven by consumer demand for 'clean-label' products and the desire to minimize the use of overtly synthetic chemical compounds in dietary supplements.
What is the primary role of AI in excipient formulation?
The primary role of AI in excipient formulation is predictive modeling and optimization. AI algorithms analyze extensive datasets relating to API properties, excipient performance, and process parameters to predict the optimal binder type, concentration, and manufacturing process needed to achieve desired tablet attributes (hardness, dissolution), significantly reducing experimental trial time and costs.
How does the type of granulation technique affect binder choice?
The choice of granulation technique dictates binder requirements. Wet granulation requires binders (like PVP or HPMC) that form strong bridges when wetted, while dry granulation relies on binders that deform plastically under high pressure (like certain MCC grades). Direct compression requires binders that exhibit excellent flowability and strong compactibility without requiring moisture.
What challenges do poorly soluble APIs present to binder excipient selection?
Poorly soluble APIs present the challenge of maintaining dissolution rates while ensuring adequate tablet strength. Binders must be selected that do not inhibit API wetting or dissolution. Often, specialized polymeric binders or co-processed systems are utilized alongside solubility enhancers to achieve the necessary physical and chemical performance, requiring complex formulation design.
What is the significance of particle size and morphology in binder performance?
Particle size and morphology are critically significant, especially for direct compression, as they directly influence powder flowability and compactibility. Uniform, spherical particles are typically preferred for better flow, while highly porous or irregularly shaped particles (like specific MCC grades) offer increased surface area for mechanical interlocking and stronger tablet formation under pressure.
How is sustainability affecting the sourcing of binder raw materials?
Sustainability is increasingly impacting the sourcing of binders, driving demand for excipients derived from renewable resources and manufactured using eco-friendly processes. This push favors wood-derived cellulose and starch-based products, encouraging suppliers to ensure ethical sourcing, minimize waste, and achieve certifications demonstrating reduced environmental impact.
What is the long-term forecast for pricing in the Binders Excipients Market?
The long-term forecast suggests mixed pricing trends. Pricing for bulk, standard-grade excipients (like commodity starches) will remain competitive and susceptible to raw material price volatility. However, prices for specialized, high-functionality, and co-processed excipients are expected to remain high and potentially increase due to the extensive R&D investment and superior value they offer in complex formulations.
What is the difference between a binder and a disintegrant?
A binder holds the tablet components together, providing mechanical strength and cohesion. Conversely, a disintegrant (or superdisintegrant) works to break the tablet apart rapidly once exposed to aqueous fluids in the body. These two excipient functions must be carefully balanced in formulation: strong binding ensures stability, but sufficient disintegrant ensures the drug is released efficiently.
Which binder materials are most commonly used in controlled-release formulations?
In controlled-release formulations, the most commonly used binders are hydrophilic polymers such as high molecular weight Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC). HPMC forms a gel layer when hydrated, controlling the rate at which water penetrates the tablet and thereby regulating the dissolution and release rate of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) over an extended period.
Why is Povidone (PVP) widely used, especially in wet granulation?
Povidone (PVP) is widely used, particularly in wet granulation, due to its excellent solubility in water and various organic solvents, and its strong adhesive properties. It forms effective binding bridges during the granulation process, resulting in hard, stable granules that translate into robust tablets after compression, making it highly versatile for diverse API formulations.
How do impurities in binders affect the final drug product?
Impurities in binders can significantly compromise the final drug product quality, potentially leading to chemical instability, reduced shelf life, color changes, or poor functional performance (e.g., poor dissolution). Highly purified, pharmaceutical-grade binders are essential to mitigate the risk of adverse drug-excipient interactions that could lead to product failure or non-compliance.
What factors are driving the demand for specialized functional binders?
The demand for specialized functional binders is driven by the increasing need to formulate complex drugs, including highly potent compounds, poorly soluble APIs, and advanced drug delivery systems (e.g., personalized medicines). These specialized binders offer unique properties, such as enhanced plasticity, improved flow, or controlled-release capabilities, simplifying complex formulation challenges.
How is the food and beverage industry utilizing excipients?
In the food and beverage industry, excipients, particularly starch and cellulose derivatives, are utilized primarily as thickeners, stabilizers, texture modifiers, and non-caloric fillers. They are crucial for maintaining the desired consistency, shelf life, and sensory attributes of products such as sauces, dairy alternatives, and baked goods, often requiring food-grade certification rather than pharmaceutical grade.
What technological advancements are optimizing binder manufacturing?
Technological advancements optimizing binder manufacturing include the use of continuous processing techniques (instead of batch processing), advanced drying technologies (like spray drying to control particle morphology), and the integration of Process Analytical Technology (PAT) to ensure real-time quality monitoring and control over crucial parameters such as moisture content and particle size uniformity.
What are the primary differences between synthetic and natural binders?
Synthetic binders (e.g., PVP) offer high binding strength, customizable molecular weights, and consistent performance, often preferred for difficult or high-speed formulations. Natural binders (e.g., starch, cellulose) are generally perceived as safer, widely available, and cost-effective, often used in bulk products and favored by the nutraceutical industry, though they may offer less functional flexibility than their synthetic counterparts.
How does the aging global population influence market demand?
The aging global population significantly influences market demand by increasing the overall consumption of prescription and over-the-counter medications, most of which are administered as oral solid dosage forms. This demographic shift ensures a steady and growing baseline requirement for all categories of binders and excipients globally, necessitating expanded manufacturing capacities.
Why are traceability and documentation critical in the excipient supply chain?
Traceability and documentation are critical due to stringent pharmaceutical regulations that require a clear audit trail for every ingredient used in drug manufacturing. This ensures the source, quality, and history of the binder can be verified, mitigating the risk of counterfeit materials, ensuring compliance, and allowing for rapid recall or investigation if quality issues arise with the final drug product.
What market opportunities exist in Latin America for binder suppliers?
Market opportunities in Latin America stem from increasing investment in local pharmaceutical manufacturing and improved healthcare spending. Suppliers can leverage this growth by offering cost-effective, yet reliably quality-assured, standard excipients, supported by local distribution networks and technical service tailored to regional regulatory requirements.
How do binders impact the cost of goods sold (COGS) for drug manufacturers?
Binders are major non-API components of a tablet, directly impacting COGS. While they are usually cheaper than the API, the efficiency and cost of the binder selection significantly influence total manufacturing throughput. Using a higher-cost, high-functionality binder that allows for faster direct compression can ultimately reduce processing costs and lower the overall COGS compared to a cheaper binder requiring slow, multi-step granulation.
What are the challenges associated with using Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) as a binder?
While MCC is highly valued, challenges include its tendency to exhibit reduced compactibility at very high doses and its sensitivity to moisture content, which can affect flowability and compression performance. Formulators must carefully select the grade and particle size of MCC to avoid issues like capping or lamination during high-speed tableting operations.
What is the future outlook for the adoption of plant-based excipients?
The future outlook for plant-based excipients is highly positive, driven by both consumer preference for natural ingredients in nutraceuticals and pharmaceutical industry efforts toward sustainable sourcing. Continued research aims to enhance the functional properties of plant-derived excipients to match the performance levels currently achieved by synthetic polymers, broadening their applicability in complex drug delivery systems.
Why is it important for excipients to be chemically inert?
It is crucial for excipients, including binders, to be chemically inert to avoid reacting with the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or other formulation components. Chemical interaction can lead to API degradation, reduced efficacy, or the formation of toxic degradation products, compromising the stability, safety, and shelf life of the final drug product.
How does drug loading capacity influence binder requirement?
High drug loading (a large proportion of API relative to excipients) often requires a binder with exceptionally high binding efficiency and plasticity to ensure the tablet maintains adequate strength despite the low concentration of excipient. Conversely, low drug loading allows for greater flexibility in binder choice, often utilizing bulk, lower-cost binders.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager