Cold Saw Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 435725 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 253 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Cold Saw Market Size
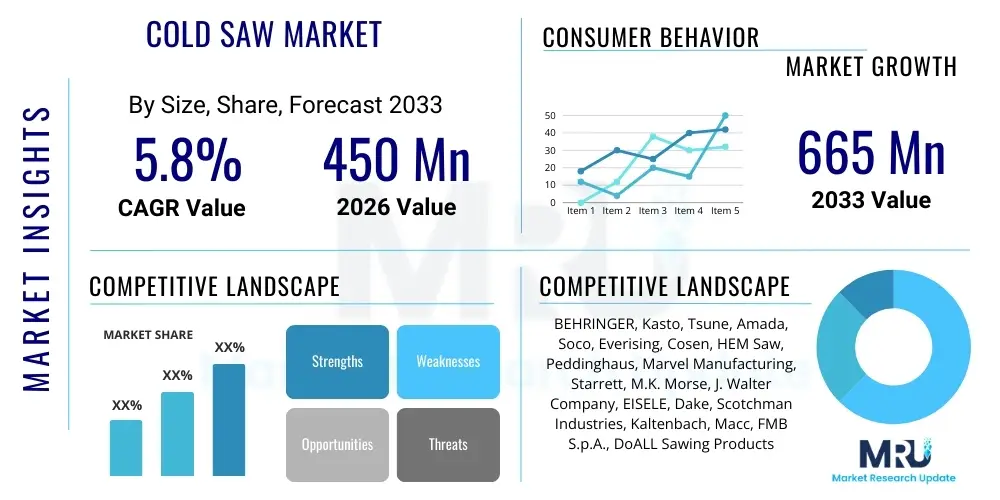
The Cold Saw Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Rate (CAGR) of 5.8% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 450 Million in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 665 Million by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Cold Saw Market introduction
The Cold Saw Market encompasses specialized cutting equipment meticulously engineered for the precision severing of metals and various hard materials, fundamentally operating on the principle of minimal thermal distortion. These industrial machines utilize large, circular, multi-toothed blades that operate at significantly lower peripheral speeds compared to abrasive or friction saws. This low-speed, high-torque operation ensures that the heat generated during the cutting process is predominantly absorbed by the resulting metal chips rather than being transferred into the workpiece itself. The resultant cut is characteristically clean, exhibits a superior surface finish, and is virtually free of burrs, often eliminating the need for subsequent, time-consuming deburring or finishing operations. This capability is paramount in industries where material integrity and tight dimensional tolerances are non-negotiable standards. Products range from foundational manual systems, suitable for intermittent use in small workshops, to sophisticated, fully automated Computer Numerical Control (CNC) models designed for continuous, high-volume production lines.
The core application sectors driving the demand for cold saws are multifaceted and globally distributed, prominently including heavy metal fabrication, the automotive original equipment manufacturing (OEM) sector, critical infrastructure construction, and the specialized aerospace and defense industries. In fabrication, cold saws are the linchpin for material preparation, providing the necessary accurate, square, or angled cuts crucial for subsequent welding and assembly integrity. The inherent advantages offered by this technology are significant and contribute directly to enhanced operational efficiency. These benefits include vastly superior cutting accuracy, minimal material waste due to the narrow kerf thickness of the blades, and substantial ergonomic and safety improvements compared to traditional high-speed cutting methods. Furthermore, the robust construction of modern cold saws allows them to handle extremely thick materials and high-tensile alloys reliably, ensuring repeatable, high-tolerance outputs essential for modern manufacturing standards.
Market expansion is robustly supported by several macroeconomic and technological drivers. Globally, the continuous expansion of the construction sector, particularly involving large-scale commercial and civil infrastructure projects, necessitates high volumes of processed structural metal. Rapid industrialization across Asia Pacific and Latin America accelerates the adoption of efficient manufacturing technologies, replacing older, less precise machinery. Critically, ongoing technological advancements focused on integrated automation, such as sophisticated material handling systems, highly intuitive digital control interfaces, and continuous improvements in blade metallurgy and coating technology, consistently increase the productivity and longevity of cold saw equipment. Manufacturers are concentrating research and development efforts on maximizing throughput, mitigating operational noise and vibration, and implementing smart features for real-time blade monitoring and condition-based maintenance, thereby lowering the total operational expenditure for end-users operating in demanding environments.
Cold Saw Market Executive Summary
The Cold Saw Market is navigating a transformative phase characterized by an accelerating shift towards digitalization and integration within holistic manufacturing ecosystems. Current business trends underscore a strong market preference for highly sophisticated, fully automated CNC cold saw systems capable of complex nesting and automated material sorting. This migration is directly linked to global pressures to achieve higher production speeds while simultaneously reducing reliance on manual labor, particularly in high-wage economies. A notable trend involves manufacturers focusing on modular designs, allowing for easy scalability and integration of auxiliary features such as automated loading magazines and robotized stacking systems. Furthermore, supply chain resilience, particularly for specialized components like carbide tips and servo drives, is becoming a crucial competitive differentiator among leading machinery suppliers, necessitating localized component production and diversified sourcing strategies to mitigate geopolitical risks and supply chain disruptions which could hamper market growth and profitability across the value chain.
Geographically, market dynamics are sharply delineated. The Asia Pacific (APAC) region stands as the undisputed epicenter of market growth, driven by aggressive investment in new manufacturing capacity, extensive urbanization efforts, and high demand from domestic automotive and construction sectors in key economies like China, India, and South Korea. This region benefits from favorable demographics, supportive government policies promoting industrial output, and the establishment of global manufacturing hubs, driving high volume sales, particularly of semi-automatic and basic automatic models. Conversely, mature markets in North America and Europe are distinguished by their focus on technology refreshment and premiumization. These regions prioritize the procurement of high-specification machinery that incorporates advanced safety features, superior energy efficiency, and sophisticated data analytics capabilities, crucial for compliance with rigorous domestic industrial standards and the implementation of advanced Industry 4.0 strategies, ensuring sustained growth in the high-value segment.
Analysis of market segmentation reveals distinct demand patterns that guide product development. The automatic and semi-automatic segments collectively hold the majority market share, clearly indicating the industry's sustained commitment to optimized efficiency and labor reduction across high-volume metal processing operations. Blade type segmentation shows a pronounced shift toward high-performance carbide-tipped blades, displacing traditional HSS blades in heavy-duty applications due to their superior longevity and speed capabilities when cutting high-strength alloys, which lowers the cost per cut in the long run. In terms of end-use, while traditional metal fabrication remains a core pillar, the rapid expansion of the electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing supply chain is creating specialized demand for cold saws optimized for cutting aluminum and high-strength, lightweight steel alloys, compelling cold saw manufacturers to perpetually refine their machine rigidity, spindle technology, and Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) systems to accommodate the evolving material science landscape efficiently.
AI Impact Analysis on Cold Saw Market
Common inquiries from industry stakeholders regarding the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Cold Saw Market predominantly focus on methodologies for minimizing operational uncertainties and maximizing asset lifespan through real-time process control. Users frequently ask how AI can be leveraged to move beyond reactive maintenance towards truly predictive operational paradigms, specifically targeting costly blade wear, gear box failures, and unscheduled machine stops resulting from minor component degradation. Concerns also surround the feasibility and return on investment (ROI) of implementing complex machine vision systems for real-time quality assurance, ensuring zero-defect output without slowing down high-speed production lines. The prevailing user expectation is that AI will function as a self-monitoring, self-optimizing layer above the core mechanics, drastically reducing human input errors and allowing for optimal cutting strategies to be determined dynamically based on instantaneous sensor feedback related to material variability, coolant status, and tool pressure, leading to profound improvements in overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) scores and significant reductions in consumables expenditure.
The integration of AI into cold saw machinery fundamentally alters the traditional operational model, transforming basic cutting equipment into intelligent manufacturing assets capable of learning and adapting to fluctuating production demands and material inconsistencies. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of historical performance data, maintenance records, and real-time operational metrics (such as torque fluctuations, harmonic distortion signatures captured by accelerometer sensors, and thermal gradients) to construct precise digital models of tool degradation and mechanical stress. This allows the system to accurately predict the residual useful life (RUL) of a saw blade or critical bearing, enabling maintenance schedules to be optimized weeks in advance, thereby eliminating guesswork and ensuring necessary consumables are stocked precisely when needed. This predictive capability translates directly into higher utilization rates, minimizing unexpected downtime that can halt an entire production line, and significant reductions in maintenance expenditures associated with premature part replacement or labor-intensive, unscheduled failure remediation.
Furthermore, AI facilitates advanced process control that was previously impossible using conventional static or proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers. Machine learning models can analyze material composition variations and instantly adjust critical parameters, including feed rate consistency, acceleration curves, and spindle speed, to maintain optimal chip load per tooth—a critical factor for maximizing blade efficiency, ensuring cut quality, and preventing costly blade chipping. In sophisticated CNC cold saws, AI algorithms manage complex multi-cut sequences, optimizing nesting patterns and minimizing run time and material wastage based on current machine status and scheduled production priorities. This continuous, data-driven optimization ensures the cold saw operates at its highest potential efficiency across all jobs, representing a paradigm shift towards truly smart manufacturing workflows within metal processing environments, offering competitive advantages in markets demanding speed and precision.
- AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance Systems: Utilizes integrated IIoT sensors to monitor vibration frequency, acoustic emission, and thermal signatures, providing early warnings of mechanical faults or imminent blade failure, transitioning operations from rigid, time-based maintenance schedules to highly efficient condition-based protocols.
- Adaptive Cutting Parameter Control: Machine learning models analyze real-time material feedback (e.g., hardness variation, material grade consistency detected via torque profiling) to dynamically fine-tune feed rates, clamp pressure, and cutting lubricant application, guaranteeing optimal chip formation, minimizing thermal stress, and extending blade longevity across heterogeneous materials.
- Automated Quality Inspection via Computer Vision: Deployment of high-resolution cameras and deep learning models to conduct instantaneous surface integrity checks and dimensional analysis post-cut, ensuring every workpiece meets tolerance requirements before proceeding downstream, drastically reducing the potential for scrap and rework.
- Nesting and Scheduling Optimization: AI algorithms analyze incoming job orders and available stock lengths to generate optimized cutting plans that minimize material scrap and maximize machine utilization through complex optimization routines, particularly vital in high-value material processing like stainless steel and aerospace alloys where material costs are substantial.
- Remote Diagnostics and Fleet Management: Leveraging cloud-based AI platforms to monitor the performance of multiple cold saws across geographically dispersed manufacturing sites, facilitating centralized troubleshooting, standardized performance benchmarking, and proactive intervention from expert technicians irrespective of location.
- Enhanced Operator Assistance: AI provides real-time guidance and contextual feedback to operators, assisting in complex setup procedures, material changeovers, and detailed trouble-shooting steps, accelerating training curves for new employees and reducing dependence on highly specialized, expert technicians for routine operational management.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Cold Saw Market
The Cold Saw Market is propelled by several robust internal and external drivers that reinforce its foundational necessity in modern manufacturing. Foremost among these is the escalating global demand for high-tolerance manufactured goods, particularly from the automotive industry (driven by the transition to EV chassis and battery structures requiring lightweight, complex alloys) and the stringent requirements of the aerospace sector for precision component preparation. The fundamental efficiency of cold sawing—delivering burr-free cuts that eliminate secondary processes—represents a substantial operational cost saving, making it highly attractive to manufacturers seeking lean production methodologies and higher quality outputs. Furthermore, government initiatives focused on large-scale infrastructure renewal and expansion across both developed and developing economies create a sustained, high-volume requirement for structural steel and pipe cutting, directly bolstering sales of heavy-duty, automatic cold saw equipment necessary for these large-scale construction projects.
However, the market faces significant restraining factors that temper its growth trajectory and limit adoption among smaller businesses. The initial acquisition cost of advanced, fully automated CNC cold saw systems, often running into hundreds of thousands of dollars, remains a major deterrent, particularly for small-to-midsize enterprises (SMEs) in developing regions that require heavy reliance on favorable financing options or subsidies. Operational complexity poses another significant restraint; sophisticated cold saws require highly specialized maintenance expertise and skilled operators capable of managing complex CNC programs, diagnosing electronic faults, and performing precise tool offset adjustments, leading to higher overhead costs associated with intensive training and the retention of specialized technical labor. Moreover, the cold saw market is intimately tied to the cyclical nature of the global metals, construction, and capital machinery industries, making investment decisions vulnerable to macroeconomic downturns, unforeseen geopolitical trade disputes, and sudden, unpredictable volatility in raw material commodity prices, which can stall capital machinery procurement decisions for prolonged periods.
Opportunities for market growth are strongly tied to technological advancement and strategic geographical penetration into underserved industrial regions. The continued refinement and accelerated industrial adoption of Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) systems represent a major environmental and operational opportunity, significantly reducing coolant consumption and associated disposal costs while simultaneously adhering to stricter global environmental regulations and improving operator safety. Geographically, considerable untapped potential remains in rapidly industrializing regions of Africa and specific areas of Southeast Asia, where local governments are actively encouraging foreign direct investment in manufacturing and infrastructure development, creating a nascent but rapidly growing market for reliable, efficient machinery. Furthermore, the niche market of advanced materials processing—including composite-metal hybrids and precision materials produced via additive manufacturing (AM)—requires new generations of highly precise, low-vibration cold saws for post-process trimming and preparation, offering specialized and high-margin revenue streams for innovative manufacturers focused on highly customized, complex cutting solutions.
Segmentation Analysis
Comprehensive analysis of the Cold Saw Market segmentation provides critical insights into the underlying structure of industrial demand, technological adoption rates, and competitive positioning across global markets. Segmentation by Operation Type—Manual, Semi-Automatic, and Fully Automatic (CNC)—reveals the industry's inexorable progression toward automation, which is profoundly driven by the necessity for economies of scale, repeatable precision, and the increasing cost and diminishing availability of low-cost, skilled manual labor in developed economies. While manual systems maintain their essential niche for versatility and lower capital outlay in small job shops and maintenance facilities, the high-throughput requirements of Tier 1 suppliers in the automotive and major construction sectors necessitate the investment in high-speed, fully integrated automatic CNC systems capable of 24/7 operation. This operational distinction directly correlates with the machine's price point, technical complexity, and ultimate target end-use volume capacity being offered by machinery vendors globally.
The segmentation based on End-Use Application clearly indicates market reliance on foundational industrial sectors, with heavy metal fabrication and automotive manufacturing consistently representing the largest and most dynamic segments. The automotive industry’s requirement for fast, accurate processing of metal tubes, structural profiles, and safety components across millions of units annually ensures continuous, high-volume demand for robust, dedicated cold saws capable of handling specific material challenges, such as lightweight alloys. Conversely, the aerospace segment, while smaller in terms of sheer volume, disproportionately drives innovation in ultra-precision, low-vibration cutting and specialized material handling due to the cutting of high-cost, specialized superalloys (like nickel and titanium) where material integrity and minimal thermal impact are absolutely paramount to avoid structural failure. The core construction sector remains a stable, fundamental consumer, needing reliable, large-capacity machines for processing standard structural shapes efficiently on-site or in large centralized cutting centers.
Further delineation by Blade Type—HSS, Carbide-Tipped, and Cermet—is crucial as the blade composition and geometry fundamentally dictate the saw's effective material handling capabilities, operational speed, and the maintenance schedule required. The sustained migration toward advanced carbide technology reflects an industry-wide prioritization of reduced tool change frequency and superior cutting performance, even though these blades represent a higher initial capital cost compared to HSS alternatives. This shift is universally justified by the significantly lower total cost of ownership (TCO) achieved through faster cutting cycle times, superior surface finishes, and prolonged service life when cutting demanding ferrous and non-ferrous alloys. This detailed segmentation helps market participants align their core research and development efforts, technical sales training, and commercial strategies with the specific, evolving metallurgical needs of various high-value material and application environments worldwide.
- By Operation Type:
- Manual Cold Saws: Simple operation, lowest capital cost, highest versatility for small batches, custom jobs, and highly varied materials, often found in small repair and general maintenance shops.
- Semi-Automatic Cold Saws: Incorporate power clamping, automatic blade feed, and often basic digital readouts, requiring manual material repositioning between cuts, balancing automation benefits with moderate capital expenditure.
- Fully Automatic Cold Saws (including CNC systems): Feature automated material feeding magazines, complex programming interfaces, digital job management, and the highest throughput and precision levels, essential for continuous, high-volume production runs in Tier 1 supply environments.
- By End-Use Application:
- Metal Fabrication Workshops: Largest volume segment, characterized by high output of structural steel, pipe, angle, and general profile cutting for diverse industrial applications.
- Automotive Industry: Mass production cutting of chassis parts, exhaust tubing, suspension components, and structural frames, with a growing focus on precise cutting of lightweight aluminum alloys for EV platforms.
- Construction and Infrastructure: Processing large structural beams, columns, bridge sections, and heavy-gauge rebar with demanding requirements for precise angle cuts and high volume capacity in centralized yards.
- Aerospace and Defense: Specialized, ultra-precision cutting of exotic and expensive alloys (e.g., titanium, Inconel) demanding minimal heat affected zone (HAZ) and zero material contamination.
- General Machining and Industrial Manufacturing: Diverse material cutting for machinery components, tools, fixtures, and general workshop use where quick changeover and versatility are highly valued.
- Tube and Pipe Manufacturing: Dedicated systems, often rotary or orbital cold saws, designed for clean, square cuts on cylindrical materials without internal burr formation or material deformation, crucial for fluid transfer systems.
- By Blade Type:
- High-Speed Steel (HSS) Blades: Standard, general-purpose option, suitable for soft to medium hardness ferrous materials and lower-speed, less demanding applications where initial tool cost is the primary consideration.
- Carbide-Tipped Blades: Premium, high-performance option offering superior cutting speed, heat resistance, and exceptional longevity when cutting hard steel, stainless steel, and high-strength non-ferrous alloys, dominating modern automated lines.
- Cermet Blades: Specialized composite blades used for very high-temperature applications and continuous, heavy-duty cutting of stainless steel and high-nickel alloys, offering exceptional thermal stability and minimal material adhesion.
- By Material Cut:
- Ferrous Metals (Steel, Stainless Steel): Historically the largest segment, driven predominantly by construction, heavy machinery, and traditional fabrication activities globally.
- Non-Ferrous Metals (Aluminum, Copper, Brass): Fastest-growing segment, fueled by rapid lightweighting trends in transportation, expansion of electronics manufacturing, and high demand from electrical infrastructure projects.
Value Chain Analysis For Cold Saw Market
The commencement of the Cold Saw Market value chain is deeply rooted in upstream component sourcing and critical material procurement, which dictates the performance ceiling and stability of the final machinery. This initial phase involves securing specialized high-grade tool steels and powder metallurgy components necessary for constructing the robust machine chassis, high-wear precision gears, and the crucial cutting tools. The quality, purity, and consistent global supply of tungsten carbide powder, cobalt binders, and specialized alloy steels are paramount, as they directly dictate the performance characteristics, wear resistance, lifespan, and overall cost base of the resulting precision saw blades and critical mechanical components. Suppliers of sophisticated electronic and mechanical components, such as high-torque servo motors, precision gearboxes designed for low-backlash operation, advanced Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), and high-resolution encoder systems, hold significant leverage due to the complexity and specialization of these inputs. Manufacturers must focus intensively on strategic supplier relationship management and geographical diversification of sourcing to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical trade tensions and disruptions in the complex global supply networks for critical electronic and metallurgical inputs.
The midstream phase, comprising the design, manufacturing, and assembly of cold saws, is where substantial intellectual property and intrinsic value addition occur, differentiating high-end machinery brands. Leading manufacturers invest heavily in continuous research and development to optimize machine rigidity, develop proprietary vibration damping technologies utilizing specialized composite materials or heavy castings, and refine high-efficiency spindle transmission systems to maximize cutting efficiency across vastly varied material characteristics and thicknesses. Manufacturing processes involve high-precision machining of heavy cast iron or specialized mineral composite frames, meticulous assembly of complex mechanical and electronic subsystems, and rigorous, multi-stage quality control testing to ensure dimensional accuracy, operational safety compliance, and maximum output consistency. The distribution strategy at this midstream level is bifurcated: high-value, custom-built, fully integrated CNC systems are typically sold directly, allowing for bespoke installation, extensive customized operator training, and the establishment of long-term, high-margin service contracts. Standard or semi-automatic models are distributed indirectly through established, regional industrial distributors and value-added resellers (VARs) who offer localized technical sales expertise, flexible financing options, and immediate inventory access to local fabrication and machine shops, thereby extending the manufacturer's market reach efficiently.
Downstream activities focus entirely on delivering and sustaining value throughout the operational product lifecycle, a segment that often generates significant, stable recurring revenue streams crucial for long-term profitability. Key downstream activities include professional installation, thorough commissioning, the execution of preventative maintenance contracts, and the crucial, continuous supply of consumables, primarily replacement precision saw blades and specialized cutting lubricants (such as Minimum Quantity Lubrication, or MQL, fluids). Customer proximity and responsive technical support are essential factors influencing repeat purchase decisions, particularly for high-volume users in automotive or infrastructure sectors where every hour of machine downtime is extremely costly. The emergence of sophisticated digital service models, powered by remote diagnostics and IIoT connectivity, is significantly enhancing downstream efficiency, allowing manufacturers to monitor machine health remotely, proactively schedule maintenance interventions based on usage data, optimize spare parts logistics, and conduct firmware updates, ensuring superior long-term customer satisfaction and maximized operational continuity for the end-user.
Cold Saw Market Potential Customers
The primary cohort of potential customers for cold saw technology consists of large-scale structural metal fabricators and specialized processing centers that handle significant throughput of steel beams, channels, and tubing destined for the civil engineering, commercial building, and construction sectors. These buyers operate in environments where volume and robustness are critical, requiring heavy-duty automatic or CNC systems capable of handling large cross-sectional dimensions with relentless accuracy and speed. They prioritize features such as automatic bundle loading and advanced programming interfaces for efficient job scheduling and nesting optimization. Their procurement decisions are heavily influenced by the machine’s documented reliability, its capacity to interface seamlessly with existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, and compliance with high international standards for structural component preparation, where precise angular cuts are mandatory for subsequent welding strength and structural integrity, often necessitating automated measuring systems to guarantee tolerances.
A second crucial customer segment is the expansive automotive manufacturing supply chain, ranging from Tier 1 component suppliers to original equipment vehicle assembly plants. With the accelerated global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs), there is increasing, specialized demand for highly precise cold saws capable of processing complex, thin-walled extruded aluminum profiles and high-strength, low-alloy (HSLA) steels used in lightweight body structures, motor housings, and battery frames. These customers prioritize fully automated, high-speed systems that integrate seamlessly into continuous robotic assembly lines, demanding exceptionally high cycle rates, minimal vibration, and the ability to maintain micron-level tolerances consistently across millions of parts annually. The specialized requirements of aerospace and defense manufacturers—dealing with high-nickel alloys, titanium, and other high-cost superalloys—represent a critical niche customer base that demands absolute machine stability, advanced carbide blade technology, and sophisticated monitoring systems optimized to prevent material hardening or thermal stress during cutting, justifying investment in the highest-specification, custom-engineered cold saws available in the market.
Additional target customers include general engineering job shops, machinery repair and maintenance facilities, and manufacturers of high-pressure fluid power systems (hydraulics and pneumatics) requiring precision tube cutting. These smaller enterprises often purchase manual or semi-automatic cold saws, valuing versatility, a compact footprint, ease of operation suitable for varied, low-volume tasks, and a strong local service presence. Furthermore, dedicated pipe and tube mills are continuous buyers of specialized orbital or rotary cold saws designed to cut materials without internal burr formation or tube deformation, often requiring high-speed cutoff lines integrated with material forming processes. Across all customer types, the decision matrix is evolving intensely beyond the initial purchase price to focus heavily on demonstrable efficiency gains, long-term blade life, low energy consumption metrics, and the availability of sophisticated software that aids in material utilization, real-time data logging, and seamless integration into future smart factory environments.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 450 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 665 Million |
| Growth Rate | 5.8% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | BEHRINGER, Kasto, Tsune, Amada, Soco, Everising, Cosen, HEM Saw, Peddinghaus, Marvel Manufacturing, Starrett, M.K. Morse, J. Walter Company, EISELE, Dake, Scotchman Industries, Kaltenbach, Macc, FMB S.p.A., DoALL Sawing Products |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Cold Saw Market Key Technology Landscape
The contemporary technology landscape of the Cold Saw Market is characterized by a persistent pursuit of cutting precision, speed, and automation efficiency, heavily reliant on sophisticated mechatronics and software integration derived from Industry 4.0 principles. Central to this evolution is the refinement of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems, which now offer highly dynamic multi-axis positioning, automated stock length measurement, and seamless integration with upstream inventory and order management systems. Modern CNC human-machine interfaces (HMIs) provide highly graphical, intuitive platforms for operators to manage complex job queues, optimize cut sequencing through advanced nesting algorithms to minimize scrap, and perform remote diagnostics. The sustained shift from traditional hydraulic power systems to precision servo motor drives is a defining technological trend, offering superior energy efficiency, significantly quieter operation, instantaneous feedback control, and the critical ability to finely tune both feed rates and pressures necessary for cutting difficult, inconsistent, or layered materials without compromising structural integrity or causing blade deflection.
Blade metallurgy and tooling technology continue to evolve rapidly to meet the challenge of cutting newer, harder materials efficiently. The market standard is increasingly migrating towards specialized carbide-tipped blades, particularly those featuring high-performance ceramic-based coatings like TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride) and TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride), applied using advanced Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) techniques. These coatings dramatically improve thermal resistance, hardness, and lubricity at the cutting edge, enabling operators to use higher cutting speeds and significantly extending the blade's operational lifespan, thereby directly reducing per-cut costs and tool change frequency. Furthermore, blade design innovations focus intensely on optimizing tooth geometry (e.g., triple chip grind) and chip breaker design to ensure efficient, safe chip evacuation, which is critical in preventing dangerous chip weldment, reducing machine load, and maintaining the superior surface finish characteristic of cold sawing operations across various material types, especially stainless steel.
Another pivotal technological area driving efficiency is the management of cutting fluids and lubrication, led by the widespread adoption of Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) systems. MQL represents a foundational advancement in sustainability, replacing traditional flood coolants with highly focused, micro-doses of environmentally benign oil mist directed precisely at the point of cut. This technology dramatically reduces the overall environmental footprint associated with fluid consumption and disposal, minimizes the need for rigorous post-cut parts cleaning, and significantly improves chip separation and handling, leading to cleaner work environments and substantial cost savings in consumables and waste management. Furthermore, comprehensive integrated sensor technology, aligned with modern Industry 4.0 standards, is now standard in high-end automatic cold saws. These embedded sensors monitor spindle load, vibration harmonics, motor torque, and even acoustic emissions, generating rich datasets that feed into onboard analytical software and cloud platforms. This data is essential for enabling sophisticated features like active vibration dampening, automated material recognition, and, critically, for delivering the necessary inputs for AI-driven predictive maintenance and closed-loop process control, solidifying the cold saw's necessary role as an intelligent, indispensable component of the fully integrated, digitalized factory floor.
Regional Highlights
- Asia Pacific (APAC): APAC is the global revenue leader and fastest-growing market, primarily due to large-scale government stimulus in infrastructure and expansion of new industrial zones, coupled with lower operating costs that attract foreign direct investment. China and India are the dominant consumers, driven by rapid urbanization, massive production output from automotive (both ICE and EV), and extensive steel production. The region sees high demand for high-capacity, cost-effective semi-automatic models, alongside significant investment in fully automated CNC systems by large multinational manufacturers establishing regional manufacturing hubs.
- North America: This market is mature, highly consolidated, and focused intensely on high-technology adoption and fleet replacement cycles, driven by high labor costs and the necessity for maximum operational efficiency. Growth is driven by the stringent quality demands of the aerospace, defense, and high-precision machinery sectors. Demand is characterized by a high preference for customized, high-specification automatic cold saws featuring advanced AI diagnostics, MQL systems, and robust integration with existing Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) to minimize manual labor dependencies and maximize operational visibility and data compliance.
- Europe: The European market, robustly anchored by industrial powerhouses like Germany, Italy, and Scandinavia, is defined by technological innovation, rigorous regulatory compliance (especially concerning environmental impact and worker safety), and a strong export-oriented industrial base. Investment focuses on sophisticated, energy-efficient cold saws that excel in highly specialized applications, such as large-diameter tube processing for specialized machinery, oil and gas, or wind energy components. European manufacturers are key innovators in developing advanced blade coatings, servo-driven feed systems, and non-contact monitoring systems to achieve near-perfect cut quality and zero-defect output.
- Latin America: Market stability and growth in this region are closely tied to regional commodity cycles, including mining and agriculture, and state-funded infrastructure projects, particularly in industrial centers in Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. The demand profile typically skews toward rugged, reliable semi-automatic machines offering a good balance between capital cost and performance for general fabrication. Economic uncertainty and currency volatility often delay major capital equipment investments, but the long-term trend favors gradual automation as local manufacturing bases mature and seek to compete internationally on quality and consistency.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): This is the smallest but highly dynamic regional market, concentrating growth around massive construction and energy sector projects, particularly in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. Demand is highly specific, requiring extremely robust, high-capacity saws capable of handling harsh operating conditions and large material sizes necessary for critical oil pipelines, specialized processing facilities, and massive urban developments. Infrastructure expansion, combined with governmental diversification efforts away from pure oil dependence and into manufacturing, is stimulating industrial growth and subsequent demand for quality metal processing machinery.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Cold Saw Market.- BEHRINGER GmbH
- Kasto Maschinenbau GmbH & Co. KG
- Tsune Seiki Co., Ltd.
- Amada Co., Ltd.
- Soco Machinery Co., Ltd.
- Everising Machine Co., Ltd.
- Cosen Saws
- HEM Saw, LLC
- Peddinghaus Corporation
- Marvel Manufacturing Co. Inc.
- Starrett Company
- M.K. Morse Company
- J. Walter Company (Emmegi Group)
- EISELE GmbH
- Dake Corporation
- Scotchman Industries, Inc.
- Kaltenbach Group
- Macc S.p.A.
- FMB S.p.A.
- DoALL Sawing Products
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Cold Saw market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What defines a cold saw and how does it differ from abrasive saws?
A cold saw is defined by its ability to cut metal utilizing specialized circular blades operating at low RPMs, transferring heat primarily into the chips rather than the workpiece. This critical distinction results in clean, accurate, burr-free cuts, unlike abrasive saws which frictionally burn material, producing significant heat and rough edges. Cold saws offer superior material integrity and reduce the need for secondary finishing operations, optimizing manufacturing workflows.
Which factors are driving the adoption of fully automatic cold saws?
The primary drivers for fully automatic cold saw adoption include the global focus on reducing labor costs, the necessity for high-volume, repeatable production throughput, and the requirement for consistent cutting accuracy mandated by high-specification industries like automotive and aerospace. Automated systems minimize operator fatigue, integrate into CNC production lines, and facilitate material handling efficiency, leading to higher Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
What is the significance of carbide-tipped blades in the Cold Saw Market?
Carbide-tipped blades are significant because they offer drastically improved wear resistance and permit much faster cutting speeds compared to traditional High-Speed Steel (HSS) blades. This superiority is essential for efficiently processing hard materials like stainless steel and specialized high-strength alloys, significantly enhancing overall manufacturing productivity and reducing tool change downtime, despite their higher initial purchase price.
How does the integration of AI impact the operational costs of cold saws?
AI integration reduces operational costs primarily through predictive maintenance, preventing catastrophic failures and minimizing unplanned downtime by forecasting blade and component lifespan using real-time sensor data. Furthermore, AI optimizes cutting parameters dynamically, extending tool life, reducing material scrap through precise quality control, and lowering energy consumption, leading to a substantial decrease in Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Which regional market shows the highest growth potential for cold saw equipment?
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region exhibits the highest growth potential, primarily driven by large-scale infrastructure investments, burgeoning metal fabrication sectors, and the rapid expansion of manufacturing capabilities, particularly in emerging economies such as India, Vietnam, and Indonesia. This growth is sustained by strong domestic automotive production and urbanization trends requiring processed structural materials.
What is Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) and why is it preferred?
Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) is an advanced lubrication system that applies a minute, highly controlled amount of lubricant mixed with compressed air directly to the cutting zone, replacing large volumes of conventional flood coolants. MQL is preferred due to its environmental benefits (reduced waste and fluid disposal), improved chip quality for easier recycling, and cleaner machine operation, meeting increasing industrial sustainability and occupational health standards.
In the Value Chain, where is the highest value addition achieved for cold saws?
The highest value addition is achieved in the midstream manufacturing phase, involving precision engineering, development of proprietary vibration dampening technology, integration of sophisticated CNC and servo drive systems, and the rigorous assembly process. Additionally, the downstream provision of specialized high-performance blades, predictive maintenance software, and responsive technical support generates high recurring value for manufacturers throughout the machine's operational lifespan.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
