CVD Cutting Insert Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 434590 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 258 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
CVD Cutting Insert Market Size
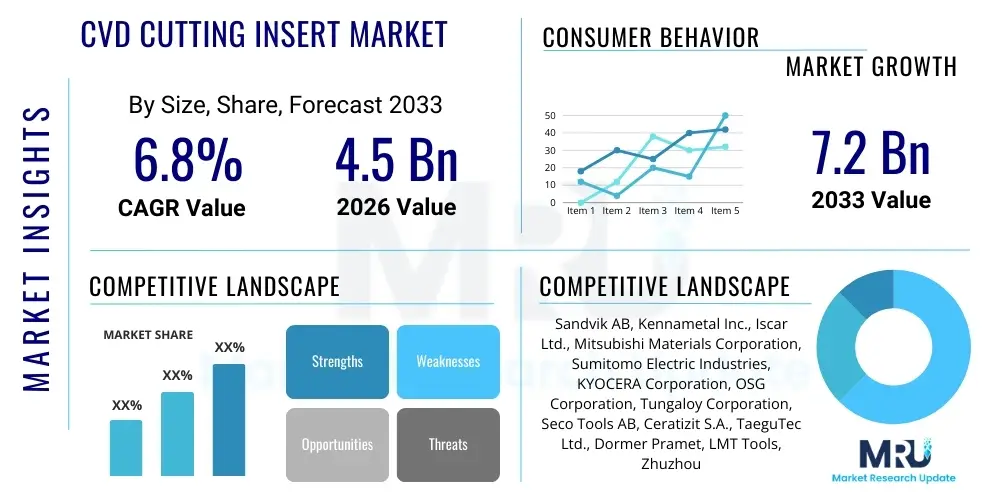
The CVD Cutting Insert Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.8% between 2026 and 2033. This robust growth trajectory is underpinned by increasing global industrial automation, rising demand from the automotive and aerospace sectors for high-precision components, and continuous innovation in coating material science to enhance tool life and performance. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) inserts are highly valued in heavy-duty and high-speed machining applications dueishing to their exceptional wear resistance, thermal stability, and superior edge integrity, positioning them as essential consumables in advanced manufacturing processes worldwide.
The market is estimated at USD 4.5 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 7.2 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033. This significant valuation increase reflects the shift toward processing hard-to-machine materials such as nickel-based superalloys and titanium alloys, particularly within critical sectors like aerospace and energy. Furthermore, the integration of Industry 4.0 principles, including predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of machining processes, necessitates the use of high-reliability tooling like CVD-coated inserts, driving up volume and average selling prices for premium products. The market expansion is also geographically concentrated, with Asia Pacific exhibiting the fastest growth due to rapid industrialization and escalating manufacturing output, especially in China and India.
CVD Cutting Insert Market introduction
CVD Cutting Inserts are specialized cutting tools primarily used in turning, milling, and drilling operations, characterized by a hard, wear-resistant coating applied through Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) onto a substrate, typically cemented carbide. The CVD process involves chemical reactions between gaseous precursors at high temperatures (typically 800°C to 1000°C), resulting in a tightly adhered, dense layer of materials such as Titanium Carbide (TiC), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), Titanium Nitride (TiN), or Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3). This coating significantly enhances the insert’s properties, offering superior resistance to abrasive wear, crater wear, and thermal deformation, which are critical in demanding high-speed and high-feed machining environments.
The product's primary function is to optimize material removal rates and extend tool life, thereby reducing production costs and machine downtime across various industries. Major applications span the automotive sector for machining engine blocks and components, the aerospace industry for processing high-strength alloys required in turbine blades and structural parts, general engineering, heavy machinery manufacturing, and the energy sector, particularly in oil and gas and power generation equipment. Key benefits driving market adoption include enhanced surface finish quality, stability under extreme heat, and applicability across a wide spectrum of workpiece materials, from standard steels to exotic superalloys. The market is primarily driven by continuous advancements in CVD coating technology, the accelerating pace of global automation, and the inherent requirement for improved efficiency and precision in modern manufacturing settings.
CVD Cutting Insert Market Executive Summary
The CVD Cutting Insert Market is characterized by intense technological competition focused on multi-layer coatings and optimized substrate grades to meet increasingly stringent performance requirements. Business trends highlight a consolidation among major players, who are investing heavily in R&D to develop tailor-made coatings for specific high-performance applications, such as dry machining and continuous cutting of difficult-to-machine materials. Strategic partnerships with end-user industries (OEMs) are becoming crucial for market penetration and obtaining real-time performance feedback. Furthermore, sustainability is emerging as a critical trend, driving the demand for longer-lasting tools that reduce material waste and energy consumption during manufacturing. The integration of digital technologies, facilitating smart tooling and condition monitoring, represents a significant avenue for future market growth and competitive differentiation.
Regional trends indicate that Asia Pacific (APAC) dominates the market share due to its vast, rapidly expanding automotive and general engineering base, particularly in major manufacturing hubs like China, South Korea, and Japan. While North America and Europe are mature markets, their focus remains on high-value, complex machining operations, driving demand for premium CVD grades designed for aerospace and medical applications. Segments trends show that the Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) coating segment is experiencing accelerated growth due to its superior performance in high-speed dry turning applications, offering exceptional resistance to heat and chemical wear. Concurrently, the cemented carbide substrate segment maintains its stronghold, though demand for specialized materials like Ceramic and Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) inserts, coated via adapted CVD methods, is expanding in niche, high-hardness material applications, underscoring a continuous push towards specialized, performance-driven tooling solutions across the industrial landscape.
AI Impact Analysis on CVD Cutting Insert Market
Users frequently inquire about how Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) can be leveraged to improve CVD coating quality, predict tool wear with higher accuracy, and automate tool selection processes in complex machining setups. Key concerns revolve around the integration cost of AI systems, the requirement for vast datasets from manufacturing environments, and the ability of AI to optimize the extremely sensitive and parameter-rich CVD coating process (temperature, gas flow, pressure) to achieve superior adhesion and uniformity. Expectations are high regarding AI’s capacity to move beyond traditional reactive tool replacement toward predictive maintenance, dramatically extending the useful life of expensive CVD inserts, reducing unscheduled downtime, and enabling manufacturers to achieve zero-defect coating batches, thus significantly enhancing overall operational efficiency and product quality in the tooling sector.
- AI-driven optimization of CVD process parameters (temperature, vacuum levels, gas ratios) to achieve uniform, defect-free, multi-layer coatings, reducing batch variability.
- Machine learning algorithms utilized for predictive tool wear modeling, using sensor data (vibration, force, temperature) to anticipate the end-of-life of the CVD insert, optimizing replacement cycles.
- Integration of vision systems and AI for automated quality inspection of finished inserts, detecting microscopic coating imperfections and guaranteeing high-precision edge preparation.
- AI-assisted material selection and coating customization, recommending optimal substrate/coating combinations based on the specific workpiece material, machine dynamics, and cutting operation parameters.
- Enhanced supply chain management using AI to forecast demand for specific high-performance CVD grades, optimizing inventory levels and reducing lead times for manufacturers.
DRO & Impact Forces Of CVD Cutting Insert Market
The CVD Cutting Insert market is significantly influenced by a dynamic interplay of Drivers, Restraints, and Opportunities (DRO). Major drivers include the global expansion of high-volume manufacturing sectors, particularly automotive and general engineering, where CVD inserts offer the best balance of longevity and cost-effectiveness for mass production. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of automated and CNC machining centers worldwide requires highly reliable tooling that can sustain continuous operation at high speeds and feeds, directly favoring CVD inserts due to their exceptional thermal stability and wear resistance provided by coatings like Al2O3. The continuous innovation in coating technology, enabling thinner, more cohesive multi-layer structures, also acts as a potent driver, continually pushing performance boundaries and opening up new application areas.
Conversely, the market faces significant restraints. A primary concern is the volatility and increasing cost of essential raw materials, particularly tungsten and cobalt, which form the cemented carbide substrate. Supply chain disruptions and dependence on specific geographic regions for these minerals introduce cost inflation and uncertainty for insert manufacturers. Additionally, the inherent brittleness of certain thick CVD coatings, making them sensitive to mechanical and thermal shock (especially in interrupted cutting operations), limits their application compared to more ductile PVD alternatives in some demanding scenarios. Stringent environmental regulations related to hazardous chemicals used in the CVD process and the energy-intensive nature of high-temperature deposition also present long-term operational challenges that manufacturers must address through sustainable process innovation.
Opportunities for market expansion are substantial, primarily driven by the increasing demand for machining hard-to-machine superalloys in the aerospace and power generation sectors, where only high-performance CVD inserts can maintain necessary production speeds and tolerances. The rapid growth of the electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing industry provides a fresh application segment, requiring specialized tools for machining lightweight aluminum and highly resistant battery components. Moreover, the refinement of low-pressure CVD (LPCVD) and Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) techniques allows for deposition at lower temperatures, minimizing substrate degradation and broadening the range of applicable substrates, thereby creating technologically superior products that address existing market limitations and capture high-margin, niche applications globally.
Segmentation Analysis
The CVD Cutting Insert market is comprehensively segmented based on coating type, substrate material, primary application, and end-use operation, allowing for precise market tracking and strategic focus. Understanding these segments is crucial as the choice of insert is highly dependent on the specific machining requirement—for example, the material being cut, the cutting speed, and whether the operation involves continuous or interrupted cuts. The complexity of modern manufacturing, which often involves diverse materials and stringent quality standards, dictates a highly specialized product portfolio. Thus, manufacturers continuously tailor their CVD offerings, focusing on developing proprietary multi-layer architectures to serve distinct operational niches, such as heavy roughing versus fine finishing. The cemented carbide segment remains the foundational material, while the Al2O3 coating type is recognized for its superior thermal barrier properties, crucial for high-speed machining.
- By Coating Type:
- Titanium Nitride (TiN)
- Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN)
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
- Multi-layer Coatings (e.g., TiN/TiCN/Al2O3)
- Others (e.g., specific carbides and nitrides)
- By Material:
- Cemented Carbide
- Ceramics
- Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN)
- Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD)
- By Application:
- Automotive Industry
- Aerospace & Defense
- General Engineering
- Heavy Machinery
- Energy and Power Generation
- By End-Use Operation:
- Turning
- Milling
- Drilling
- Grooving and Parting
Value Chain Analysis For CVD Cutting Insert Market
The value chain for the CVD Cutting Insert market begins with the upstream procurement and processing of critical raw materials, primarily tungsten (in the form of tungsten carbide powder) and cobalt (used as a binder in the cemented carbide substrate). The stability of this upstream segment is paramount, as fluctuations in global commodity prices, geopolitical risks in sourcing regions, and increasing regulatory scrutiny over mineral extraction directly impact the production cost and pricing strategy of the finished inserts. Major tooling manufacturers often integrate backwards or establish long-term contracts with specialized powder producers to ensure a consistent supply of high-purity, standardized cemented carbide blanks (green bodies) required for the subsequent deposition process.
The core manufacturing stage involves the preparation of the insert blanks (sintering, grinding, and edge preparation) followed by the high-temperature CVD coating process. This intermediate stage, which includes proprietary CVD reactor technology and specific gas chemistries, represents the highest value-addition step, defining the insert’s performance characteristics, wear resistance, and thermal stability. Downstream analysis focuses on distribution and end-user engagement. Distribution channels are typically dual: direct sales to major OEM manufacturers in automotive or aerospace for specialized, large-volume orders, and indirect sales through extensive networks of industrial distributors and specialized tooling suppliers, who serve the vast general engineering and smaller fabrication shops. The success of the downstream activities relies heavily on technical support, application engineering, and rapid inventory fulfillment to minimize customer downtime.
The final consumption stage involves the end-users, where the insert’s efficiency is proven under real operational conditions. Feedback loops from end-users, managed often through the indirect distribution network, are vital for continuous product improvement and the development of new coatings tailored to emerging materials (e.g., composites or new superalloys). The efficiency of this value chain is increasingly reliant on digitalization, with major manufacturers deploying e-commerce platforms and utilizing IoT tools to track tool performance and manage inventory replenishment, effectively linking the high-tech production stage with the diverse and demanding global customer base, thereby ensuring market relevance and competitiveness.
CVD Cutting Insert Market Potential Customers
Potential customers for CVD cutting inserts span a diverse range of manufacturing sectors that require high material removal rates, excellent surface finish, and extended tool life when machining challenging or high-volume materials. The primary buyers are large-scale Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Tier 1 suppliers within the automotive industry, particularly those involved in producing engine components, transmission parts, and structural elements from steel, cast iron, and increasingly, specialized light alloys. These customers prioritize inserts capable of high-speed, continuous cutting with minimal wear, ensuring high throughput on automated production lines, making the highly abrasive-resistant characteristics of CVD coatings essential for cost control.
A second major customer group includes aerospace and defense contractors. These end-users specialize in machining expensive, high-performance materials such as titanium, nickel-based superalloys (Inconel, Hastelloy), and heat-resistant superalloys (HRSAs) for critical components like turbine blades, engine casings, and airframe structures. For this segment, tool reliability and precision are paramount, as the cost of component failure far outweighs the cost of the insert. CVD inserts, especially those with advanced thermal barrier coatings like Al2O3, are indispensable for these operations due to their ability to withstand the extreme heat generated during the machining of these high-temperature alloys. Smaller, yet significant buyers include general engineering workshops, mold and die makers, and heavy machinery manufacturers (e.g., construction and mining equipment), who rely on distributors to supply a versatile range of CVD inserts for general turning and milling tasks, emphasizing product durability and multi-purpose performance.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 4.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 7.2 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 6.8% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Sandvik AB, Kennametal Inc., Iscar Ltd., Mitsubishi Materials Corporation, Sumitomo Electric Industries, KYOCERA Corporation, OSG Corporation, Tungaloy Corporation, Seco Tools AB, Ceratizit S.A., TaeguTec Ltd., Dormer Pramet, LMT Tools, Zhuzhou Cemented Carbide Group Co., Ltd., ZCC-CT, Korloy Inc., Walter AG, Allied Machine & Engineering Corp., NACHI-FUJIKOSHI CORP., Mapal GmbH & Co. KG |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
CVD Cutting Insert Market Key Technology Landscape
The technology landscape of the CVD Cutting Insert market is defined by continuous process innovation aimed at enhancing coating adherence, reducing residual stress, and enabling complex multi-layer deposition. Traditional CVD, which operates at very high temperatures, remains prevalent but is increasingly being supplemented by advanced techniques such as Medium Temperature CVD (MT-CVD) and Low-Pressure CVD (LP-CVD). MT-CVD, specifically, allows for the deposition of thicker, tougher Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) layers with reduced brittle phases, significantly improving the insert's toughness and making it more suitable for varying cutting conditions. LP-CVD, operating at lower temperatures and pressures, helps minimize the thermal degradation of the cemented carbide substrate and provides better control over the grain structure of the deposited layers, resulting in superior performance in precision applications.
A crucial technological development is the refinement of multi-layer coating architectures. Modern CVD inserts rarely use a single layer; instead, they feature complex structures, often comprising a base layer of TiCN for toughness, an intermediate layer of Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) for superior heat and chemical wear resistance, and a top layer of TiN for friction reduction and wear indication. The focus now is on nanostructured coatings, where the grain size of the coating material is reduced to the nanometer scale. This nanostructuring significantly increases hardness and density while maintaining toughness, thus pushing the limits of high-speed machining capabilities and increasing tool life, particularly when dealing with abrasive materials and dry cutting environments, where heat dissipation is a major challenge.
Furthermore, post-treatment technologies play an increasingly important role in optimizing the final product. Techniques such as polishing or shot peening are utilized after the CVD process to reduce surface roughness, improve chip flow, and mitigate tensile residual stresses in the coating layer that often lead to micro-chipping or early failure. Edge preparation technology—the controlled dulling or honing of the cutting edge prior to coating—is also critical, as the geometry of the edge significantly influences the performance and stability of the CVD layer during cutting. These combined technological advancements, spanning from novel gas chemistries in the reactor to mechanical finishing processes, collectively ensure that CVD inserts remain the leading choice for heavy-duty, high-performance machining operations across global manufacturing sectors.
Regional Highlights
- Asia Pacific (APAC): APAC represents the largest and fastest-growing market due to the robust expansion of manufacturing sectors, led by China, Japan, South Korea, and India. China's dominance in general engineering, automotive manufacturing, and consumer electronics drives immense demand for cost-effective, high-volume CVD inserts. Japan and South Korea, conversely, focus on high-technology, precision manufacturing, demanding premium, multi-layer CVD grades for specialized machinery and tooling. The trend toward domestic production and government initiatives supporting high-end manufacturing are key factors propelling market size and technological adoption in this region.
- North America: This region is characterized by high demand for specialized, high-performance CVD inserts, driven predominantly by the aerospace and defense sectors, along with sophisticated medical device manufacturing. The market here emphasizes quality, reliability, and tooling solutions for hard-to-machine alloys (titanium, nickel superalloys). Manufacturers in North America focus on specialized grades and often require customized coatings, contributing to higher average selling prices compared to high-volume regions. The strong push towards Industry 4.0 adoption also drives demand for smart tooling embedded with tracking capabilities.
- Europe: The European market, highly mature and technology-intensive, is driven by the strong presence of the German automotive industry (including electric vehicle production), high-end machinery builders, and precision engineering firms. Europe is a leader in sustainable manufacturing practices, leading to stringent demands for inserts that offer exceptional longevity and efficiency, reducing overall tool consumption and waste. Key European countries, particularly Germany, Italy, and Sweden, show high adoption rates for advanced MT-CVD and tailor-made coating architectures to optimize complex high-speed machining tasks.
- Latin America (LATAM): This region exhibits moderate growth, primarily centered around Brazil and Mexico, fueled by their respective automotive assembly and infrastructure development projects. The market demand is predominantly for standard, versatile CVD grades suitable for general engineering and mass production of steel and cast iron components. Economic volatility and dependency on imported specialized inserts occasionally restrain rapid market expansion, though increasing localized manufacturing investment presents long-term growth opportunities.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): The MEA market growth is predominantly linked to the large oil and gas sector and expanding infrastructure projects. The demand for CVD inserts is critical for manufacturing and maintenance operations involving heavy machinery and drilling equipment, often requiring specialized coatings that withstand extreme heat and abrasive environments. Saudi Arabia and the UAE are primary consumers, focusing on robust tooling for energy-related applications.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the CVD Cutting Insert Market.- Sandvik AB
- Kennametal Inc.
- Iscar Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Materials Corporation
- Sumitomo Electric Industries
- KYOCERA Corporation
- OSG Corporation
- Tungaloy Corporation
- Seco Tools AB
- Ceratizit S.A.
- TaeguTec Ltd.
- Dormer Pramet
- LMT Tools
- Zhuzhou Cemented Carbide Group Co., Ltd.
- ZCC-CT
- Korloy Inc.
- Walter AG
- Allied Machine & Engineering Corp.
- NACHI-FUJIKOSHI CORP.
- Mapal GmbH & Co. KG
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the CVD Cutting Insert market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What differentiates CVD inserts from PVD inserts, and when should each be used?
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) coatings are typically thicker (5–20 µm), applied at high temperatures (800°C–1000°C), resulting in superior adhesion, high resistance to crater wear, and thermal stability. They are ideal for heavy-duty, continuous cutting, and high-speed turning of cast iron and steel. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coatings are thinner (1–5 µm), applied at lower temperatures, preserving edge sharpness and substrate toughness, making them preferred for interrupted cutting, milling, and machining stainless steels and non-ferrous alloys.
How does the volatility of raw material prices, particularly tungsten, affect the CVD insert market?
Tungsten, a key component of the cemented carbide substrate, experiences significant price volatility due to concentrated mining and processing in specific geographical regions. This fluctuation directly impacts the cost of goods sold for insert manufacturers. To mitigate risk, companies often invest in recycling programs and secure long-term sourcing contracts, but persistent price instability necessitates continuous adjustments in the final product pricing and supply chain management.
Which coating type offers the best performance for high-speed dry machining of steels?
Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) coatings are generally considered the best choice for high-speed dry machining of steel and cast iron. Al2O3 offers superior chemical inertness and acts as an excellent thermal barrier, preventing heat transfer into the substrate and resisting oxidation at high cutting temperatures, thereby maximizing tool life and maintaining structural integrity under extreme thermal load.
What are the primary technological challenges facing manufacturers in the CVD coating process?
Key challenges include controlling residual tensile stress within the thick coating layers, which can lead to micro-chipping; ensuring uniform coating thickness and adhesion across complex insert geometries; and managing the environmental impact and energy consumption associated with the high-temperature, gas-intensive deposition process. Research focuses on MT-CVD and post-treatment methods to address these issues.
How is the demand for CVD inserts influenced by the electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing trend?
The EV trend drives demand for specialized CVD inserts required to efficiently machine lightweight materials (aluminum, composites) for chassis and body components, and, critically, for processing the hard, abrasive materials used in battery casing and complex transmission systems. While the materials differ from traditional internal combustion engines, the need for high-throughput, reliable tooling remains essential, fueling specific segment growth.
What is the significance of multi-layer coatings in modern CVD inserts?
Multi-layer coatings combine the benefits of different materials into a single insert, providing optimized performance across multiple wear mechanisms. For example, a TiCN layer provides toughness and abrasive resistance, while an Al2O3 layer offers thermal protection. This architecture maximizes tool versatility and extends operational life far beyond what single-layer coatings can achieve, crucial for complex manufacturing environments.
What role does edge preparation play in the performance of CVD inserts?
Edge preparation, the precise shaping of the cutting edge prior to coating, is paramount. An optimally honed edge supports the typically brittle CVD coating, preventing premature chipping during entry and exit of the cut. Improper edge preparation leads to early tool failure, even with a high-quality coating. Modern techniques use precision brushing and micro-blasting to ensure the perfect, consistent edge geometry required for high-performance CVD applications.
Which end-use operation segment consumes the largest volume of CVD cutting inserts?
The Turning segment traditionally consumes the largest volume of CVD cutting inserts globally. This is because CVD coatings excel in continuous cutting operations typical of turning, especially in the high-volume production of automotive components (shafts, cylinders, brakes) and general rotational parts where consistent wear resistance and thermal stability are critically required.
How are environmental regulations impacting the production process of CVD inserts?
Environmental regulations primarily target the use of precursor gases and the high energy consumption of the CVD process. Manufacturers are compelled to invest in cleaner technologies, such as recycling byproduct gases, implementing closed-loop systems, and exploring low-temperature deposition methods (like MT-CVD or LP-CVD) to reduce the overall carbon footprint and compliance risk associated with the manufacturing of the cutting tools.
In the aerospace industry, why are CVD coatings favored over non-coated materials for superalloys?
Aerospace superalloys (like Inconel) generate extremely high heat during machining, causing rapid chemical reaction and diffusion wear in non-coated tools. CVD coatings, particularly those featuring robust Al2O3 layers, provide the essential thermal barrier and chemical stability needed to maintain the cutting edge's integrity, ensuring required precision, extended tool life, and preventing costly damage to expensive workpiece materials.
What is the future outlook for the use of Ceramic and CBN substrates in conjunction with CVD techniques?
The outlook is positive, albeit in niche markets. While cemented carbide dominates, specialized ceramic and Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) substrates, traditionally difficult to coat with standard CVD due to temperature sensitivity, are increasingly being paired with customized LP-CVD or specialized bonding layers. This combination aims to deliver superior performance for extremely hard ferrous materials or highly abrasive cast iron, catering to high-value, high-performance segments.
How does Industry 4.0 affect the demand and specifications for CVD inserts?
Industry 4.0 drives demand for higher quality, more consistent CVD inserts capable of sustained, automated operation. Specifications now include requirements for smart tooling compatibility, such as precise geometric consistency for automated tool changing, and the need for extremely reliable performance validated by digital twin simulations, reducing the tolerance for failure in fully autonomous production lines.
What is the typical lifespan improvement achieved by a high-quality CVD coating?
A high-quality, multi-layer CVD coating can extend the operational life of a cemented carbide insert by a factor of 3 to 10 times, depending on the application and workpiece material. This substantial increase in tool life is due to the coating's ability to resist abrasive, crater, and flank wear mechanisms simultaneously, translating directly into significant reductions in machine downtime and overall tooling costs for the end-user.
What is the primary function of the TiCN layer often used in CVD multi-layer coatings?
The Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) layer in CVD multi-layer systems provides excellent abrasive wear resistance and increased toughness compared to pure TiC. It is often deposited using MT-CVD techniques to achieve a columnar grain structure, which enhances the layer's resistance to mechanical shock and serves as a tough intermediary layer between the substrate and the outer Aluminum Oxide layer.
Which regional market is exhibiting the highest growth rate and why?
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region is exhibiting the highest Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) due to rapid industrial expansion, massive investments in infrastructure development, and the establishment of large-scale automotive and electronics manufacturing centers, particularly in emerging economies like China, India, and Vietnam, driving exceptional volume demand for standard and advanced CVD tooling solutions.
How do manufacturers ensure the adhesion of thick CVD coatings to the substrate?
Adhesion is ensured through meticulous pre-treatment of the substrate, including advanced cleaning and etching, and the precise control of the intermediate bonding layer chemistry during the CVD process. Graded interfaces, where the chemical composition transitions gradually from the substrate to the coating, are often employed to manage thermal expansion differences and minimize internal stresses, significantly enhancing the bond strength.
What specific challenges does machining titanium alloys present that necessitate specialized CVD inserts?
Titanium alloys are difficult to machine due to their low thermal conductivity, which concentrates heat at the cutting edge, and their tendency to chemically react with the tool material. Specialized CVD inserts use optimized edge geometries and highly thermal-resistant coatings (like Al2O3) to reduce chemical diffusion, manage heat effectively, and prevent catastrophic tool failure.
Are recycled CVD inserts gaining traction in the market, and why?
Yes, recycled CVD inserts are gaining significant traction, driven primarily by sustainability mandates and the high cost of raw materials like tungsten. Recycling programs allow manufacturers to recover the expensive cemented carbide substrate, reducing their reliance on volatile virgin material markets and providing customers with more environmentally friendly and often cost-competitive tooling options.
How is competition intensifying in the CVD cutting insert market?
Competition is intensifying through technological differentiation, where major players focus on developing proprietary multi-layer coating chemistries and optimized substrate grades for highly specific applications. Furthermore, competitive pricing pressure, particularly from Asian manufacturers focused on high-volume standard grades, forces global leaders to continually innovate and focus on high-margin, specialized tooling solutions.
What is the role of Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) in the cutting insert industry?
While traditional CVD is favored for thick, high-temperature coatings, PECVD is utilized to deposit specific, high-performance coatings at much lower temperatures. The lower processing heat minimizes the degradation of the substrate's mechanical properties, making PECVD crucial for coating heat-sensitive materials or for applying highly specialized, often nanostructured, top layers that enhance lubricity and friction reduction.
What primary metrics are used to evaluate the performance of a CVD cutting insert?
The primary performance metrics include tool life (measured in minutes or parts produced), surface finish quality achieved on the workpiece, material removal rate (MRR), and the cutting speed and feed rate at which the insert can reliably operate. These metrics are benchmarked against cost-per-part to determine the overall economic efficiency of the CVD tooling solution.
How do global economic slowdowns typically affect the CVD insert market?
Global economic slowdowns generally lead to reduced capital expenditure and decreased manufacturing output in sectors like automotive and heavy machinery. This results in lowered demand for new tooling. However, during downturns, manufacturers often intensify focus on optimizing efficiency, leading to a compensatory demand for premium, long-life CVD inserts that reduce operational waste and downtime.
Which industry segment is driving demand for CVD inserts designed for non-ferrous materials?
While PVD often dominates non-ferrous machining, certain CVD applications are driven by the general engineering sector and the rising demand for efficient machining of hard non-ferrous materials like certain bronzes or specialized aluminum alloys requiring heavy roughing. However, most non-ferrous cutting requiring sharp edges still heavily relies on PCD or specialized uncoated PVD tools.
What distinguishes the latest generation of CVD coatings from those 10 years ago?
The latest generation features significantly improved residual stress control, nanostructured grain sizes resulting in higher hardness and toughness, and more sophisticated multi-layer architectures that seamlessly integrate superior thermal barriers (Al2O3) with shock-resistant intermediate layers (TiCN). These advancements enable reliable high-speed operation under previously impossible conditions, such as high-temperature dry machining.
Why is the demand for custom CVD coatings rising among Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs)?
OEMs dealing with high-volume, specific components (e.g., specialized engine blocks or unique aerospace parts) require tooling that is perfectly optimized for their exact material, machine dynamics, and cutting path. Custom CVD coatings, tailored for optimal thickness, material composition, and edge preparation, minimize tooling costs per unit by maximizing tool longevity and ensuring precise, repeatable quality far better than standard, off-the-shelf options.
What is the impact of digitalization on the distribution channel for CVD inserts?
Digitalization has streamlined the distribution channel through e-commerce platforms and automated inventory management systems. Customers can now use online configurators to select the optimal insert grade, and IoT-enabled vending machines at client sites ensure real-time inventory tracking and automated replenishment, minimizing stockouts and improving overall supply chain efficiency for both direct and indirect sales channels.
How do manufacturers mitigate the risk of chipping in CVD inserts during interrupted cuts?
Manufacturers mitigate chipping risks by optimizing the substrate grade for increased toughness (higher cobalt content), refining the cutting edge geometry (heavier honing), and utilizing thinner, stress-managed MT-CVD coatings that are inherently tougher than standard high-temperature CVD. While PVD remains superior for heavy interrupted cuts, these advancements expand the application range of CVD.
What are the key differences in tooling needs between the general engineering sector and the aerospace sector?
The general engineering sector typically requires versatile, cost-effective CVD grades for machining common steels and cast iron in high volume. The aerospace sector demands highly specialized, premium CVD inserts tailored for low-volume, high-value machining of exotic alloys (HRSAs, titanium), prioritizing reliability, precision, and thermal performance over initial cost due to the extremely high value of the workpiece.
What is the significance of the cemented carbide recycling process for the market?
Cemented carbide recycling is vital as it provides a stable, secondary source of tungsten and cobalt, reducing reliance on primary mining. Techniques like the Zinc process allow for the environmentally friendly recovery of the carbide, significantly lowering the material cost for the insert manufacturers and contributing to a circular economy model within the tooling industry.
In which regional market are high-performance PVD coatings posing the most significant competitive threat to CVD?
In mature markets like North America and Europe, where precision milling and complex interrupted cutting operations are prevalent, specialized high-performance PVD coatings (using advanced techniques like HiPIMS) pose a strong competitive threat. These PVD coatings offer superior mechanical shock resistance and preserve edge sharpness better than standard CVD, capturing market share in medium-duty and finishing applications.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
