Dicing Blade Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 436542 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 251 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Dicing Blade Market Size
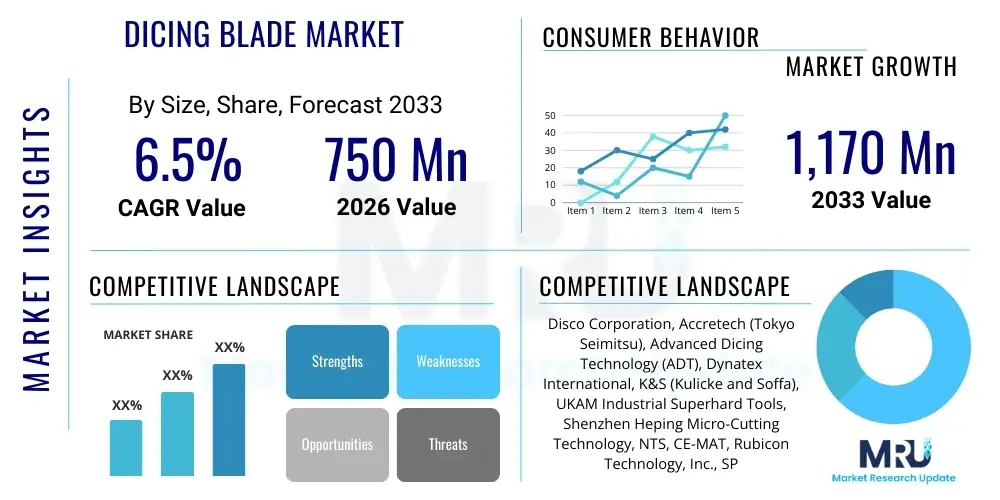
The Dicing Blade Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 750 Million in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 1,170 Million by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Dicing Blade Market introduction
The Dicing Blade Market encompasses the manufacturing and distribution of precision cutting tools primarily utilized in the semiconductor industry for separating individual integrated circuits (ICs) or dies from a silicon, ceramic, or glass wafer. These highly specialized blades are essential components in the back-end manufacturing process, requiring extreme precision, durability, and minimal kerf loss to maximize yield. The demand is intrinsically linked to global semiconductor production volumes, technological advancements in wafer materials, and the increasing complexity of microelectronic packaging, particularly in applications requiring ultra-thin die separation, such as advanced memory chips and System-in-Package (SiP) solutions. The precision and material composition of these blades—typically diamond abrasive suspended in a metal or resin matrix—are critical determinants of the final product quality and manufacturing efficiency.
Dicing blades are categorized based on their bonding material (resin, nickel, or metal bond) and the size and concentration of the embedded diamond particles, which dictates their suitability for various substrate materials like silicon, gallium arsenide (GaAs), glass, and ceramic. Major applications span across consumer electronics, automotive components, medical devices, and high-performance computing, all driven by the pervasive integration of microprocessors and sensor technology. Benefits derived from optimized dicing processes include higher throughput, reduced material waste (kerf loss), superior edge quality (minimizing chipping and microcracks), and the ability to handle larger, more complex wafers with higher precision. The relentless push toward smaller feature sizes and three-dimensional (3D) stacking necessitates continuous innovation in blade thinness and abrasive quality.
Key driving factors fueling market expansion include the exponential growth in the Internet of Things (IoT) devices, the accelerated deployment of 5G infrastructure, and the massive increase in data center construction, all demanding greater numbers of high-density semiconductor chips. Furthermore, the rise of advanced packaging techniques, such as wafer-level chip-scale packaging (WLCSP) and fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP), places stringent requirements on dicing equipment and consumables, thereby driving demand for premium, high-performance blades. The automotive sector’s transition towards electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving systems, which heavily rely on power management ICs and complex sensor arrays, also acts as a significant catalyst for market growth, requiring specialized blades for processing materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN).
Dicing Blade Market Executive Summary
The Dicing Blade Market is experiencing robust growth, primarily fueled by global semiconductor industry expansion and the increasing complexity of microelectronic devices. Key business trends indicate a strong shift towards ultra-thin dicing blades (less than 20 micrometers) and highly specialized diamond abrasive compositions necessary for handling fragile, compound semiconductor materials like SiC and GaN, essential for 5G and high-power applications. Leading manufacturers are investing heavily in material science R&D to enhance blade life, reduce thermal stress during cutting, and improve yield rates for sensitive wafer materials. Consolidation among smaller, specialized suppliers by major industry players is also a noticeable trend aimed at securing proprietary bonding technologies and expanding geographic reach, particularly into high-growth Asian manufacturing hubs.
Regionally, Asia Pacific (APAC) continues to dominate the market share, driven by the concentration of global semiconductor foundries, assembly, and packaging operations (OSATs) in countries such as Taiwan, South Korea, China, and Japan. Governments across APAC are actively supporting domestic semiconductor production through subsidies and policy initiatives, which directly translates into heightened demand for dicing consumables. North America and Europe, while smaller in volume, represent critical markets for advanced technology adoption, focusing on R&D for next-generation silicon photonics and wide-bandgap semiconductor devices, driving demand for premium, high-precision tools. Regulatory compliance and environmental standards related to manufacturing processes are increasingly influencing material choices and disposal methods, particularly in mature Western markets.
Segment trends highlight the dominance of resin-bonded blades due to their superior performance on standard silicon wafers and improved adaptability for thinner dicing applications, although nickel-bonded blades remain critical for high-rigidity cuts required by hard materials. Application-wise, memory devices and microprocessors remain the largest consumers, but the fastest growth is observed in the photonics and power semiconductor segments due reflecting the electrification and digitization megatrends. The adoption of alternative dicing technologies, such as laser dicing, poses a long-term challenge but concurrently drives innovation in hybrid solutions where specialized blades are still required for pre-scoring or final separation tasks. The market’s overall health remains closely tied to capital expenditure cycles within the global semiconductor fabrication industry.
AI Impact Analysis on Dicing Blade Market
Common user inquiries regarding AI's influence on the Dicing Blade Market center on how artificial intelligence and machine learning (ML) optimize the physical dicing process, particularly concerning yield management, predictive maintenance, and quality control. Users often question if AI can reduce the dependence on highly skilled human operators by automating process parameter settings and compensating for minute material variations in real-time. The core expectation is that AI algorithms will enhance the operational efficiency of dicing equipment, predicting blade wear out with high accuracy, optimizing feed rates and spindle speeds based on wafer type and thermal profile, and identifying potential failures before they impact production yield, thereby reducing consumable usage and downtime. There is also significant interest in AI’s role in analyzing defect data post-dicing to provide actionable feedback for blade design improvements and process adjustments.
- AI-driven Predictive Blade Maintenance: Algorithms analyze vibration data, current draw, and historical cutting logs to forecast blade lifespan and schedule replacement precisely, minimizing unplanned downtime and maximizing material utilization.
- Real-Time Process Optimization: Machine learning models dynamically adjust dicing parameters (feed rate, coolant flow, spindle speed) based on live feedback from sensors, optimizing chip edge quality and reducing chipping for various wafer types.
- Enhanced Defect Detection: AI-powered vision systems automatically classify and map dicing-related defects (e.g., chipping, microcracks) with greater speed and accuracy than conventional methods, leading to faster feedback loops for manufacturing adjustments.
- Automated Recipe Generation: AI helps generate optimal dicing recipes for new or complex wafer materials (e.g., SiC, GaN, ultra-thin silicon), significantly reducing the time required for manual process development and qualification.
- Supply Chain and Inventory Management: Predictive analytics optimize inventory levels for various blade types based on anticipated fabrication schedules and global demand shifts, ensuring timely supply and reducing warehousing costs.
- Simulation and Digital Twin Technology: AI integrates into digital twin environments to simulate the dicing process under various conditions, aiding in the design of blades with optimized geometry and abrasive distribution.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Dicing Blade Market
The Dicing Blade Market is driven by the relentless advancement of semiconductor technology (miniaturization and integration), while being constrained by the high cost of raw materials and the emergence of non-contact cutting alternatives. Opportunities arise from niche markets like MEMS and SiC/GaN processing, demanding highly specialized, high-performance blades. The critical impact forces include technological complexity (requiring precision), cost pressures (driving efficiency), and competitive dynamics (forcing constant innovation). These elements interact to shape the market trajectory, where superior yield and throughput ultimately define successful product adoption.
Drivers include the booming demand for advanced logic and memory chips necessary for cloud computing, 5G devices, and automotive electronics, which mandates increased wafer throughput and requires consumables capable of handling larger wafer sizes (300mm and 450mm). Restraints predominantly involve the significant operational expenditure associated with high-precision dicing equipment and the blades themselves, especially customized or ultra-thin variants. Furthermore, environmental and disposal concerns related to diamond-containing waste and cooling liquids pose regulatory challenges, particularly in stringent regions. The continuous development of alternative dicing technologies, particularly femtosecond laser dicing, represents a substantial long-term threat by potentially displacing traditional mechanical cutting methods in certain high-value applications, compelling traditional blade manufacturers to diversify or innovate hybrid solutions.
Opportunities are significant within the wide-bandgap (WBG) semiconductor sector, namely Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN), which are notoriously hard and brittle, demanding specialized, highly durable blades that command premium pricing. The proliferation of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) and sensor arrays also presents a unique opportunity, as these heterogeneous structures require complex, multi-stage dicing processes. Impact forces are dominated by the need for superior edge quality to ensure die reliability, which pressures manufacturers to perfect blade bonding techniques and abrasive alignment. Economic impact forces are tied directly to semiconductor fabrication capital expenditures (CapEx), making the market highly sensitive to global economic cycles and geopolitical stability affecting trade and supply chains.
Segmentation Analysis
The Dicing Blade Market is segmented extensively based on material type, bonding method, blade thickness, primary application, and end-user industry, reflecting the high customization required for semiconductor manufacturing processes. Segmentation based on bonding material—Resin, Nickel, and Metal—is crucial, as each offers distinct performance characteristics tailored to different wafer hardness and desired kerf width. Resin blades offer flexibility and high cutting speeds suitable for mainstream silicon, while nickel-bonded blades provide rigidity necessary for harder materials or challenging geometries. Blade thickness defines precision capability, with ultra-thin blades (<20µm) commanding premium pricing due to their complexity and essential role in advanced packaging like 3D stacking and WLCSP, maximizing the number of usable dies per wafer.
The application segmentation is complex, covering standard dicing for ICs, memory modules (DRAM, NAND), power semiconductors (SiC, GaN), optoelectronics, and various MEMS devices. Each application imposes unique demands on blade properties regarding chipping control, thermal dissipation, and wear rate. End-user classification typically divides the market between Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) that handle the entire process internally and Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) companies, which are large-scale consumers of dicing blades and often drive demand for standardized high-volume products. Regional segmentation reflects the geographical concentration of semiconductor production, with Asia Pacific being the dominant consuming region.
Strategic analysis of these segments reveals that while the traditional IC dicing segment retains the largest volume share, the highest growth and profitability margins are found in niche segments such as SiC/GaN dicing and ultra-thin blades used in advanced heterogeneous integration. Companies focusing on specialized materials science for bonding agents and optimized diamond grit formulations are strategically positioned to capitalize on these high-growth segments. Furthermore, the market is moving towards total process solutions, where blade providers offer integrated cutting parameters and application support, rather than just selling the consumable, thereby enhancing customer stickiness and optimizing overall operational performance in high-stakes manufacturing environments.
- By Material Type:
- Standard Silicon Dicing Blades
- Compound Semiconductor Dicing Blades (e.g., GaAs, InP)
- Wide-Bandgap (WBG) Semiconductor Dicing Blades (SiC, GaN)
- Glass and Ceramic Substrate Dicing Blades
- Sapphire Dicing Blades (for LED manufacturing)
- By Bonding Method:
- Resin Bond Blades: Offer higher flexibility, lower cutting forces, suitable for standard silicon and fragile materials.
- Nickel (Electroplated) Bond Blades: High abrasive protrusion, aggressive cutting, often used for initial deep cuts or hard materials.
- Metal Bond Blades (Sintered): Excellent wear resistance, higher rigidity, preferred for demanding, high-volume applications or extremely hard substrates.
- Hybrid Bond Blades: Combining resin and metal characteristics for specialized cutting requirements.
- By Blade Thickness:
- Standard Thickness (>40 µm)
- Thin Thickness (20 µm to 40 µm)
- Ultra-Thin Thickness (Below 20 µm): Critical for advanced packaging like WLCSP and 3D stacking to maximize die count and minimize kerf loss.
- By Application:
- Integrated Circuits (ICs) and Microprocessors
- Memory Devices (DRAM, NAND Flash)
- Power Semiconductors and Devices
- Optoelectronics and Photonics
- Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS)
- LED/OLED Manufacturing
- Radio Frequency (RF) Devices
- By End User:
- Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs)
- Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) Providers
- Wafer Fabrication Houses (Foundries)
- Other Research Institutions and Specialty Manufacturers
- By Abrasive Type:
- Natural Diamond Blades
- Synthetic Diamond Blades (Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline)
- Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) Blades (Niche applications)
Value Chain Analysis For Dicing Blade Market
The Dicing Blade market value chain is characterized by a high degree of specialization, starting with the procurement of critical raw materials, primarily industrial diamonds (natural or synthetic) and specialized bonding agents (nickel powder, high-performance resins). Upstream analysis involves rigorous quality control of these raw materials, as the concentration and uniformity of the diamond grit directly dictate the final blade performance and lifespan. Key upstream players are specialized material suppliers and chemical manufacturers providing proprietary compounds essential for blade longevity and cutting efficiency. The complexity of synthesizing uniform, high-grade diamond particles suitable for ultra-thin blades is a critical entry barrier at this stage.
The core manufacturing process, involving the precise blending of abrasive materials with the bonding matrix and the subsequent sintering or electroplating, constitutes the midstream. Manufacturers often employ proprietary vacuum processing and specialized molding techniques to ensure dimensional accuracy and structural integrity, especially for blades operating at high rotational speeds. Distribution channels are varied but rely heavily on direct sales or specialized technical distributors. Due to the high-stakes nature of semiconductor production, end-users prefer direct engagement with manufacturers for technical support, rapid prototyping of new blade designs, and process qualification. Indirect distribution often handles standardized or high-volume resin-bonded blades for established processes.
Downstream, the market is defined by the end-user—semiconductor fabrication plants (Fabs), OSATs, and packaging houses—where the blades are used in high-precision dicing saws. Customer relationships are strengthened through technical partnerships focused on yield optimization and cost per cut minimization. The after-market services, including technical consultation, process optimization support, and inventory management, are integral parts of the value delivery. The value captured by the blade manufacturer is high due to the intellectual property surrounding bonding technology and the necessity for continuous innovation to keep pace with shrinking geometries and novel substrate materials like thin-film glass and advanced polymer coatings used in flexible electronics.
Dicing Blade Market Potential Customers
The primary consumers of dicing blades are large entities involved in the final stages of semiconductor manufacturing and packaging, categorized mainly as Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) and Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test (OSAT) providers. IDMs, such as Intel, Samsung, and Micron, utilize these blades in their captive back-end facilities to process their own manufactured wafers for various product lines, demanding highly customized solutions that align precisely with their proprietary process controls and yield targets. These companies often seek blades optimized for high-volume production of specific memory or logic chip architectures, focusing on minimizing kerf loss and maximizing throughput.
OSAT companies, including ASE Group, Amkor Technology, and Powertech Technology, form the largest and fastest-growing customer segment. They serve a broad client base (fabless companies, foundries) and require a vast array of standardized and specialty blades to handle diverse wafer materials and packaging formats, ranging from simple plastic packages to complex 3D stacked chips. Their purchasing decisions are heavily influenced by the total cost of ownership (TCO), blade lifespan consistency, and the vendor’s ability to guarantee consistent supply across multiple international manufacturing sites. As OSATs handle the manufacturing intricacies for countless clients, the flexibility and robustness of the dicing solutions they procure are paramount.
Beyond the core semiconductor sector, potential customers include manufacturers of specialized electronic components such as LED lighting companies requiring blades for sapphire substrate cutting, suppliers of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) devices (e.g., accelerometers, gyroscopes, pressure sensors), and emerging players in the power electronics field utilizing SiC and GaN materials. Furthermore, research laboratories and academic institutions involved in microfabrication and prototype development represent a smaller, but technically demanding, customer base requiring specialized blades for non-standard material processing and small batch runs. The common denominator among all these buyers is the absolute necessity for precision and reliability in separating microelectronic components without compromising their functionality.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 750 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 1,170 Million |
| Growth Rate | 6.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Disco Corporation, Accretech (Tokyo Seimitsu), Advanced Dicing Technology (ADT), Dynatex International, K&S (Kulicke and Soffa), UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools, Shenzhen Heping Micro-Cutting Technology, NTS, CE-MAT, Rubicon Technology, Inc., SPTS Technologies (Orbotech), Asahi Diamond Industrial Co., Ltd., Shanghai Sijin Intelligence, Tsubaki Diamond Industrial Co., Ltd., Nippon Diamond Co., Ltd., Dr. Fritsch GmbH, Diamond Tool & Abrasives, Meccaniche Veneziane. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Dicing Blade Market Key Technology Landscape
The technology landscape for dicing blades is centered on material science innovation, focusing on optimizing the microstructure of the abrasive layer and the chemical composition of the bonding matrix to achieve superior performance metrics. A significant area of development involves the synthesis of specialized, high-purity synthetic diamond grits, which are engineered for uniformity in size, shape, and crystallographic orientation, crucial for maintaining a consistent cut and reducing chipping in sensitive silicon wafers. Blade manufacturers employ advanced techniques like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) to potentially create thin diamond films or use sophisticated sintering processes in metal-bonded blades to ensure even distribution and strong retention of the diamond particles, leading to extended blade life and reduced frequency of replacement in high-volume production environments. Furthermore, the push towards achieving extremely narrow kerf widths mandates technological advancements in core material selection and manufacturing precision to produce ultra-thin blades that maintain necessary rigidity and stability during high-speed rotation without fracturing.
Another pivotal technological advancement involves the development of proprietary bonding technologies, particularly for resin-bonded blades. Modern resin bonds often incorporate specialized fillers and polymers designed to enhance thermal stability and dissipate heat more effectively during the dicing process, mitigating thermal stress on the wafer which can lead to microcracks. This is crucial for dicing brittle materials and ultra-thin wafers. For nickel-bonded blades, advanced electroplating techniques are utilized to control the nickel matrix density and diamond protrusion height with nanometer precision. Furthermore, manufacturers are exploring multi-layered or gradient blade designs, where the abrasive concentration or bond hardness varies across the blade width to optimize both the initial cutting action and the subsequent side wall smoothing, enhancing overall die quality and reliability, especially for deep cuts required in through-silicon via (TSV) applications.
The integration of dicing blade technology with the dicing saw equipment itself forms a crucial part of the ecosystem. Innovations in saw technology, such as dynamic spindle speed control, advanced vision alignment systems (using machine learning for precision alignment), and improved coolant delivery systems, directly impact blade performance. The shift towards dry dicing or reduced-coolant dicing methods also requires corresponding blade material innovations that can withstand higher friction and thermal load without degrading rapidly. The competitive edge is often gained by companies that offer a comprehensive solution, combining highly optimized blades with compatible machine control software and operational methodologies, thereby ensuring maximum yield for customers engaging in sophisticated processes like stepped dicing, bevel dicing, or the handling of highly brittle wide-bandgap materials that require precise control over material removal rates and minimized surface damage.
Regional Highlights
The Dicing Blade Market exhibits significant regional variations in demand, driven largely by the geographical clustering of semiconductor manufacturing and packaging operations.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): APAC is the global powerhouse for semiconductor manufacturing, commanding the largest market share by volume and value. Countries like Taiwan (TSMC, ASE), South Korea (Samsung, SK Hynix), China (rapidly expanding domestic fabrication), and Japan (specialized equipment and material suppliers like Disco) are central to the industry. The region drives demand for both high-volume standard blades and advanced ultra-thin blades necessary for WLCSP and 3D integration packaging techniques. Government incentives supporting local chip production further solidify APAC’s dominance.
- North America: This region focuses heavily on R&D, advanced material processing, and specialized high-reliability components (e.g., aerospace and defense). While manufacturing volume is lower compared to APAC, the demand is strong for premium, specialized blades used in cutting compound semiconductors (GaAs, SiC) and high-density computing chips. The push for semiconductor self-sufficiency through initiatives like the CHIPS Act is expected to boost domestic fabrication capacity and, consequently, blade consumption.
- Europe: Characterized by strong growth in the automotive and industrial electronics sectors. Europe is a key consumer for dicing blades used in manufacturing power semiconductors (especially SiC and GaN devices required for EVs and industrial automation) and highly complex sensor technologies (MEMS). Germany, France, and Ireland are focal points for advanced manufacturing and R&D activities, driving demand for technologically complex cutting solutions.
- Latin America (LATAM): Currently represents a nascent market for dicing blades, mainly focused on assembly and testing operations rather than full-scale fabrication. Growth is steady, driven by increasing foreign investment and the expansion of electronics assembly operations, particularly in Mexico and Brazil. The demand primarily centers on high-volume, cost-effective standard resin-bonded blades.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): This region holds the smallest share but shows potential growth tied to regional diversification strategies focusing on technology infrastructure and data center construction. Current demand is highly centralized and sourced primarily through established international distributors supplying specialized maintenance and low-volume assembly operations. Future growth is dependent on the realization of large-scale technology investment projects.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Dicing Blade Market.- Disco Corporation
- Accretech (Tokyo Seimitsu)
- Advanced Dicing Technology (ADT)
- Dynatex International
- Kulicke and Soffa (K&S)
- ASAHI Diamond Industrial Co., Ltd.
- UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools
- NTS (Nippon Tool System)
- Shenzhen Heping Micro-Cutting Technology Co., Ltd.
- SPTS Technologies (Orbotech)
- Tsubaki Diamond Industrial Co., Ltd.
- Nippon Diamond Co., Ltd.
- Dr. Fritsch GmbH
- MECCANICHE VENEZIANE
- CE-MAT
- Precision Micro-Optics Inc.
- Meyer Burger Technology AG
- Rubicon Technology, Inc.
- Shanghai Sijin Intelligence Co., Ltd.
- Diamond Tool & Abrasives, Inc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Dicing Blade market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What are the key performance metrics for evaluating dicing blades?
Key performance metrics include kerf width (material removal width, minimized for higher yield), chipping level (measured in microns, minimized for die reliability), blade life (total operational hours or cuts achieved), and cutting speed (throughput optimization). Manufacturers focus on minimizing chipping and kerf width while maximizing speed and life.
How does the shift to Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN) wafers impact dicing technology?
SiC and GaN are significantly harder and more brittle than traditional silicon, necessitating the use of specialized, highly durable, metal-bonded or hybrid-bonded diamond blades with optimized abrasive particle size and concentration. This shift drives demand for premium, high-wear-resistance consumables capable of handling higher thermal loads.
Which bonding method (Resin, Nickel, or Metal) dominates the Dicing Blade Market?
Resin-bonded blades typically dominate the market volume, particularly for processing standard silicon wafers and thinner die structures, due to their flexibility, reduced heat generation, and good balance of performance and cost. However, nickel and metal bonds are critical for high-rigidity cutting of hard compound and wide-bandgap materials.
What is the competitive threat posed by laser dicing technology?
Laser dicing offers non-contact, cleaner cutting with reduced kerf loss, making it highly competitive for ultra-thin and fragile materials, particularly in memory and advanced packaging. However, mechanical dicing remains dominant for thick wafers and high throughput, often leveraging hybrid solutions where blades perform complementary tasks alongside lasers.
What role does the Asia Pacific region play in the Dicing Blade Market?
The Asia Pacific region is the largest consumer and primary growth engine of the Dicing Blade Market, hosting the majority of global semiconductor foundries and OSAT providers. The region dictates demand trends, focusing on efficiency, high-volume consumables, and the rapid adoption of ultra-thin blades required for cutting-edge packaging technologies.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
