E-Visa Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 432854 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 253 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
E-Visa Market Size
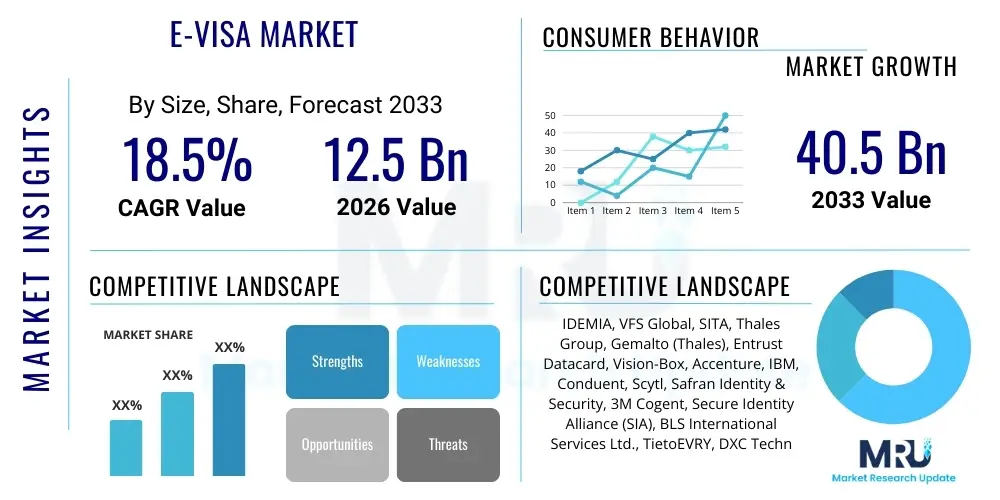
The E-Visa Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 18.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 12.5 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 40.5 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
E-Visa Market introduction
The E-Visa Market encompasses the digital transformation of conventional visa issuance processes, allowing travelers to apply for and receive travel authorization electronically, often entirely online. This streamlined system significantly reduces processing times, eliminates the need for physical visits to consulates or embassies, and enhances security through integrated digital checks. E-Visas are typically granted for short-term travel purposes, such as tourism, business meetings, or transit, acting as a crucial enabling technology for global mobility in the 21st century. The product description centers on highly secure, interoperable online portals supported by robust backend government infrastructure designed to manage high volumes of applications and cross-border data exchange efficiently.
Major applications of E-Visas span across leisure travel, commercial visits, medical tourism, and educational short courses. The primary benefit derived from the E-Visa system is operational efficiency, dramatically improving the user experience for applicants while simultaneously enabling national governments to better manage border security and immigration flows using advanced analytics. For users, the convenience and speed of application submission represent a major shift from traditional paper-based methods, aligning the travel documentation process with modern digital expectations. Governments benefit from enhanced revenue collection traceability and improved statistical data regarding traveler origins and purposes, which informs better policy decisions.
Driving factors for the E-Visa market include the rising adoption of digital services globally, increasing international tourism fueled by rising middle-class disposable incomes in emerging economies, and the strategic push by governments worldwide to modernize public services. Furthermore, improvements in secure digital identification technologies, increased bilateral agreements promoting tourism, and the necessity to manage post-pandemic travel volumes efficiently are strongly propelling market expansion. The harmonization of standards among different regional economic blocs also contributes significantly to the operational feasibility and widespread acceptance of E-Visa programs, fostering a secure yet agile global travel environment.
E-Visa Market Executive Summary
The E-Visa market is characterized by robust business trends centered on technological modernization, focusing specifically on mobile application integration and AI-driven processing capabilities to minimize human intervention and error. Key business strategies include public-private partnerships, where technology providers collaborate with national governments to build and manage E-Visa platforms, leading to lucrative, long-term contractual agreements. The shift towards multi-entry and longer-validity E-Visas is becoming a crucial monetization trend, accommodating the needs of frequent business travelers and digital nomads. Moreover, integrating E-Visas with biometric data captures at the application stage and leveraging blockchain for secure record keeping are emerging trends enhancing trust and reducing fraud risk across the ecosystem.
Regionally, the market exhibits divergent maturity levels. Asia Pacific is poised for the most explosive growth, driven by rapidly expanding outbound tourism from countries like India and China, coupled with increased implementation by regional governments (e.g., Vietnam, Thailand) seeking to boost their tourism sectors post-COVID-19. North America and Europe, already mature in digital infrastructure, focus more on refining existing systems, enhancing security protocols, and integrating E-Visas with global travel databases. The Middle East, particularly the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations, is investing heavily in visa facilitation, recognizing its importance in diversifying economies away from oil and positioning themselves as global transit and leisure hubs, thus representing a high-value opportunity segment.
Segmentation trends reveal that the market is predominantly dominated by the Tourism application segment due to the sheer volume of leisure travelers worldwide. However, the Business application segment is exhibiting a higher growth rate, reflecting increasing globalization and cross-border commercial activities requiring expedited travel documentation. Based on system type, the cloud-based E-Visa platforms are gaining significant traction over on-premise solutions, primarily due to scalability, lower infrastructure costs, and the ease of incorporating real-time security updates and data synchronization across disparate border control checkpoints. This preference for cloud services accelerates deployment timelines for nations initiating new E-Visa programs.
AI Impact Analysis on E-Visa Market
User queries regarding AI in the E-Visa sector primarily revolve around efficiency gains, security implications, and potential job displacement. Common themes include "How fast can AI approve my visa?" and "Will AI reduce visa fraud?" Users are highly interested in the capacity of AI, particularly machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP), to automate document verification, assess applicant risk profiles instantaneously, and detect patterns indicative of fraudulent activity or security threats that traditional manual checks might miss. The expectation is that AI will dramatically cut processing times from days to hours, or even minutes, while maintaining or exceeding current security standards. However, concerns persist regarding algorithmic bias, transparency in decision-making (the "black box" problem), and the fairness of automated rejection systems, driving the need for human oversight protocols.
AI's integration fundamentally transforms the E-Visa lifecycle by automating preliminary screening and risk assessment. Machine learning algorithms are now employed to analyze vast datasets, including financial history, travel patterns, and background information, providing dynamic risk scores for applicants. This rapid, data-driven assessment allows government agencies to focus manual review efforts only on high-risk or complex cases, achieving resource optimization. Furthermore, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are being deployed to handle routine applicant inquiries and troubleshoot common issues, significantly improving customer service availability and reducing the administrative burden on visa processing centers worldwide.
The future application of AI will involve predictive modeling to anticipate border congestion and manage resource allocation for peak travel seasons, leading to smoother operational execution. Advanced deep learning techniques are also being utilized for biometric verification, ensuring higher accuracy in facial recognition and fingerprint matching against international security databases. This enhanced authentication layer is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the E-Visa system against identity theft and impersonation attempts, solidifying the E-Visa as a reliable and secure travel credential. As AI systems become more sophisticated, the market anticipates a shift toward fully autonomous processing for low-risk, repeat travelers.
- AI enhances fraud detection through predictive analytics and pattern recognition.
- Machine Learning accelerates application processing and risk scoring based on historical data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) automates data extraction from submitted documents and forms.
- AI-powered chatbots provide 24/7 applicant support, improving user experience.
- Biometric verification systems utilize deep learning for highly accurate identity confirmation.
- Predictive modeling optimizes resource allocation at border control checkpoints.
- Algorithmic bias mitigation remains a key challenge requiring regulatory oversight.
DRO & Impact Forces Of E-Visa Market
The E-Visa market is heavily influenced by a combination of strong drivers and critical restraints, while significant opportunities shape its long-term trajectory. Key drivers include the overwhelming global demand for convenient and rapid travel documentation spurred by globalization and the proliferation of low-cost international air travel. Governments are increasingly adopting E-Visas (Drivers) as a revenue stream and a tool for modernizing public services. Restraints often center on the substantial initial capital investment required for establishing secure, interoperable digital infrastructure and the inherent cybersecurity risks associated with handling massive volumes of sensitive personal data (Restraints). Opportunities (Opportunities) lie in expanding E-Visa programs to cover longer-stay permits (e.g., student visas, retirement visas) and leveraging blockchain technology for enhanced data security and cross-border verification.
The Impact Forces determining the competitive landscape are multifaceted. Geopolitical stability acts as a foundational force; periods of international tension or conflict can drastically affect travel flows and the willingness of nations to open their borders digitally. Technological disruption, particularly the advent of robust AI and advanced biometrics, is a significant force pushing existing providers to continuously upgrade their platforms. Regulatory and legal frameworks are paramount, as the market is entirely dependent on bilateral and multilateral government agreements and compliance with evolving data privacy laws like GDPR and similar regional mandates. These forces mandate high levels of security and compliance, creating steep barriers to entry for non-specialized providers.
A crucial dynamic involves the delicate balance between national security requirements and facilitation of commerce and tourism. Governments are constantly navigating this trade-off, with the E-Visa system serving as the primary technological solution to manage both objectives simultaneously. The push toward frictionless travel initiatives, such as pre-cleared traveler programs integrated into E-Visa systems, exemplifies the market’s focus on optimizing flow. This environment requires technology providers to offer not just functional software but highly consultative services, aiding governments in policy implementation and phased digital rollout strategies tailored to specific national security profiles and existing infrastructure capacities.
Segmentation Analysis
The E-Visa market is comprehensively segmented based on its application type, system deployment model, and the categories of visa issued. Understanding these segments is crucial for technology providers and governments aiming to tailor their strategies and investments. Application segmentation highlights the difference in volume and complexity between leisure travel and high-value business applications. Deployment models reflect the shifting infrastructural preferences of national entities, moving toward scalable, flexible solutions. Visa categories define the regulatory framework and duration of stay, influencing the required security checks and supporting documentation, making certain categories more resource-intensive than others.
- By Application:
- Tourism
- Business
- Medical
- Transit
- Others (Short-term Education, Cultural Exchange)
- By System Type:
- Cloud-based
- On-premise
- By Visa Category:
- Single Entry
- Multiple Entry
- By Technology Platform:
- Web Portals
- Mobile Applications
Value Chain Analysis For E-Visa Market
The E-Visa market value chain begins with upstream activities focused on foundational infrastructure and technology development. This involves government entities setting policy frameworks and private technology companies specializing in secure digital identity solutions, database management, and biometric verification software (Upstream Analysis). These specialized providers supply the essential tools and platforms required for the electronic application process. The development phase includes rigorous security testing, data encryption protocols, and ensuring regulatory compliance across multiple jurisdictions, making specialized IT expertise a critical input.
The midstream segment involves the actual processing and delivery of the E-Visa service. This includes the national government immigration departments, payment gateway providers handling application fees, and third-party facilitators or Authorized Service Providers (ASPs) who manage the applicant interface and preliminary data collection. The crucial component here is the integration layer, ensuring seamless, secure communication between the front-end application portal and the government's centralized backend database. Efficiency at this stage is measured by processing speed, approval rates, and user satisfaction with the digital interface.
Downstream analysis focuses on how the approved E-Visa is utilized and verified. This involves border control agents, airport security systems, and global travel databases (Distribution Channel). Verification occurs primarily through direct connection to the issuing nation’s database via specialized scanners at ports of entry, verifying the digital credential against the traveler’s passport and biometrics. Distribution is predominantly direct—the traveler receives the visa electronically (email or mobile app) from the governmental body or its direct vendor. However, indirect channels, such as travel agencies and airline check-in systems, play a secondary role in preliminary verification and informing travelers about requirements. Continuous monitoring and data synchronization between government systems globally ensure the ongoing validity and security of the distributed digital credential.
E-Visa Market Potential Customers
Potential customers for the E-Visa Market are primarily governmental entities and specialized national agencies responsible for border control, immigration, and tourism promotion, rather than the end-user traveler. These government bodies (End-User/Buyers) procure the E-Visa solutions, including the underlying software, hardware, and integration services, from technology vendors. The decision-making unit often resides within the Ministry of Interior, Foreign Affairs, or specialized National Security Agencies, requiring vendors to navigate complex bureaucratic procurement processes and comply with stringent national security standards and geopolitical sensitivities.
Secondary customer segments include major international airports, airline alliances, and global travel technology platforms (GTPs), which require interoperable systems to verify E-Visas efficiently during check-in procedures and transit. While these entities do not directly purchase the core visa issuance system, they are critical stakeholders who demand robust, real-time access to verification data provided by the E-Visa platform. Therefore, E-Visa solution providers must ensure their offerings integrate smoothly with existing airline departure control systems (DCS) and International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) standards to maintain a viable ecosystem.
Ultimately, the successful deployment of E-Visa systems is measured by its utility to the actual consumer—the international traveler. Although the traveler is the beneficiary and fee-payer, the government remains the core B2G (Business-to-Government) buyer. The strategic buyer focus is on securing long-term contracts with governments in regions experiencing rapid infrastructure upgrades or aggressive tourism promotion drives, particularly emerging markets in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America seeking to emulate successful programs established in Europe and North America.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 12.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 40.5 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 18.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | IDEMIA, VFS Global, SITA, Thales Group, Gemalto (Thales), Entrust Datacard, Vision-Box, Accenture, IBM, Conduent, Scytl, Safran Identity & Security, 3M Cogent, Secure Identity Alliance (SIA), BLS International Services Ltd., TietoEVRY, DXC Technology, Unisys, NEC Corporation, Securiport |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
E-Visa Market Key Technology Landscape
The E-Visa market relies on a confluence of highly sophisticated and secure digital technologies to function effectively and maintain national security standards. At the core is robust database infrastructure, often utilizing cloud services due to the necessity for high availability, massive scalability, and global accessibility for verification at disparate ports of entry. Secure application processing involves advanced encryption standards (like AES-256) for data transmission and storage, protecting sensitive applicant information from interception or unauthorized access. Furthermore, sophisticated document verification software, capable of reading and validating various global travel documents and detecting forged submissions, is a non-negotiable component of the technological framework.
Biometric technology forms the critical identity verification layer, moving beyond simple passport checks. Fingerprint, facial, and iris recognition technologies are increasingly integrated into the application process (via mobile apps) and seamlessly linked to Automated Border Control (ABC) gates at airports. The shift toward integrating AI and machine learning models for risk assessment is paramount. These tools analyze behavioral patterns, cross-reference watchlists, and dynamically assess the likelihood of an applicant overstaying or posing a security risk, allowing for near real-time decision making and optimizing the workload for human immigration officers, thereby enhancing both security and efficiency.
Emerging technologies like Decentralized Identity (DID) and blockchain are poised to further revolutionize the E-Visa landscape. Blockchain offers a tamper-proof, distributed ledger for maintaining records of visa issuance and revocation, enhancing trust between nations and eliminating single points of failure. This technological advancement supports the concept of interoperability, making it easier for a traveler's digital identity and visa status to be instantly verified across borders without relying solely on centralized databases, promising future efficiencies in multi-country travel blocs and aligning the sector with global data security best practices.
Regional Highlights
Regional dynamics heavily influence the adoption and maturity of E-Visa programs, reflecting variations in digital infrastructure investment, tourism dependence, and geopolitical considerations. North America, led by the United States and Canada, focuses on highly sophisticated, integrated electronic travel authorizations (ETAs) that are deeply linked to expansive national security databases, prioritizing security enhancements and seamless integration with existing border infrastructure. Europe, driven by the Schengen Area’s common external border policies, is moving toward consolidated digital visa platforms, such as the upcoming European Travel Information and Authorisation System (ETIAS), aiming for harmonization and improved management of large cross-border travel volumes.
Asia Pacific (APAC) stands out as the fastest-growing region, characterized by massive potential due to rising middle-class populations with increased propensity for international travel, particularly outbound traffic from China and India. Governments in tourism-reliant nations like Thailand, Australia (which was an early adopter of the ETA model), and the UAE (often included in MEA statistics but highly relevant to APAC travel flows) are aggressively investing in E-Visa systems to streamline access and stimulate economic recovery post-pandemic, making this region a prime target for solution providers.
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region presents a dichotomy. The GCC nations (UAE, Saudi Arabia) are high-investment zones, using E-Visas as a core component of their Vision 2030 strategies to establish themselves as global tourism and business hubs. Conversely, many African nations are initiating pilot programs or foundational system upgrades, driven by the African Union's push for intra-African travel facilitation and economic integration, representing a significant long-term growth opportunity, albeit challenged by infrastructural disparities.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Highest CAGR, driven by rising outbound tourism and government efforts to modernize travel infrastructure (India, China, Southeast Asian nations).
- Europe: Focus on harmonization (ETIAS initiative) and integration within the Schengen zone for common border management and high security standards.
- North America: Mature market concentrating on security integration, advanced risk assessment, and refining existing Electronic Travel Authorization (ETA) systems.
- Middle East: Strategic, high-value investment region (UAE, Saudi Arabia) focusing on tourism diversification and establishing global transit corridors.
- Latin America: Emerging market with increasing adoption spurred by regional economic blocs seeking to boost intra-regional trade and tourism.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the E-Visa Market.- IDEMIA
- VFS Global
- SITA
- Thales Group
- Gemalto (Thales)
- Entrust Datacard
- Vision-Box
- Accenture
- IBM
- Conduent
- Scytl
- Safran Identity & Security
- 3M Cogent
- Secure Identity Alliance (SIA)
- BLS International Services Ltd.
- TietoEVRY
- DXC Technology
- Unisys
- NEC Corporation
- Securiport
- Mundipharma
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
- Infosys
- Fujitsu
- Wipro
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the E-Visa market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) for the E-Visa Market?
The E-Visa Market is projected to exhibit a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 18.5% between 2026 and 2033, driven primarily by increasing international travel volumes and continuous digitalization efforts by national governments worldwide.
How does the adoption of AI impact the processing time for E-Visas?
AI significantly reduces E-Visa processing time by automating initial risk assessment, document verification, and data cross-referencing, allowing governments to shift from manual, multi-day checks to automated approval processes for low-risk applicants, often reducing processing time to minutes or hours.
Which region is expected to show the fastest growth in the E-Visa market?
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region is forecasted to experience the fastest market growth. This rapid expansion is fueled by rising disposable incomes leading to increased outbound travel, coupled with aggressive initiatives by regional governments to modernize tourism infrastructure using digital visa solutions.
What are the primary restraints affecting the expansion of E-Visa systems globally?
The main restraints include the substantial initial capital investment required for secure IT infrastructure development, the necessity for continuous high-level cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive traveler data, and the complexity of ensuring interoperability and legal compliance across different international jurisdictions.
What are the key technology components of a modern E-Visa system?
Key technological components include secure cloud-based data storage, biometric verification tools (facial/fingerprint recognition), AI-driven risk assessment algorithms, robust encryption protocols for data transfer, and compliance with global standards such as those set by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
How do E-Visas enhance national security compared to traditional visas?
E-Visas enhance national security by allowing governments to conduct thorough, real-time background checks against expansive security databases and watchlists before the traveler even departs. The system integrates advanced biometrics and uses AI for predictive threat analysis, creating a more robust and proactive border management mechanism than paper-based systems.
What is the difference between an E-Visa and an Electronic Travel Authorization (ETA)?
While both are electronic, an E-Visa is typically a form of official permission that replaces a physical visa sticker and requires detailed application and review, often for countries that previously required a full visa. An ETA is usually granted to citizens of visa-exempt countries for pre-screening purposes, confirming eligibility for entry without a formal visa application process (e.g., US ESTA or planned European ETIAS).
Is the implementation of E-Visas favored by large international organizations?
Yes, large international organizations like the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) and the World Economic Forum (WEF) actively promote E-Visas and digital travel credentials. They view these systems as essential tools for maximizing tourism revenue, improving travel facilitation, and supporting sustainable economic development through seamless global mobility.
What role does blockchain technology play in the future of E-Visas?
Blockchain technology promises to secure E-Visa issuance and verification records through decentralized, tamper-proof ledgers. This enhances trust among collaborating nations and streamlines the verification process at borders, reducing the potential for fraud and dependence on single, centralized databases.
How is the market segmented by system deployment?
The E-Visa market is segmented by system type into Cloud-based and On-premise solutions. Cloud-based solutions are increasingly dominant due to their superior scalability, lower operational overhead, and flexibility in deployment across geographically dispersed border control points, contrasting with the higher infrastructure control offered by on-premise systems.
Which application segment holds the largest market share in the E-Visa market?
The Tourism application segment currently holds the largest market share. This is attributed to the high volume of leisure travelers globally, who are the primary users of short-term electronic travel authorizations designed specifically to boost tourism inflows for issuing nations.
What are the key challenges in integrating E-Visa systems with existing airport infrastructure?
Integration challenges primarily involve ensuring seamless compatibility with legacy airport Departure Control Systems (DCS), Automated Border Control (ABC) gates, and maintaining secure, high-speed data connectivity to national visa databases in real-time, especially in environments with limited bandwidth or outdated IT infrastructure.
How do public-private partnerships influence the E-Visa market landscape?
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are crucial, as governments often lack the internal expertise to develop and manage complex digital platforms. PPPs allow specialized vendors (like VFS Global or Thales) to design, build, and operate the E-Visa systems, transferring the technological burden and initial investment risk away from the public sector, while ensuring high service delivery standards.
What is the role of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in E-Visa applications?
NLP is utilized to analyze unstructured data within E-Visa applications, such as supporting documents, narrative purpose of travel statements, and correspondence. It helps in quickly extracting relevant information, verifying consistency, and automating parts of the review process, contributing to faster application intake and risk profiling.
Are E-Visas typically used for long-term residency or work permits?
Currently, E-Visas are primarily designed for short-term entry purposes, specifically tourism, transit, or short-duration business trips. While the market opportunity exists, most nations still require traditional paper-based or physically processed visas for long-term residency, work, or complex immigration categories due to stricter documentation requirements.
What demographic trends are driving the demand for E-Visas?
The increasing affluence of the global middle class, particularly in emerging economies like India, China, and Southeast Asia, coupled with the ubiquity of mobile connectivity and digital literacy, drives the strong consumer preference for convenient, fast, and fully digital travel documentation like E-Visas.
How does the E-Visa market contribute to economic diversification in the Middle East?
Middle Eastern nations, such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia, utilize E-Visas as a core strategy to dramatically increase tourism and foreign business visits, thereby reducing economic reliance on hydrocarbons. The ease of application facilitates global access, positioning these countries as competitive international business and leisure destinations.
What data privacy concerns are associated with E-Visa systems?
Major data privacy concerns involve the secure collection, storage, and cross-border sharing of highly sensitive personal data, including biometrics and travel history. Compliance with stringent regulations like GDPR and ensuring robust encryption are critical operational requirements to mitigate risks of data breach or misuse.
How is the market addressing the potential for algorithmic bias in AI risk assessment?
The market addresses algorithmic bias by focusing on developing transparent AI models, ensuring diversified and representative training datasets, and implementing strict human oversight mechanisms (Human-in-the-Loop systems) to review automated rejection decisions, thus maintaining fairness and regulatory compliance in the application process.
What is the significance of the ICAO in the E-Visa ecosystem?
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) is highly significant as it sets the global standards for machine-readable travel documents (MRTDs), electronic passports, and digital identity management. E-Visa solutions must adhere to ICAO standards to ensure global interoperability and recognition by airlines and border agencies worldwide.
How are E-Visas verified at the point of entry?
E-Visas are verified at the point of entry (e.g., airport immigration counters) through secure, real-time electronic connectivity. The officer scans the traveler’s passport, which triggers a query to the issuing nation’s central visa database, confirming the validity of the digital authorization and matching the traveler’s biometrics on file.
What are the implications of the shift from on-premise to cloud-based E-Visa systems?
The shift implies greater system flexibility, reduced long-term maintenance costs for governments, and enhanced capability for rapid scaling during peak demand periods. Cloud platforms also facilitate quicker deployment of security updates and patches, crucial for protecting against evolving cyber threats.
Which factors contribute to the competitive intensity of the E-Visa vendor market?
Competitive intensity is driven by the necessity for highly specialized technical expertise (biometrics, secure platforms), the high value of long-term government contracts, and the need for global certification and reputation, creating a market dominated by a few large, established technology integrators and identity management firms.
How do E-Visas facilitate transit travel?
E-Visas often include a specific Transit category, allowing travelers to pass through a country's airport or jurisdiction for a short, defined period without undergoing a full tourist visa application. This streamlined process is critical for major international transit hubs to maintain passenger flow and service efficiency.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on the E-Visa market?
Initially, the pandemic caused a sharp decline due to travel restrictions. However, it accelerated the long-term trend toward digitalization, as governments realized the need for agile, centralized, and highly traceable digital systems to manage health documentation (like vaccine passports) alongside traditional visas, preparing for future border reopening.
How does the concept of 'frictionless travel' relate to E-Visas?
'Frictionless travel' aims to create a seamless journey where identity and authorization checks are minimized or handled passively. E-Visas are foundational to this by pre-clearing travelers digitally, allowing them to use automated gates (ABC systems) upon arrival, significantly reducing queues and human interaction at the border.
What are the major challenges for E-Visa adoption in developing countries?
Major challenges include limited internet penetration and digital literacy among citizens, lack of funding for initial infrastructure build-out, and the need for robust electricity and data network reliability to ensure border control verification systems operate without disruption, especially in remote ports of entry.
What is the significance of the Business application segment growth rate?
The high growth rate in the Business application segment signifies increased global economic integration and mobility. Companies require faster, more reliable visa services for employees, making expedited E-Visa processing for commercial purposes a high-priority investment area for governments seeking foreign direct investment.
How are mobile applications changing the E-Visa user experience?
Mobile applications enhance the user experience by allowing travelers to apply, submit supporting documents (via smartphone camera), pay fees, and receive their digital visa credential directly on their device. This facilitates seamless, secure storage and presentation of the visa during travel and verification.
What factors influence a government's decision to launch an E-Visa program?
Key factors include stimulating tourism growth, modernizing public service delivery, enhancing national security through centralized risk assessment, generating new government revenue streams from application fees, and aligning with global standards for travel facilitation.
What is the estimated market size of the E-Visa sector in 2033?
The E-Visa Market is projected to reach an estimated value of USD 40.5 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033, reflecting substantial global investment in digital identity and border management technologies.
What is the primary characteristic of the Upstream Analysis in the E-Visa value chain?
Upstream analysis focuses on foundational technology development, including government policy setting and the provision of specialized IT infrastructure, secure software, and biometric verification tools supplied by dedicated technology vendors to build the core E-Visa platform.
How does the E-Visa system manage data synchronization across international borders?
Data synchronization is managed through secure, encrypted data links and adherence to international protocols (often utilizing standards established by Interpol and ICAO). This ensures that a traveler’s authorization status is updated and verifiable by authorized border control personnel in different countries in real-time, maintaining security integrity.
What types of technology platforms are used for E-Visa issuance?
The primary technology platforms include robust, highly secure web portals for application submission and government review, increasingly supplemented by dedicated mobile applications to improve user convenience and facilitate biometric capture using smartphone cameras.
What is meant by the 'Human-in-the-Loop' model in E-Visa processing?
The 'Human-in-the-Loop' model ensures that while AI handles the majority of low-risk applications, all complex cases, high-risk flags, or applications rejected by the algorithm are automatically escalated for mandatory review by a trained human immigration officer. This maintains ethical standards and minimizes automated error.
Who are the primary potential customers (buyers) of E-Visa solutions?
The primary buyers are national governments and specialized state agencies responsible for immigration, border control, and national security (e.g., Ministries of Interior or Foreign Affairs), who contract technology providers to develop and maintain the complex digital visa infrastructure.
How does geopolitical stability act as an impact force on the E-Visa market?
Geopolitical stability directly impacts travel flows and trust between nations. Periods of tension can lead to governments imposing stricter visa requirements or suspending E-Visa agreements, negatively affecting market operations and the number of nations willing to implement open digital border policies.
What differentiates a Single Entry E-Visa from a Multiple Entry E-Visa?
A Single Entry E-Visa permits travel and entry only once within its validity period, after which it expires. A Multiple Entry E-Visa permits the holder to enter the issuing country multiple times within a specified validity period, typically catering to business travelers or frequent tourists.
Are short-term educational courses typically covered by E-Visas?
Yes, short-term educational courses, generally those lasting less than three or six months, are often included under the 'Other' application segment of E-Visas or sometimes bundled under specialized tourist or short-term visitor categories, depending on the issuing country’s specific immigration rules.
What specific benefit does an E-Visa offer to airlines and airports?
E-Visas offer airlines and airports the benefit of reduced liability and faster passenger processing. Airlines can confirm the necessary travel authorization electronically before boarding, significantly reducing the instance of denied entry at the destination, which incurs fines and costs for the carrier.
Why is adherence to data privacy laws like GDPR critical for E-Visa providers?
Adherence to data privacy laws like GDPR is critical because E-Visa systems handle vast amounts of sensitive personal and biometric data, especially from citizens of regulatory zones like the EU. Compliance ensures legal operation, maintains public trust, and avoids massive financial penalties associated with data breaches or misuse.
How do E-Visas support medical tourism?
Specialized E-Visas or expedited electronic permits for medical tourism facilitate quick, hassle-free entry for patients seeking elective medical treatments abroad. This supports the medical sector in destination countries by enabling rapid authorization when time-sensitive health issues are involved.
Which segments of the market offer the greatest opportunity for technological innovation?
Innovation is most potent in the areas of advanced biometric integration, the development of secure, blockchain-based decentralized identity systems, and the application of machine learning for complex, non-obvious fraud detection patterns that bypass conventional security checks.
What is the typical time frame considered for the base year and forecast year in this market report?
The typical base year for this market analysis is 2025, providing a current snapshot, while the forecast period extends from 2026 to 2033, projecting long-term market trends and growth trajectories.
How is the E-Visa market defined in terms of product scope?
The E-Visa market scope is defined as the systems, software, and services dedicated to the electronic issuance, management, and verification of official travel authorizations that replace or streamline the traditional paper-based visa application and stamping process for short-term entry.
What differentiates the roles of technology vendors like IDEMIA and service providers like VFS Global?
IDEMIA is primarily a technology vendor focusing on secure identity solutions, biometrics, and core government platforms. VFS Global is a service provider that often manages the application processing interface, physical collection centers (when needed), and logistics on behalf of the client government, utilizing platforms supplied by technology vendors or proprietary systems.
In the value chain, what is the key activity in the downstream segment?
The key downstream activity involves the secure and instantaneous verification of the approved digital visa credential by border control officials, utilizing electronic scanning devices linked to the government database to confirm the traveler's authorization status against their identity documents at the port of entry.
How do E-Visas support government revenue generation?
E-Visas support revenue generation by streamlining the fee collection process, ensuring higher compliance, and reducing the administrative costs associated with manual handling. They also increase the overall volume of tourists and business visitors who pay the required application fees, directly boosting national coffers.
What is the primary constraint related to cybersecurity in the E-Visa market?
The primary constraint is the ongoing battle against sophisticated cyber threats, including data breaches and state-sponsored hacking attempts, targeting the centralized databases that store sensitive national security and personal identity information, necessitating continuous high-level investment in protective measures.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
- E-passport and E-visa Market Size Report By Type (Ordinary E-passport, Service & Diplomatic E-Passport), By Application (Adult, Child), By Region (North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, and Africa) - Share, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2025-2032
- E-passport and E-visa Market Size, Share, Trends, & Covid-19 Impact Analysis By Type (Ordinary E-passport, Service & Diplomatic E-Passport), By Application (Adult, Child), By Region - North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, and Africa | In-depth Analysis of all factors and Forecast 2023-2030
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
