Small Business Loan Market Size, By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 441383 | Date : Feb, 2026 | Pages : 241 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
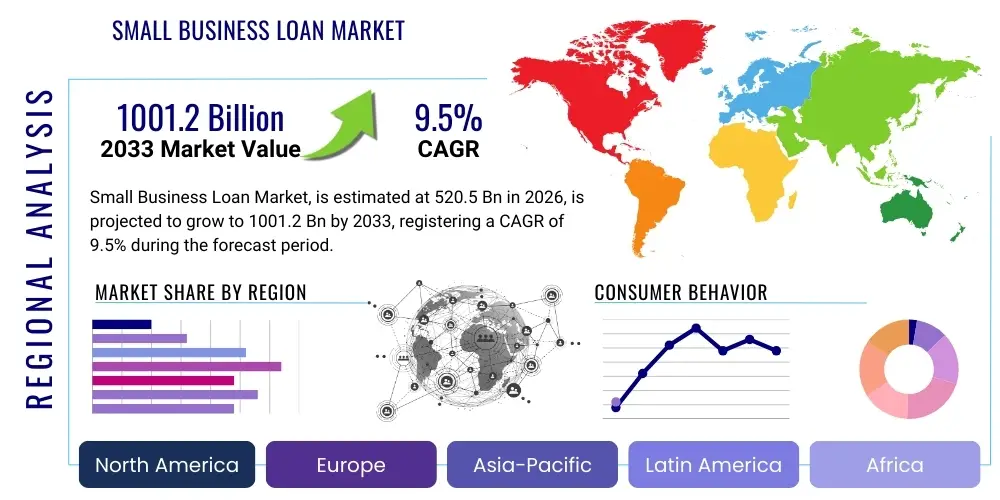
Small Business Loan Market Size
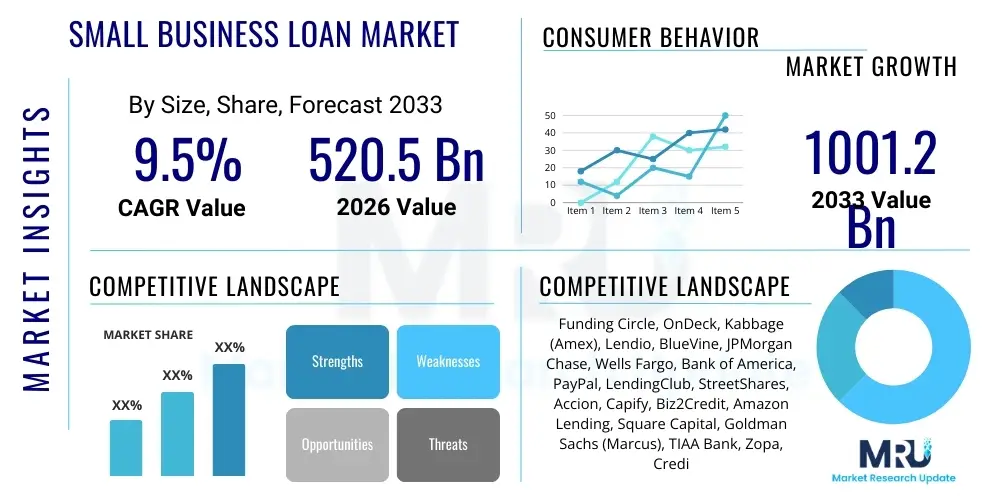
The Small Business Loan Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at $520.5 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach $1001.2 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033. This substantial expansion is fundamentally driven by the increasing global emphasis on entrepreneurship and the critical need for working capital among Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs). Traditional lending institutions are evolving their offerings, while innovative FinTech platforms are aggressively capturing market share through streamlined, digital application processes, directly contributing to market volume growth and accessibility.
The market valuation reflects the convergence of several macroeconomic factors, including robust post-pandemic economic recovery in key regions, sustained low-to-moderate interest rate environments supporting borrowing appetite, and governmental initiatives specifically designed to subsidize or guarantee loans for small businesses. Furthermore, the shift away from reliance solely on bank loans towards diverse funding instruments like lines of credit, equipment financing, and invoice factoring is broadening the definition and scope of the overall market size calculation. These diverse funding avenues provide flexibility that traditional products often lack, making financing more palatable for businesses with fluctuating cash flows or non-standard collateral assets.
Small Business Loan Market introduction
The Small Business Loan Market encompasses the provision of various debt instruments specifically tailored to finance the operational, expansion, or capital expenditure needs of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs). These products, which range from conventional term loans and lines of credit to modern alternatives like merchant cash advances, equipment financing, and peer-to-peer lending, are essential capital conduits that fuel economic activity and job creation globally. A defining characteristic of this market is the high degree of risk assessment required due to the inherent volatility and higher default rates associated with smaller enterprises, necessitating advanced analytical tools for efficient underwriting and pricing.
Major applications of small business loans include funding working capital requirements, purchasing fixed assets such as machinery or real estate, managing inventory, and financing marketing or technology adoption initiatives. The primary benefit of these loans is enabling SMEs—which often lack the retained earnings or public market access of large corporations—to scale operations and compete effectively. This market is fundamentally driven by robust SME formation rates, technological advancements that simplify loan origination and servicing (reducing administrative overhead), and the increasing availability of granular, alternative data sources that improve credit decision accuracy for previously underserved segments. Government guarantees, particularly those structured to mitigate lender risk during economic downturns, also serve as significant stimuli, encouraging financial institutions to extend credit where they might otherwise be hesitant, thereby ensuring continuous market liquidity and accessibility.
Small Business Loan Market Executive Summary
The Small Business Loan market is currently undergoing profound structural changes driven by digitization and regulatory adaptations, resulting in a dual market structure where established banks compete fiercely with agile FinTech lenders. Key business trends indicate a strong move toward product diversification, with loans becoming highly customizable based on the industry, cash flow profile, and maturity stage of the borrower. Geographically, while North America and Europe remain dominant in terms of loan volume, the Asia Pacific region, particularly countries like India and China, is experiencing exponential growth fueled by massive digitalization of commerce and strong government backing for startup ecosystems, pushing market innovation particularly in mobile-first lending solutions.
Segment trends emphasize the rapid proliferation of non-traditional loan types, notably unsecured loans and short-term working capital products, favored by small businesses for their speed and ease of access compared to traditional collateral-heavy offerings. Technology adoption, especially AI and machine learning in credit scoring, is reducing processing times from weeks to hours, effectively lowering the cost-to-serve for lenders and expanding the pool of eligible borrowers. Furthermore, regulatory environments are evolving, with many jurisdictions introducing streamlined licensing processes for digital lenders while simultaneously demanding higher transparency and consumer protection standards, impacting risk models and compliance costs across the entire market spectrum, ensuring both innovation and stability.
AI Impact Analysis on Small Business Loan Market
User inquiries regarding AI's influence on the Small Business Loan Market primarily revolve around three core themes: the automation of credit decisioning, the ability of AI to assess non-traditional data for creditworthiness, and concerns about potential algorithmic bias and transparency. Users are keen to understand how AI-driven underwriting affects loan speed and approval rates, especially for businesses with short operational histories or thin file data, seeking confirmation that these tools democratize access rather than restricting it. There is significant interest in knowing if AI can accurately predict early default indicators better than traditional FICO scores and how lenders are utilizing Machine Learning (ML) to personalize loan offers and manage relationship health post-disbursement. The overriding expectation is that AI will dramatically reduce human intervention, leading to faster, fairer, and more sophisticated lending practices, provided inherent biases in historical lending data are successfully mitigated during model training and deployment.
- AI enables highly granular and predictive credit scoring by analyzing transactional data, social media sentiment, and supply chain health.
- Automated loan origination systems powered by ML significantly reduce the time from application to funding, enhancing customer experience.
- Sophisticated fraud detection mechanisms utilize AI to identify suspicious patterns in loan applications, minimizing lender losses.
- AI optimizes portfolio management by predicting early payment distress signals, allowing lenders to intervene proactively with refinancing or forbearance options.
- Chatbots and natural language processing (NLP) enhance customer service, providing instant, personalized responses regarding loan eligibility and documentation requirements.
- Machine learning models facilitate dynamic interest rate pricing based on real-time risk assessments, ensuring competitive and risk-adjusted pricing strategies.
- The technology supports enhanced compliance by automatically monitoring regulatory changes and ensuring lending practices adhere to fair lending laws, reducing regulatory exposure.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Small Business Loan Market
The dynamics of the Small Business Loan market are defined by a complex interplay of Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, and broader Impact Forces that shape market strategy and profitability. Key drivers include the exponential global growth of the SME sector, particularly in emerging economies where small businesses represent the vast majority of commercial entities and employment. Concurrently, technological advancement, especially the widespread deployment of digital lending platforms and API integration, drastically lowers the transaction costs and improves efficiency for both borrower and lender, making credit delivery faster and more accessible. Furthermore, sustained governmental initiatives globally, such as subsidized lending programs and loan guarantee schemes (e.g., SBA loans in the US), actively de-risk SME lending for financial institutions, acting as critical accelerators of market expansion, particularly in volatile economic periods.
Conversely, the market faces significant restraints, primarily revolving around the inherently high credit risk associated with small businesses, which are more susceptible to economic fluctuations and possess higher failure rates than large corporations. This risk is often compounded by limited collateral availability and inconsistent financial reporting among smaller entities, making traditional underwriting challenging. Regulatory complexities, particularly varying jurisdictional requirements regarding data privacy, interest rate caps, and consumer protection (even for commercial loans), introduce substantial compliance burdens and inhibit the standardization of cross-border lending operations. These constraints mandate meticulous risk management practices and significant investment in regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions to maintain operational viability and market trust, slowing down potential market entrants.
Opportunities for growth are concentrated in the adoption of alternative data sources for credit scoring, leveraging open banking APIs to access real-time financial health data, which allows lenders to serve previously marginalized or thin-file segments of the SME population more accurately. The increasing acceptance of specialized loan products, such as supply chain finance and embedded lending solutions offered at the point-of-sale or within B2B platforms, presents expansive avenues for market penetration, shifting lending from a standalone transaction to an integrated component of business operations. Impact forces, such as global macroeconomic instability, sudden interest rate shifts, and the competitive threat posed by Big Tech companies entering financial services, constantly pressure lenders to innovate quickly, maintain liquidity, and optimize operational resilience against external shocks, forcing continuous strategic re-evaluation of product portfolios and risk appetite. These forces dictate that resilience and adaptability are crucial for long-term success in the dynamic Small Business Loan ecosystem.
Segmentation Analysis
The Small Business Loan Market is segmented based on the type of product offered, the end-use application of the funds, the enterprise size, and the nature of the lending institution. This granular segmentation is essential for lenders to tailor risk profiles, pricing, and distribution strategies accurately. Product segmentation highlights the shift from long-term, collateral-backed term loans towards shorter, unsecured, and highly flexible financing options like business lines of credit and specialized asset-backed instruments. Enterprise size differentiation is critical as underwriting requirements, loan amounts, and risk mitigation strategies differ substantially between micro-enterprises and larger SMEs. Furthermore, the segmentation by end-use (e.g., working capital, equipment purchase, real estate acquisition) allows for the creation of targeted financial products with optimized repayment structures matching the intended purpose of the capital, ensuring effective resource allocation.
- By Product Type:
- Term Loans (Short-term, Medium-term, Long-term)
- Lines of Credit (Revolving and Non-revolving)
- Equipment Financing
- SBA Loans / Government-Guaranteed Loans
- Invoice Factoring / Accounts Receivable Financing
- Merchant Cash Advances (MCAs)
- Real Estate and Mortgage Loans
- Specialized Industry Loans (e.g., Agriculture, Healthcare)
- By Enterprise Size:
- Micro Enterprises (Typically 1-9 employees)
- Small Enterprises (Typically 10-49 employees)
- Medium Enterprises (Typically 50-250 employees)
- By Lender Type:
- Banks and Credit Unions (Traditional Financial Institutions)
- Alternative Lenders (FinTechs, Online Platforms)
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lenders
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- By Application/End-Use:
- Working Capital Management
- Expansion and Growth
- Equipment and Asset Purchase
- Debt Refinancing
- Inventory Financing
Value Chain Analysis For Small Business Loan Market
The value chain for the Small Business Loan Market commences with upstream activities involving capital sourcing and technology development. Capital is aggregated from retail deposits, institutional investors, and wholesale funding markets, heavily influenced by global interest rates and monetary policy set by central banks. Simultaneously, technology providers, including specialized FinTech developers and internal IT departments, develop and maintain the complex origination, servicing, and risk management software critical for efficient lending operations. The quality and cost of upstream capital and technology directly determine the competitive positioning and profitability of the lending institution, necessitating robust treasury management and continuous technological upgrades to maintain efficiency in a high-volume market.
The core of the value chain involves midstream activities: loan origination, underwriting, and disbursement. Origination involves marketing, application submission (increasingly through digital channels), and initial data collection. Underwriting, the most critical step, involves sophisticated risk analysis, utilizing credit scoring models—now heavily augmented by AI—to assess default probability and determine appropriate loan terms. Downstream activities focus on servicing and collection. Servicing includes managing payments, customer support, and handling modifications or renewals. Collection processes, especially crucial in high-risk SME lending, involve managing delinquencies and recovering capital, often utilizing advanced analytics to predict the best collection strategy based on borrower behavior. The efficiency of this downstream servicing directly impacts the lender's Net Interest Margin (NIM) and overall portfolio health.
Distribution channels for small business loans are segmented into direct and indirect methods. Direct channels involve the lender interacting directly with the borrower, such as through bank branches, proprietary online portals, or dedicated sales teams. Indirect channels leverage intermediaries to reach the customer base; these include loan brokers, aggregators (marketplaces that match borrowers with multiple lenders), and embedded finance partnerships where loans are offered directly at the point of need (e.g., through accounting software or e-commerce platforms). FinTech lenders heavily rely on indirect digital channels and embedded finance to scale rapidly and reduce customer acquisition costs, whereas traditional banks often prioritize direct relationships through physical branches and established relationship managers, providing a tailored, consultative approach often preferred for larger, more complex loan structures.
Small Business Loan Market Potential Customers
Potential customers for small business loans are highly diversified across numerous industry verticals and stages of business maturity, ranging from newly established startups requiring initial seed capital to mature SMEs seeking expansion funding or refinancing for debt consolidation. These end-users, or borrowers, are segmented not just by size (micro, small, medium) but also fundamentally by their financial health, growth trajectory, and industry risk profile. Customers operating in recession-resistant sectors, such as specialized healthcare services, essential logistics, or niche manufacturing, are typically viewed as lower-risk profiles, while those in highly cyclical sectors like retail, construction, or hospitality often face stricter underwriting criteria or higher interest rates due to inherent volatility. The primary need for these customers is liquidity and capital expenditure funding that cannot be met through internal cash flow generation.
A crucial and growing segment of potential customers includes micro-enterprises and solo entrepreneurs, often lacking formal financial statements or traditional collateral. These borrowers increasingly turn to alternative lenders and FinTech platforms that specialize in utilizing alternative data—such as social media presence, vendor payment history, or real-time sales data from POS systems—to evaluate creditworthiness, offering products like merchant cash advances or small lines of credit. Furthermore, SMEs undergoing digital transformation represent a high-opportunity customer base, seeking loans specifically for technology acquisition, cloud migration, and cybersecurity upgrades. Lenders must continuously adapt their product suite to meet the evolving working capital and CapEx needs of this diverse array of potential borrowers, ensuring rapid access to funds that aligns with their specific operational cycles.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | $520.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | $1001.2 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 9.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Funding Circle, OnDeck, Kabbage (Amex), Lendio, BlueVine, JPMorgan Chase, Wells Fargo, Bank of America, PayPal, LendingClub, StreetShares, Accion, Capify, Biz2Credit, Amazon Lending, Square Capital, Goldman Sachs (Marcus), TIAA Bank, Zopa, Credit Suisse. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Small Business Loan Market Key Technology Landscape
The Small Business Loan market is undergoing a fundamental technological shift, moving away from manual, paper-intensive processes toward hyper-automated digital ecosystems, largely driven by advancements in cloud computing, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and application programming interfaces (APIs). Cloud infrastructure provides the necessary scalability and resilience for digital lending platforms to manage volatile transaction volumes and store vast quantities of structured and unstructured data efficiently. AI and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are the backbone of modern underwriting, enabling lenders to process applications almost instantaneously, utilize proprietary risk models, and continuously monitor loan performance in real-time. This technological foundation drastically lowers the marginal cost of loan origination and significantly improves the speed of access to capital, which is a decisive competitive advantage in the SME segment.
API integration and Open Banking frameworks represent another critical technological pillar. Open Banking initiatives, particularly prevalent in Europe and increasingly adopted globally, mandate data sharing (with borrower consent) between banks and third-party FinTech providers. APIs facilitate seamless data exchange, allowing lenders to integrate directly with borrower accounting software, payroll systems, and bank transaction histories to obtain immediate, verified financial snapshots. This integration eliminates manual submission of documents, reduces the risk of fraud, and provides a comprehensive, dynamic view of the borrower's cash flow, enabling products like embedded finance where lending decisions are made instantly within the commercial workflow, such as when purchasing inventory through a vendor platform. The deployment of robust API gateways is essential for facilitating these partnerships and ensuring secure, compliant data transfer across the financial ecosystem.
Furthermore, distributed ledger technology (DLT), commonly known as Blockchain, is being explored for its potential to revolutionize the collateral management and loan syndication processes. While still nascent, the use of smart contracts on a blockchain could automate payment processing, verify the ownership of assets used as collateral (particularly in supply chain finance), and provide an immutable, transparent record of loan status, potentially reducing disputes and increasing trust among syndicate partners. Security technology, including advanced encryption methods, multi-factor authentication, and sophisticated cybersecurity protocols, remains paramount, given the sensitive nature of financial data handled. Lenders must invest heavily in these defense mechanisms to comply with stringent regulatory requirements and protect against evolving cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the digital lending infrastructure that supports the entire Small Business Loan marketplace.
Regional Highlights
The global Small Business Loan market exhibits significant regional variations in growth patterns, product preferences, and regulatory oversight, demanding localized strategies from international lenders. North America, dominated by the United States, represents the largest and most mature market segment. Growth here is primarily fueled by the strong presence of alternative lenders (FinTechs) that leverage technology to serve segments underserved by traditional banks, particularly utilizing SBA loan programs and short-term working capital products. The US market is highly competitive, characterized by rapid technological innovation in credit scoring and aggressive marketing focused on speed and convenience. Canada also exhibits steady growth, supported by governmental financing programs and robust commercial banking sectors focusing on relationship lending and longer-term stability.
Europe presents a highly fragmented but evolving landscape, heavily influenced by the implementation of Open Banking (PSD2) and rigorous regulatory standards like GDPR. The UK and Germany are market leaders, seeing high adoption of invoice factoring and asset-backed finance, alongside strong activity from non-bank lenders. The shift towards digitized lending is accelerating, with a focus on streamlining cross-border lending within the Eurozone, though local regulatory disparities regarding credit registry access and insolvency laws still pose challenges. The key trend involves banks actively partnering with FinTechs to offer integrated digital lending solutions, balancing compliance demands with the need for competitive speed, particularly targeting underserved micro-enterprises across the continent.
Asia Pacific (APAC) is the fastest-growing region, driven by sheer SME volume and rapid urbanization, notably in China, India, and Southeast Asia. This region is characterized by high mobile internet penetration and a younger, digitally native consumer base, resulting in massive adoption of mobile-first and platform-based lending solutions. Governments in APAC frequently use state-owned banks and direct subsidies to channel capital to SMEs, viewing them as crucial for economic stability. The challenge remains the relatively underdeveloped credit bureau infrastructure in many emerging APAC countries, necessitating innovative approaches to risk assessment, often relying heavily on transactional data from large platform ecosystems (e.g., Alibaba, Tencent) that facilitate lending through embedded finance models, creating lending ecosystems unique to the region.
Latin America (LATAM) faces challenges related to economic volatility and high interest rate environments, yet it offers tremendous untapped potential due to a vast number of unbanked or underbanked SMEs. Market growth is concentrated in Mexico, Brazil, and Colombia, where digital lenders are effectively bridging the gap left by often-conservative traditional banking sectors. The focus here is on micro-lending and short-term working capital loans, often collateralized through future receivables or unique local guarantee structures. Regulatory harmonization remains a hurdle, but local FinTech adoption, spurred by high smartphone penetration, is rapidly democratizing access to capital, focusing on transparency and simple digital onboarding to gain market trust amidst historical banking skepticism.
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region is emerging, driven by diversification efforts away from resource-based economies, leading to increased support for entrepreneurship, especially in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa. Regulatory sandboxes and government-led digitalization initiatives (e.g., in UAE and KSA) are fostering a supportive environment for FinTech development, particularly targeting high-growth sectors like technology and renewable energy. Africa’s vast mobile money infrastructure provides a unique foundation for digital lending, where alternative credit scoring based on mobile transaction data is essential due to the lack of formal credit histories for most SMEs. While the market size is smaller, the growth trajectory is steep, focused on bridging the significant funding gap experienced by small businesses through technology-enabled, Shariah-compliant financing options in specific sub-regions.
- North America: Market maturity, strong FinTech penetration, heavy reliance on government-backed programs (SBA); high demand for working capital and equipment financing.
- Europe: Regulatory complexity (GDPR, PSD2), increasing FinTech-bank partnerships, high adoption of invoice factoring and sophisticated asset-based lending products.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Highest growth rate, driven by digitalization, massive SME volume, mobile-first lending solutions, and government support in China and India.
- Latin America (LATAM): High volatility, significant unbanked segment, rapid growth in digital micro-lending, focused on economic stability and anti-inflationary measures.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): Focus on economic diversification, growth supported by regulatory sandboxes, reliance on mobile money data for credit assessment, and demand for Shariah-compliant financing options.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Small Business Loan Market.- Funding Circle
- OnDeck
- Kabbage (Amex)
- Lendio
- BlueVine
- JPMorgan Chase
- Wells Fargo
- Bank of America
- PayPal
- LendingClub
- StreetShares
- Accion
- Capify
- Biz2Credit
- Amazon Lending
- Square Capital
- Goldman Sachs (Marcus)
- TIAA Bank
- Zopa
- Credit Suisse
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Small Business Loan market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary factor driving the growth of the Small Business Loan Market?
The primary factor driving market growth is the widespread adoption of digital lending platforms and FinTech solutions. These technologies significantly accelerate the loan application and approval process, reduce operational costs for lenders, and expand credit access to previously underserved SMEs through advanced, data-driven credit scoring models.
How is Artificial Intelligence (AI) fundamentally changing the SME lending process?
AI is transforming SME lending by enabling automated, real-time underwriting decisions through the analysis of vast, non-traditional data sets, such as cash flow statements and transactional data. This improves predictive accuracy, minimizes human bias, and drastically cuts the time required for loan disbursement.
What are the key differences between traditional bank loans and alternative FinTech loans for small businesses?
Traditional bank loans typically offer lower interest rates and longer repayment terms but involve rigorous collateral requirements and lengthy approval processes. FinTech loans, conversely, are faster, often unsecured, and rely on simpler digital applications, though they may carry higher interest rates or fees reflective of the increased speed and convenience they provide.
Which geographical region exhibits the fastest growth potential in the Small Business Loan Market?
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region, particularly countries like India and China, demonstrates the fastest growth potential. This is driven by large, digitalizing SME populations, high mobile penetration, and strong governmental backing for digital financing and entrepreneurship ecosystems.
What are the main risks associated with lending to Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs)?
The main risks include the inherently high rate of business failure among SMEs, often leading to default risk; inconsistent or inadequate financial reporting, which complicates accurate credit assessment; and vulnerability to macroeconomic shifts, making repayment stability challenging, necessitating careful portfolio diversification and collateral management by lenders.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager