Green Energy Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 438942 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 257 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Green Energy Market Size
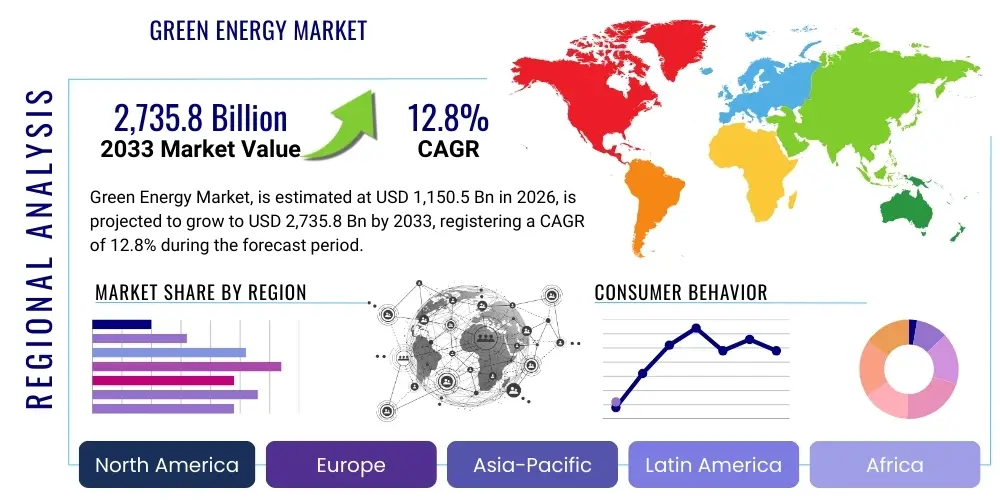
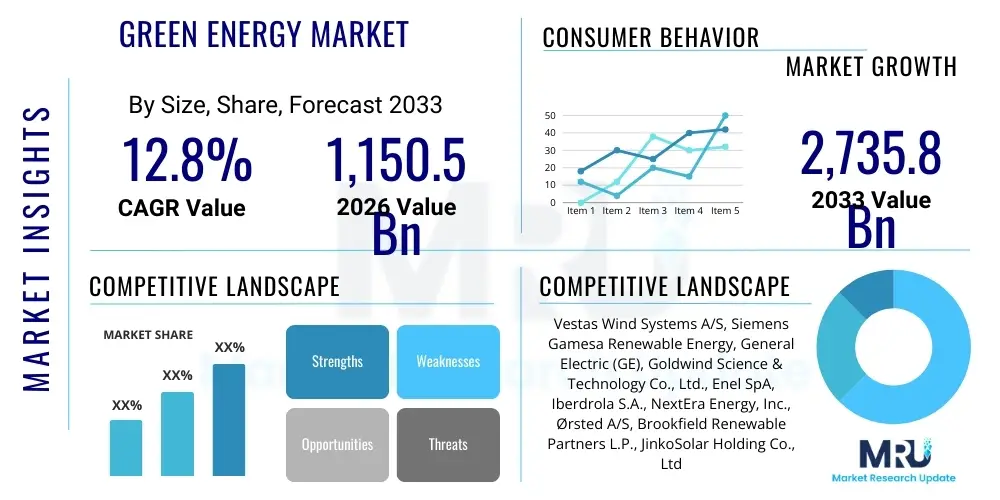
The Green Energy Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.8% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at $1,150.5 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach $2,735.8 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Green Energy Market introduction
The Green Energy Market encompasses the production, distribution, and consumption of electricity and heat derived from renewable sources that naturally replenish themselves, such as solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. This market includes the technologies and infrastructure necessary to convert these natural resources into usable energy forms, significantly contributing to the global transition away from fossil fuels. Key products within this domain include photovoltaic (PV) systems, onshore and offshore wind turbines, advanced battery storage solutions, and infrastructure for green hydrogen production, all aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing energy security.
Major applications of green energy span across utility-scale power generation, distributed power systems for commercial and industrial use, and residential installations. The integration of renewable energy sources into the existing power grids is a critical application, requiring sophisticated grid modernization and smart technology deployment to manage intermittency. Furthermore, green energy is increasingly applied in transportation (electric vehicles charged by renewable sources) and industrial processes (decarbonization of heavy industry through green hydrogen or renewable electricity), expanding its utility beyond traditional power generation.
The primary benefits of transitioning to green energy include enhanced energy independence, reduced exposure to volatile fossil fuel prices, and significant environmental protection through lowered carbon emissions and improved air quality. Driving factors accelerating market growth include stringent governmental regulations and international climate agreements (like the Paris Agreement), rapidly declining Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) for solar and wind power, and substantial corporate commitment towards Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria. These drivers collectively position green energy as the economic and ecological imperative for global energy infrastructure development.
Green Energy Market Executive Summary
The Green Energy Market is experiencing transformative growth, underpinned by favorable regulatory landscapes and massive private sector investment, especially in key regions like Asia Pacific and Europe. Business trends indicate a strong move toward hybridization and decentralization, where projects increasingly combine solar PV, wind, and battery energy storage systems (BESS) to provide firm, reliable power, thus mitigating the traditional challenge of intermittency. Furthermore, the burgeoning green hydrogen sector is poised to revolutionize hard-to-abate industries, establishing a new major revenue stream within the renewable energy ecosystem. Strategic mergers, acquisitions, and cross-sector collaborations between technology firms, utilities, and infrastructure investors are shaping a highly competitive and innovative market structure focused on efficiency and grid integration.
Regionally, Asia Pacific maintains dominance due to aggressive capacity expansion in China and India, driven by electrification needs and policy support mechanisms aimed at energy security. Europe continues its leadership in offshore wind development and ambitious decarbonization targets, propelling investments in interconnected smart grids and hydrogen infrastructure. North America is characterized by robust policy stability (such as tax credits and incentives) fostering significant utility-scale solar and BESS deployment, alongside rapid technological advancements in grid flexibility and modernization. These regional trends reflect a localized optimization strategy based on resource availability and governmental mandate intensity.
Segmentation trends highlight the increasing importance of Energy Storage Technology (specifically lithium-ion batteries and flow batteries) as an essential component, rather than just an ancillary service, fundamentally enabling higher renewable penetration. While solar and wind power remain the primary source segments by installed capacity, geothermal and sustainable biomass are capturing niche but crucial markets in regions with specific resource endowments. The utility segment remains the largest consumer, but decentralized commercial and industrial (C&I) installations, especially those leveraging power purchase agreements (PPAs), are demonstrating the fastest growth rates, signaling a shift toward distributed energy resource (DER) management and localized resilience.
AI Impact Analysis on Green Energy Market
User queries regarding AI’s influence on the Green Energy Market frequently center on themes such as improving grid reliability, optimizing renewable energy forecasting accuracy, and enabling predictive maintenance for complex assets like wind farms. Users are keenly interested in how machine learning algorithms can manage the inherent variability of solar and wind resources, expecting AI to provide actionable insights that reduce operational costs (OPEX) and maximize energy capture (yield). A major concern often raised relates to the computational energy requirements of AI itself and whether its deployment genuinely leads to net sustainability gains. Overall user expectation is that AI will be the foundational technology enabling the reliable, widespread integration of high percentages of intermittent renewable energy into global power systems.
The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) is fundamentally transforming the operational paradigm of green energy systems, moving them from reactive management to proactive optimization. AI facilitates highly accurate prediction models for weather patterns and energy yield, allowing grid operators and project owners to minimize forecasting errors and better schedule energy dispatch. This is crucial for managing the stability of grids with high renewable penetration. Furthermore, AI algorithms analyze vast datasets from sensors embedded in renewable assets (turbines, solar panels, inverters) to detect subtle anomalies, predicting equipment failure before it occurs, thereby dramatically reducing downtime and extending asset lifespan.
Beyond asset management and forecasting, AI plays a pivotal role in optimizing energy storage utilization and establishing smart grids. ML models determine the optimal charge and discharge cycles for Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) based on real-time market prices, grid congestion, and future demand predictions, maximizing economic returns and grid stability. AI-driven smart grids enable decentralized energy resource management (DERM), allowing two-way communication between consumers and providers, optimizing load balancing, and facilitating virtual power plant (VPP) operations. This sophisticated level of control is necessary to manage millions of distributed solar and storage assets efficiently.
- AI enhances predictive maintenance for wind turbines and solar farms, decreasing unplanned downtime by 15-20%.
- Machine Learning algorithms significantly improve renewable resource forecasting accuracy, crucial for grid stability management.
- AI optimizes BESS charging/discharging schedules based on dynamic market pricing and grid demands, maximizing arbitrage opportunities.
- Smart grid systems utilize AI for real-time load balancing, demand response management, and congestion mitigation.
- AI accelerates the discovery and development of next-generation materials for more efficient solar cells and battery components.
- Advanced analytics supports site selection for new renewable projects by evaluating complex geographical and environmental variables.
- AI is instrumental in developing Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) by coordinating thousands of distributed energy resources.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Green Energy Market
The dynamics of the Green Energy Market are governed by a powerful interplay of technological maturity, policy mandates, and macroeconomic shifts. The principal drivers—decline in LCOE and urgent climate mitigation mandates—provide robust foundational growth, while persistent constraints like grid modernization needs and intermittency challenges impose friction on accelerated deployment. Opportunities, particularly in nascent areas like green hydrogen and deep offshore wind, promise substantial future market expansion. These factors coalesce to form significant impact forces, dictating the speed and direction of global energy transition strategies.
Drivers: The most compelling driver is the continuous and steep reduction in the Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) for solar and wind energy, often making them the cheapest sources of new power generation globally, even without subsidies. This economic competitiveness has shifted renewable energy from a subsidized alternative to a mainstream, economically rational choice. Concurrently, increasing global political and corporate commitments to achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century, formalized through national policies and corporate ESG goals, necessitates massive investment in green energy infrastructure. Furthermore, growing concerns over energy security and the desire to reduce reliance on geopolitically sensitive fossil fuel supplies strongly drive the adoption of domestically sourced renewable energy.
Restraints: Significant restraints hinder seamless market acceleration. Foremost among these is the intermittency of solar and wind resources, requiring extensive and costly energy storage solutions and flexible generation capacity to maintain system stability. The current electrical grid infrastructure in many established economies is outdated, requiring substantial investment in upgrades, digitalization, and transmission capacity expansion to handle the bidirectional flow and high variability of renewable energy. Additionally, challenges related to the supply chain volatility for key raw materials (e.g., lithium, polysilicon, rare earth elements) and the potential environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of renewable energy components (like wind turbine blades) present ongoing logistical and reputational hurdles that the industry must address systematically.
Opportunities: Major growth opportunities lie in breakthrough technologies and underserved sectors. Green hydrogen production, powered entirely by renewable electricity, offers a scalable solution for decarbonizing heavy industry (steel, cement) and long-haul transportation, unlocking entirely new markets. Advances in Long-Duration Energy Storage (LDES), such as flow batteries and compressed air energy storage, promise to overcome the daily and seasonal intermittency constraints that current lithium-ion technology struggles with. Moreover, the massive, untapped potential of deep-sea offshore wind resources, coupled with developing floating turbine technologies, represents a future growth frontier, especially in regions with limited shallow water access like Japan and the Mediterranean.
Segmentation Analysis
The Green Energy Market is meticulously segmented based on the energy source utilized, the nature of the application, and the scale of the deployment. Analyzing these segments provides a clear map of investment priorities and technological maturity across the market. The primary segmentation revolves around the physical source of energy, where solar and wind dominate due to their scalability and global resource availability. However, the rapidly evolving Energy Storage segment is increasingly viewed as a co-dependent market, essential for unlocking the full potential of intermittent renewables.
The categorization by application or end-user highlights the shift from purely utility-scale projects to distributed generation. While utilities remain the largest consumer, seeking centralized power generation, the commercial, industrial, and residential sectors are rapidly adopting behind-the-meter solutions, driven by self-consumption incentives and resilience concerns. This decentralization trend is crucial for supporting localized power grids and microgrid development, especially in regions prone to extreme weather events or grid instability. The competitive dynamics within each segment, from large turbine manufacturing to small-scale inverter production, differ significantly based on required capital and technological expertise.
- By Source Type:
- Solar Energy (Photovoltaic, Concentrated Solar Power)
- Wind Energy (Onshore, Offshore, Floating)
- Hydroelectric Power (Large Hydro, Small Hydro, Pumped Storage)
- Bioenergy (Biomass, Biofuels, Biogas)
- Geothermal Energy (Flash, Dry Steam, Binary)
- Green Hydrogen (Electrolysis powered by renewables)
- By End-User:
- Utility (Centralized Power Generation)
- Commercial and Industrial (C&I)
- Residential
- Transportation (EV Charging Infrastructure)
- By Technology:
- Inverters and Power Electronics
- Energy Storage Systems (BESS, LDES)
- Turbines and Generators
- Smart Grid and Monitoring Systems
Value Chain Analysis For Green Energy Market
The Green Energy Value Chain is characterized by highly specialized segments, starting from raw material extraction and processing (upstream) to large-scale project deployment and distribution (downstream). Upstream activities involve the procurement of critical components such as polysilicon for solar cells, rare earth magnets for wind turbines, and lithium/cobalt for batteries. This stage is dominated by specialized manufacturers and commodity traders, heavily influenced by geographical concentration, particularly in Asia Pacific, which controls much of the processing capacity. Efficiency and sustainable sourcing are key performance indicators at this stage.
The core manufacturing and assembly phase involves the production of major system components—solar modules, wind turbine towers and blades, and energy storage cells. This midstream phase requires high capital expenditure and sophisticated robotics and automation. Technological innovation focuses on increasing efficiency (e.g., PERC, heterojunction cells, larger turbine sizes) and reducing material consumption. Downstream activities involve project development, financing, engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC), culminating in system installation and connection to the grid. This phase is characterized by localized regulatory knowledge and strong project management capabilities.
The distribution channel operates through a mix of direct sales and indirect channels. Large utility-scale projects typically involve direct contracts between project developers/EPC firms and the technology providers (e.g., direct purchase of turbines from manufacturers). Conversely, the residential and small C&I markets rely heavily on indirect distribution through a network of certified installers, distributors, and value-added resellers (VARs). Post-installation, the value chain extends into operations, maintenance (O&M), and asset management, which are increasingly critical for ensuring the long-term profitability and reliability of renewable assets, often leveraging digital twins and predictive analytics for maximized performance.
Green Energy Market Potential Customers
The primary customers in the Green Energy Market are large electric utility companies, responsible for generating, transmitting, and distributing power across established grids. Utilities are compelled by regulatory mandates and public pressure to integrate substantial renewable capacity, making them the largest buyers of utility-scale solar farms, wind parks, and integrated energy storage solutions. Their purchasing decisions are driven by long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs), grid stability requirements, and competitive bidding processes for new generation capacity.
Another major customer base comprises Commercial and Industrial (C&I) enterprises, especially those with high energy consumption or strict corporate sustainability targets. These buyers often invest in behind-the-meter solutions—rooftop solar, onsite batteries, and direct access to offsite renewable energy through corporate power purchase agreements (CPPA). Industries such as technology, data centers, manufacturing, and heavy industry (seeking green hydrogen) are aggressively driving demand to hedge against energy price volatility and meet supply chain decarbonization requirements.
Lastly, residential consumers constitute a significant and rapidly growing segment, driven primarily by favorable governmental incentives, rising electricity prices, and the desire for household energy independence and resilience. Residential customers typically purchase smaller-scale rooftop solar PV systems, often bundled with home battery storage, facilitated through local installers and flexible financing options like leases or green loans. This segment is characterized by decentralized procurement and highly localized market dynamics.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | $1,150.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | $2,735.8 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR 12.8% |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Vestas Wind Systems A/S, Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, General Electric (GE), Goldwind Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Enel SpA, Iberdrola S.A., NextEra Energy, Inc., Ørsted A/S, Brookfield Renewable Partners L.P., JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd., LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd., Trina Solar Co., Ltd., First Solar, Inc., Canadian Solar Inc., Tata Power Company Ltd., Adani Green Energy Ltd., AES Corporation, Tesla, Inc., CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited), BYD Company Ltd. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Green Energy Market Key Technology Landscape
The technological landscape of the Green Energy Market is defined by continuous innovation focused on efficiency, cost reduction, and grid compatibility. Core technologies revolve around highly efficient conversion and storage. In solar PV, advancements focus on technologies like Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact (TOPCon) and Heterojunction Technology (HJT), which improve module efficiency beyond traditional PERC structures, leading to higher energy yield per square meter. The push for bifacial modules, which capture sunlight from both sides, further increases performance and reduces the overall system LCOE. In wind power, the trend is toward ever-larger turbines, particularly in the offshore segment, leveraging higher capacity factors and optimized blade aerodynamics to capture energy more effectively and economically.
Crucially, the maturity of energy storage technology is paramount. While lithium-ion batteries dominate short-duration storage applications (up to 4 hours), significant technological efforts are focused on developing commercially viable Long-Duration Energy Storage (LDES) solutions. Technologies such as compressed air energy storage (CAES), pumped hydro storage (PHS) modernization, and novel flow battery chemistries are gaining traction, addressing the need for reliable energy supply over days or weeks. This innovation is critical for integrating higher percentages of intermittent renewables without compromising grid stability. Furthermore, advancements in power electronics, specifically smart inverters and converters, are essential for enabling grid-forming capabilities and managing the complex interaction between distributed energy resources and the centralized grid.
A burgeoning technological frontier is Green Hydrogen production, utilizing electrolyzers powered by dedicated renewable sources. Electrolyzer technologies, primarily Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) and Alkaline, are seeing rapid cost reduction and scale-up, driven by global policy pushes. Sophisticated digital technologies, including Artificial Intelligence and machine learning, are overlaid across all these hardware segments, optimizing operation, predicting faults, and managing complex energy trading in real time. The integration of advanced sensors and the implementation of digital twin technology for asset management ensure that these increasingly complex renewable systems operate at peak efficiency and reliability throughout their multi-decade lifespans.
Regional Highlights
- Asia Pacific (APAC): APAC is the epicenter of global green energy deployment, largely driven by China’s ambitious renewable capacity expansion targets and India’s goal to drastically increase its non-fossil fuel capacity. China is the world leader in both solar PV manufacturing and deployment, hosting the largest installed base for both solar and onshore wind. The region is characterized by aggressive governmental subsidies, competitive project financing, and high energy demand due to rapid urbanization and industrialization. While centralized utility-scale projects dominate, distributed generation is accelerating in countries like Japan, South Korea, and Australia. Investment focus is shifting towards integrated renewable parks and enhancing transmission infrastructure to handle the scale.
- Europe: Europe remains a global leader in decarbonization policy, characterized by ambitious binding targets set by the European Union (EU) and individual member states. The region dominates the offshore wind market, with the North Sea serving as a critical hub for massive, multi-gigawatt projects and transnational grid interconnectors. Policies focusing on phasing out coal and accelerating the implementation of the European Green Deal are driving continuous investment. Europe is also at the forefront of the green hydrogen value chain development, investing heavily in large-scale electrolyzer projects and repurposing gas infrastructure.
- North America: North America, particularly the United States, is experiencing substantial market acceleration driven by supportive federal policies such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which provides long-term tax credits for renewable energy and energy storage. The market is characterized by robust corporate PPAs and significant utility-scale development, primarily in the Sun Belt states for solar and central plains for wind. The region leads in the deployment and commercialization of utility-scale Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), focusing heavily on grid resilience, flexibility, and managing peak demand.
- Latin America: This region presents substantial untapped potential, leveraging excellent solar resources (Chile, Brazil) and existing hydroelectric capacity. Brazil is a powerhouse in bioenergy and small hydro, while Chile is a leader in solar PV and emerging green hydrogen exports. Market growth is often dependent on stable political and regulatory frameworks, with international financing playing a critical role in mitigating project risk and ensuring the timely development of large-scale renewable infrastructure required to meet rapidly increasing power needs.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): The MEA region is emerging as a significant green energy market, particularly the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. These nations, aiming to diversify their economies away from oil dependence, are investing billions in world-record low-cost solar projects (e.g., in the UAE and Saudi Arabia). Africa, while facing infrastructural challenges, is seeing accelerated deployment of decentralized and off-grid solar solutions to address severe energy access deficits, driven by international development aid and private sector microgrid initiatives.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Green Energy Market.- Vestas Wind Systems A/S
- Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy
- General Electric (GE)
- Goldwind Science & Technology Co., Ltd.
- Enel SpA
- Iberdrola S.A.
- NextEra Energy, Inc.
- Ørsted A/S
- Brookfield Renewable Partners L.P.
- JinkoSolar Holding Co., Ltd.
- LONGi Green Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
- Trina Solar Co., Ltd.
- First Solar, Inc.
- Canadian Solar Inc.
- Tata Power Company Ltd.
- Adani Green Energy Ltd.
- AES Corporation
- Tesla, Inc.
- CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited)
- BYD Company Ltd.
- Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd.
- Wartsila Corporation
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Green Energy market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary factor driving the current growth of the Green Energy Market?
The primary factor driving growth is the dramatic and sustained decline in the Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) for solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind power, making these sources economically competitive with, or cheaper than, fossil fuels globally, even without subsidies.
How is energy storage technology transforming the Green Energy Market?
Energy storage systems, particularly Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), are crucial as they mitigate the intermittency challenge of renewables by storing surplus power and releasing it when needed, thereby stabilizing the grid and enabling higher renewable penetration levels.
Which region currently dominates global green energy deployment and manufacturing?
Asia Pacific (APAC) dominates global green energy deployment and manufacturing, largely due to the massive capacity additions and the extensive solar and wind supply chain control held by countries like China and, increasingly, India.
What role does Green Hydrogen play in the future of the Green Energy Market?
Green Hydrogen is vital for decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors like heavy industry (steel, cement) and long-haul transportation. It acts as a clean energy carrier, utilizing surplus renewable electricity to produce fuel, thus expanding the application scope of green energy beyond the power sector.
What are the main regulatory challenges affecting green energy expansion?
The main regulatory challenges include streamlining permitting processes for large-scale projects, reforming electricity market structures to properly value renewable energy flexibility and grid services, and investing in the necessary transmission infrastructure upgrades.
How does AI contribute to the efficiency of wind energy operations?
AI significantly improves wind energy operations by providing predictive maintenance analyses based on real-time sensor data, optimizing turbine blade pitch and yaw angles based on localized wind conditions, and accurately forecasting power output to minimize imbalance penalties.
What is the difference between onshore and offshore wind energy deployment?
Onshore wind utilizes land-based turbines and is typically cheaper but often faces spatial and noise constraints. Offshore wind, particularly deep-sea projects, utilizes larger turbines, captures steadier, stronger winds, and offers massive capacity potential, though it requires higher initial capital investment and specialized maritime infrastructure.
What is a Corporate Power Purchase Agreement (CPPA)?
A CPPA is a contract where a commercial or industrial company agrees to purchase electricity directly from a renewable energy producer, usually for a long term (10-20 years), enabling the development of new renewable projects without relying solely on utility mandates.
What technologies are considered Long-Duration Energy Storage (LDES)?
LDES technologies include mechanical storage (Compressed Air Energy Storage or CAES), thermal storage, and non-lithium-ion battery chemistries such as flow batteries. These are designed to store energy for periods ranging from 8 hours to several weeks, crucial for seasonal energy balancing.
How do governments incentivize residential adoption of solar energy?
Governments typically incentivize residential solar adoption through mechanisms such as net metering (allowing homeowners to sell excess electricity back to the grid), solar tax credits (reducing installation costs), and feed-in tariffs (guaranteed price for generation).
What are the environmental concerns related to Green Energy technology?
Environmental concerns include the end-of-life management and recycling of solar panels and wind turbine blades, the extraction impacts of critical battery raw materials (like lithium and cobalt), and the land use requirements for utility-scale projects.
Why is grid modernization critical for the Green Energy Market?
Grid modernization, including the implementation of smart grid technologies, is critical because the existing infrastructure was designed for unidirectional power flow from large centralized plants; it must be updated to manage the variability and bidirectional flow from numerous distributed renewable sources.
What is the significance of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the US market?
The IRA provides substantial, long-term tax incentives and credits for renewable energy projects, manufacturing, and deployment, offering unprecedented policy certainty that drives massive investment and domestic supply chain establishment in the US green energy sector.
How do the geothermal and bioenergy segments contribute to grid stability?
Geothermal and sustainable bioenergy contribute valuable baseload power. Unlike solar and wind, these sources can operate continuously, providing reliable, dispatchable power that helps to stabilize the grid and complement intermittent generation.
What defines a 'Smart Inverter' in the context of renewable energy?
A smart inverter is an advanced power electronic device used in solar and storage systems that can actively communicate with the grid operator, adjust power factor, provide voltage support, and perform fault ride-through capabilities, contributing to overall grid stability.
Which industry vertical is most likely to benefit significantly from Green Hydrogen?
The heavy manufacturing industry, particularly steel and cement production, is most likely to benefit, as these sectors require high-temperature heat or chemical inputs that are difficult to decarbonize with just electricity; Green Hydrogen offers a clean alternative fuel or chemical feedstock.
What are the current investment trends in the Green Energy financing sector?
Current investment trends focus on green bonds, sustainable investment funds (ESG focus), and significant private equity funding targeted at integrated energy storage solutions, green hydrogen infrastructure, and large-scale transmission projects necessary for renewable capacity integration.
How is the concept of a Virtual Power Plant (VPP) relevant to the market?
A VPP aggregates numerous distributed energy resources (like rooftop solar and small batteries) into a single controllable entity using AI software. This allows the combined capacity to operate like a centralized power plant, providing services such as frequency regulation and peak load reduction to the grid.
What technological advancement is currently dominating solar PV research?
Currently, research is heavily focused on tandem solar cells, particularly perovskite-silicon tandems. These structures layer different materials to capture a broader spectrum of sunlight, promising efficiencies well beyond the theoretical limits of single-junction silicon cells.
Why is the sustainability of the renewable energy supply chain a growing concern?
It is a growing concern because the rapid scaling of renewable deployment requires vast amounts of materials, raising issues regarding ethical sourcing, resource scarcity (especially for rare earth magnets and battery minerals), and the energy intensity of manufacturing processes.
How is hydropower adapting to climate change impacts?
Hydropower is adapting through modernization efforts, including installing variable speed turbines and upgrading infrastructure to handle fluctuating water levels. Furthermore, pumped storage hydro (PSH) is being expanded for use as large-scale, long-duration energy storage rather than primary generation.
What are the key differences in market structure between North America and Europe?
North America’s market structure is heavily influenced by state-level Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) and corporate demand, while Europe is driven by binding supranational mandates (EU targets) and structured auction systems for capacity development, fostering a high level of cross-border grid integration.
What are the challenges in integrating biomass energy sustainably?
Challenges include ensuring the biomass feedstock is genuinely sustainable (avoiding deforestation or land-use change that increases carbon debt), efficient logistics for transporting large volumes of materials, and managing air quality impacts during combustion.
How do tariffs and trade regulations affect the Green Energy Market?
Tariffs and trade regulations, such as anti-dumping duties on solar components, can significantly disrupt the global supply chain, increasing project costs in importing countries and potentially slowing the pace of deployment, particularly impacting the highly globalized solar PV sector.
What is 'Curtailed Energy' and how does the market address it?
Curtailed energy refers to renewable electricity generation that is deliberately reduced or shut down because the grid cannot handle the excess power at that moment. The market addresses this through energy storage deployment, improved transmission capacity, and AI-driven dynamic scheduling to better utilize available power.
How does the decline in oil prices potentially restrain the Green Energy Market?
While often decoupled from power generation, extremely low oil prices can temporarily restrain the market by reducing the economic incentive for adopting renewables in the transportation sector and slowing investment in alternative fuels, although the long-term trend favors renewables due to climate policy.
What technological role do advanced power converters play in grid connectivity?
Advanced power converters act as the interface between renewable generators (like solar farms and wind parks) and the grid. They are essential for transforming DC power to AC, maintaining power quality, and actively supporting the grid through functions like voltage and frequency regulation, known as "grid forming" capability.
Why is the EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) phase crucial in the value chain?
The EPC phase is critical because it translates the project plan into physical reality. Efficiency in procurement, quality control during construction, and timely connection to the grid are essential determinants of the project's long-term operational performance, cost efficiency, and final energy output.
How are geothermal resources classified and utilized for electricity generation?
Geothermal resources are typically classified as dry steam, flash steam, or binary cycle. Dry and flash steam plants use high-temperature reservoirs directly, while binary cycle plants use moderate-temperature fluid to vaporize a secondary fluid (like isobutane) to drive a turbine, allowing for wider utilization globally.
What is the concept of 'Net Zero' and how does Green Energy contribute to it?
'Net Zero' refers to achieving an overall balance between greenhouse gas emissions produced and greenhouse gases taken out of the atmosphere. Green Energy contributes fundamentally by eliminating emissions from the electricity generation sector, which is a major source of global greenhouse gases.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager