Hydrogen Furnace Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 432968 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 255 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Hydrogen Furnace Market Size
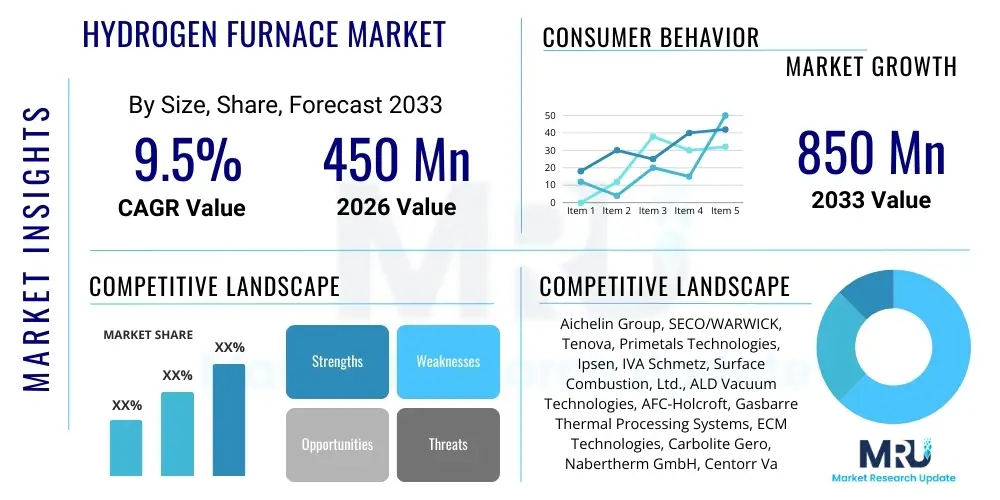
The Hydrogen Furnace Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 450 Million in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 850 Million by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Hydrogen Furnace Market introduction
The Hydrogen Furnace Market is fundamentally driven by the global imperative for industrial decarbonization, particularly within high-temperature processing sectors such as steel manufacturing, glass production, ceramics, and advanced materials. These furnaces utilize hydrogen, either pure or blended with natural gas, as a primary fuel source, yielding water vapor as the main combustion byproduct instead of carbon dioxide. This critical shift positions hydrogen furnaces as essential technology for achieving net-zero emissions targets mandated by international regulatory bodies and sovereign commitments, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuel-fired equipment.
Hydrogen furnaces encompass a range of industrial heating equipment, including batch furnaces, continuous furnaces, and vacuum furnaces, designed specifically to handle the unique combustion characteristics and safety requirements of hydrogen fuel. Key applications span annealing, brazing, sintering, and heat treatment of metals and semiconductor materials, demanding precise temperature control and atmospheric purity. The intrinsic benefits of using hydrogen include superior energy efficiency when integrated into highly optimized systems, reduced operational emissions, and enhanced product quality in certain metallurgical processes where hydrogen acts as a reducing agent, preventing unwanted oxidation.
Major driving factors fueling this market expansion include stringent environmental regulations concerning industrial emissions, substantial governmental investments in the green hydrogen infrastructure globally, and the rising demand for high-performance, low-carbon materials from sectors like electric vehicle manufacturing and renewable energy infrastructure development. Furthermore, technological advancements in hydrogen burner design, safety sensors, and refractory materials that can withstand high temperatures and hydrogen atmospheres are increasing the viability and adoption rate of these specialized furnaces across diverse manufacturing landscapes.
Hydrogen Furnace Market Executive Summary
The Hydrogen Furnace Market is poised for significant expansion, characterized by a rapid technological maturation focused on optimizing combustion efficiency and ensuring operational safety under hydrogen environments. Business trends indicate a strong move toward retrofitting existing furnace infrastructure with hydrogen compatibility kits, offering a cost-effective pathway for rapid decarbonization, alongside the increasing procurement of new, purpose-built hydrogen furnaces, especially in Asia Pacific and Europe. Key strategic collaborations between equipment manufacturers, industrial gas suppliers, and end-users (like steel producers) are accelerating the commercial scaling of hydrogen heating solutions, establishing integrated supply chains necessary for mass deployment.
Regionally, Europe, heavily influenced by the EU Green Deal and robust carbon pricing mechanisms, leads the adoption curve, specifically within Central and Northern European industrial clusters where green hydrogen production is being prioritized. North America, stimulated by fiscal incentives like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), is witnessing significant capital investment in low-carbon industrial hubs, focusing on utilizing blue and green hydrogen. Asia Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, presents the largest potential market size due to its massive industrial base and increasing political commitment to achieving carbon neutrality goals, focusing initially on steel and petrochemical industries.
Segment trends highlight the dominance of the continuous furnace segment, driven by high-volume manufacturing needs in automotive and primary metals, requiring consistent throughput. However, the vacuum furnace segment, critical for high-purity processes in semiconductor and aerospace components, is exhibiting the highest growth rate due to its reliance on extremely precise atmospheric control which hydrogen environments facilitate. The primary challenge remains the cost and consistent availability of affordable, green hydrogen supply, pushing manufacturers to develop dual-fuel furnace systems as an interim solution to manage transition risks.
AI Impact Analysis on Hydrogen Furnace Market
Users frequently inquire about how Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) can mitigate the operational complexities and safety risks associated with high-temperature hydrogen combustion, particularly concerning flame stability, material degradation, and optimal gas blending ratios. Common user concerns revolve around leveraging AI to reduce operational expenses by minimizing hydrogen consumption while maximizing thermal efficiency. The central theme emerging from user questions is the expectation that AI should provide predictive maintenance capabilities for specialized components (burners, sensors, refractory linings) and enable real-time, autonomous optimization of the entire heating process, ensuring both safety compliance and product quality in highly variable energy supply scenarios.
AI’s influence is profound, transforming hydrogen furnace operations from reactive monitoring to proactive, intelligent control. AI algorithms analyze vast datasets encompassing temperature profiles, gas flow rates, combustion metrics, sensor readings, and material stress indicators. This allows systems to instantly adjust fuel delivery and oxygen stoichiometry to maintain optimal, stable combustion, which is crucial for hydrogen due to its high flame speed and low ignition energy compared to natural gas. Furthermore, AI-driven process modeling simulates complex heat transfer phenomena, enabling engineers to design highly efficient furnace geometries and operational sequences tailored to specific material properties, significantly reducing cycle times and energy waste.
Beyond control optimization, AI is instrumental in enhancing safety protocols—a critical requirement for hydrogen infrastructure. ML models predict potential hardware failures, such as minor leaks or sensor drifts, well before they escalate into safety hazards or cause production downtime. By integrating these predictive analytics with supply chain management, AI ensures the optimized scheduling of maintenance and the efficient use of expensive green hydrogen fuel. This integration of cognitive technology enhances the overall reliability and economic viability of deploying hydrogen furnaces in demanding industrial environments, accelerating the return on investment for decarbonization initiatives.
- AI optimizes hydrogen combustion stability and stoichiometry in real time.
- Predictive maintenance schedules for burners, refractory materials, and safety systems are improved using ML.
- AI models simulate complex thermal processes, enhancing furnace design efficiency and reducing material stress.
- Autonomous control systems minimize hydrogen consumption and maximize overall thermal efficiency (AEO).
- Data aggregation via AI enhances operational transparency and compliance reporting for environmental mandates.
- AI integration supports the seamless transition between dual-fuel operations based on hydrogen availability and pricing.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Hydrogen Furnace Market
The Hydrogen Furnace Market is primarily driven by the forceful regulatory push for industrial decarbonization and the subsequent financial incentives provided by governments globally to transition to low-carbon fuels. However, this growth is significantly restrained by the high capital expenditure required for specialized hydrogen infrastructure, including storage and pipeline upgrades, coupled with the current volatility and high cost of green hydrogen supply compared to established fossil fuels. Opportunities abound in developing highly efficient, modular, and retrofittable hydrogen burner systems and expanding applications into new high-pvalue segments such as specialized ceramics and advanced battery component production, which demand precise, clean heat treatment atmospheres. These market dynamics are shaped by impact forces including intense environmental pressure from NGOs and consumers, rapid advancements in electrolyzer technology reducing hydrogen production costs, and critical shifts in geopolitical energy strategies favoring domestic, low-carbon sources.
Drivers: Stricter global climate policies, especially in the EU and North America, necessitating industrial CO2 reduction; increasing corporate commitment to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria driving demand for sustainable manufacturing processes; and significant governmental subsidies and tax credits (e.g., EU Innovation Fund, US IRA) lowering the adoption barrier. Furthermore, the technical advantages of hydrogen as a clean reducing agent in metallurgical processes improve final product quality, acting as a crucial performance driver.
Restraints: The current high cost and limited scalable availability of certified green hydrogen; safety concerns and complex regulatory standards surrounding the handling and storage of hydrogen in industrial settings; and the substantial capital investment required for completely replacing or heavily modifying existing, long-lifecycle furnace infrastructure. Operational risks associated with hydrogen embrittlement in certain materials also require careful design and monitoring, adding to overall complexity and cost.
Opportunities: Development of affordable, high-efficiency hydrogen/natural gas dual-fuel furnaces easing the transition phase; expansion into emerging high-growth industries like solid-state battery manufacturing and additive manufacturing materials requiring precise hydrogen atmospheres; and leveraging Waste Heat Recovery (WHR) technologies optimized for hydrogen furnace flue gases to boost overall system energy efficiency and reduce lifecycle costs significantly, opening new market niches for technology providers.
Impact Forces: The overarching force is the regulatory pressure stemming from climate agreements (e.g., Paris Agreement), which dictates the pace of industrial transformation. Secondarily, the technological maturation of electrolyzers (PEM, AEM) directly impacts the economic feasibility of green hydrogen adoption. Geopolitical stability and the subsequent security of global energy supply chains heavily influence investment decisions in hydrogen infrastructure, making energy resilience a key performance indicator (KPI). Finally, public perception and industrial acceptance of hydrogen safety standards significantly impact insurance and operational costs.
Segmentation Analysis
The Hydrogen Furnace Market is broadly segmented based on furnace type, operating temperature, fuel type, and critical end-use application sectors, providing granular insights into varying demand dynamics and technological requirements across industrial manufacturing. Segmentation by type differentiates between continuous furnaces, used for high-throughput processes like steel strip annealing, and batch furnaces, favored for specialized, smaller-volume high-value material processing. Operating temperature segmentation, ranging from moderate (under 1000°C) to ultra-high (above 1600°C), determines the required refractory material composition and hydrogen burner design sophistication, crucial factors in furnace longevity and efficiency.
Fuel type segmentation is particularly relevant in the transitional market, distinguishing between pure hydrogen furnaces, which offer zero direct CO2 emissions, and hydrogen-blended furnaces (often 5% to 50% hydrogen), which serve as a more immediate, lower-cost decarbonization pathway by utilizing existing natural gas pipelines with minimal modifications. The adoption speed of these segments is directly linked to regional hydrogen infrastructure maturity and government mandates regarding emission reductions, with pure hydrogen systems gaining traction in pioneering industrial parks and mandated zones.
The end-use application segment forms the largest differentiating factor in terms of market value and technological complexity. Applications are typically divided into metallurgy (ferrous and non-ferrous), glass processing, semiconductor manufacturing, and specialized materials like technical ceramics. The semiconductor sector demands extremely high purity and precision, favoring vacuum hydrogen furnaces, while the metallurgy sector focuses on massive scale and robust, high-throughput continuous furnaces. Understanding these specific application requirements is vital for equipment manufacturers to tailor their product offerings and maximize market penetration.
- By Type:
- Continuous Furnaces
- Batch Furnaces (Box, Pit)
- Vacuum Furnaces (High-Vacuum, Ultra-High Vacuum)
- Atmospheric Furnaces
- Tunnel Kilns (Hydrogen Compatible)
- By Operating Temperature:
- Low Temperature (< 600°C)
- Medium Temperature (600°C – 1200°C)
- High Temperature (1200°C – 1600°C)
- Ultra-High Temperature (> 1600°C)
- By Fuel Type/Blend:
- Pure Hydrogen Furnaces (100% H2)
- Hydrogen Blended Furnaces (H2/Natural Gas blends, e.g., H2 20%)
- Dual-Fuel Compatible Furnaces (H2 and NG switchable)
- By Application/End-Use:
- Metallurgy and Metal Processing (Annealing, Brazing, Sintering)
- Iron & Steel Production (Direct Reduced Iron - DRI)
- Non-Ferrous Metals (Aluminum, Copper)
- Aerospace Components
- Glass Manufacturing (Float Glass, Specialty Glass)
- Ceramics and Refractories Production
- Semiconductor and Electronics Fabrication
- Automotive Manufacturing (Component Heat Treatment)
- Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
Value Chain Analysis For Hydrogen Furnace Market
The Value Chain for the Hydrogen Furnace Market is complex, beginning upstream with the supply of critical raw materials, specialized components, and increasingly, the clean hydrogen fuel itself. The upstream phase involves R&D for hydrogen-resistant materials (refractories and alloys), the manufacturing of specialized low-NOx hydrogen burners, and the production of high-precision control and safety systems. The most critical upstream component is the sourcing and distribution of affordable hydrogen (green or blue), which significantly impacts the final operational cost for end-users. Partnerships between furnace manufacturers and industrial gas suppliers are paramount in this early stage to ensure standardized fuel specifications and reliable logistical networks.
Midstream activities involve the core manufacturing, assembly, and testing of the hydrogen furnace equipment. This segment requires high levels of engineering expertise to integrate complex combustion technologies with stringent safety protocols (e.g., gas detection, ventilation, pressure management). Distribution channels are primarily direct sales or through highly specialized engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) firms, particularly for large, bespoke industrial installations like those required for steel mills. Indirect channels, such as authorized system integrators, handle smaller or standardized furnace units, providing localized installation and after-sales support to medium-sized enterprises.
Downstream activities focus on installation, commissioning, maintenance, and long-term service agreements. Given the novelty and complexity of hydrogen combustion technology, downstream support, including operator training on hydrogen safety and predictive maintenance based on sophisticated sensor data, is essential. Potential customers rely heavily on reliable service contracts to ensure furnace uptime and compliance with evolving safety regulations. The strong emphasis on direct distribution and specialized EPC partners underscores the need for technical proficiency throughout the value chain, differentiating successful market players based on their comprehensive service offerings and safety track record.
Hydrogen Furnace Market Potential Customers
The potential customer base for the Hydrogen Furnace Market comprises high-temperature industrial processors across various heavy and specialized manufacturing sectors that are facing immediate and significant pressure to reduce their carbon footprint. Primary buyers are large, multinational corporations in the ferrous and non-ferrous metals industry, particularly steel manufacturers exploring hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (H-DRI) processes, which require massive, specialized furnaces and associated infrastructure. These customers are driven by regulatory compliance, competitive market positioning based on "green" materials, and access to low-carbon government procurement contracts.
Secondary but rapidly growing segments include manufacturers in the highly technical fields of aerospace and defense, which require precise, clean atmospheres for heat treating specialized alloys and composite components, where the clean reducing atmosphere of hydrogen is often technically superior. Similarly, semiconductor and advanced electronics manufacturers, requiring ultra-high purity sintering and annealing processes for sensitive silicon wafers and high-performance chips, represent premium buyers prioritizing quality and process control over initial capital cost.
Beyond these heavy industries, the expanding electric vehicle (EV) supply chain, encompassing battery component producers (anodes, cathodes) and specialized motor part manufacturers, represents a burgeoning end-user segment. These customers require high-volume, reliable heat treatment processes that align with their corporate mandates for full supply chain decarbonization. Therefore, potential customers are characterized by high energy consumption, stringent regulatory exposure, and a strong strategic commitment to carbon neutrality.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 450 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 850 Million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR 9.5% |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Aichelin Group, SECO/WARWICK, Tenova, Primetals Technologies, Ipsen, IVA Schmetz, Surface Combustion, Ltd., ALD Vacuum Technologies, AFC-Holcroft, Gasbarre Thermal Processing Systems, ECM Technologies, Carbolite Gero, Nabertherm GmbH, Centorr Vacuum Industries, C.I. Hayes, Kanthal, Fives Group, Solar Manufacturing, Siemens, and Lindberg/MPH. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Hydrogen Furnace Market Key Technology Landscape
The technology landscape for the Hydrogen Furnace Market is rapidly evolving, focusing predominantly on maximizing thermal efficiency and ensuring critical operational safety, given the high reactivity and unique properties of hydrogen fuel. Key technological advancements center around specialized low-NOx hydrogen burner design. Unlike natural gas burners, hydrogen burners must manage a significantly higher flame speed and lower radiant heat component. Manufacturers are developing porous media burners and staged combustion systems to control the combustion process, minimize thermal NOx formation (even though hydrogen combustion is inherently cleaner), and uniformly distribute heat within the furnace chamber, essential for high-quality material processing.
Another crucial area is the development and implementation of advanced safety and control systems. Hydrogen furnaces require sophisticated sensor arrays for real-time leak detection (using specialized hydrogen sensors), automatic shutdown capabilities, and robust ventilation management systems to prevent flammable gas accumulation. Furthermore, material science innovation is critical; new refractory materials and specialized furnace alloys capable of resisting hydrogen embrittlement and maintaining structural integrity under high temperatures and reducing atmospheres are being mandated. This ensures furnace longevity and reduces maintenance overheads, which is a major factor in total cost of ownership (TCO).
Furthermore, the integration of digital twins and advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling is a standard practice in modern hydrogen furnace design. These digital tools allow engineers to accurately simulate hydrogen flow, heat transfer patterns, and potential flame-out scenarios before physical construction. This simulation capability drastically reduces R&D cycles and ensures that the final installed furnace meets stringent regulatory requirements for both thermal performance and operational safety. Future advancements will focus on developing solid-state heating elements that can utilize hydrogen as a process gas while avoiding direct combustion, offering further potential for enhanced purity and efficiency in specific vacuum applications.
Regional Highlights
- Europe: Europe stands as the foremost market for Hydrogen Furnaces, driven by the ambitious targets set under the European Green Deal and the establishment of centralized hydrogen valleys across Germany, the Netherlands, and Scandinavia. The region benefits from stringent emissions trading schemes (ETS) that make carbon-intensive manufacturing economically unviable, thus accelerating the adoption of clean heating solutions, particularly in the steel, cement, and chemical sectors. Government funding mechanisms and public-private partnerships supporting hydrogen infrastructure deployment ensure the increasing availability of affordable hydrogen, making large-scale furnace retrofitting and replacement economically feasible, especially in industrial clusters surrounding key ports and renewable energy sources.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): APAC represents the largest potential market volume, characterized by massive industrial output, especially in China, Japan, and South Korea. While adoption has historically been slower due to reliance on cheaper fossil fuels, recent commitments to carbon neutrality (e.g., China by 2060, South Korea by 2050) are fueling significant investment. Japan and South Korea are pioneers in hydrogen technology deployment, particularly within the steel and electronics industries, often through state-backed pilot projects. China’s immense manufacturing base provides a large addressable market for standardized and customized hydrogen furnace solutions, though regulatory enforcement and hydrogen sourcing infrastructure remain key challenges that must be addressed for exponential growth.
- North America: The market in North America, primarily the United States and Canada, is experiencing rapid growth, largely stimulated by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which provides substantial tax credits for hydrogen production (especially green hydrogen) and industrial decarbonization projects. Adoption is concentrated in traditional manufacturing centers, focusing on the heavy metals, automotive, and petroleum refining sectors. The preference is often for hydrogen blend solutions initially, leveraging existing natural gas pipeline infrastructure, with a strategic migration path toward pure hydrogen as regional hubs scale up production capacity. Safety standardization and pipeline capacity expansion are crucial determinants of market velocity in this region.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): MEA is emerging as a critical region, not primarily as a consumer of hydrogen furnaces today, but as a global powerhouse for future green and blue hydrogen production, utilizing vast solar resources and natural gas reserves, respectively. Countries like Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Oman are investing heavily in exporting low-carbon hydrogen. As local industrial demand for ‘green’ products increases and pilot projects in domestic steel and aluminum production demonstrate viability, MEA is anticipated to become a strong buyer of hydrogen-compatible equipment, leveraging its proximity to European and Asian markets to anchor its own low-carbon manufacturing ecosystems.
- Latin America (LATAM): The LATAM market is nascent but shows promise, driven by countries like Chile and Brazil, which possess excellent renewable energy potential for green hydrogen production. While immediate adoption is limited by fragmented industrial infrastructure and relatively low capital investment capacity compared to developed regions, the long-term outlook is positive. Decarbonization efforts are focused initially on mining and select heavy manufacturing sectors, with international partnerships and investment being key catalysts for the deployment of foundational hydrogen furnace technologies.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Hydrogen Furnace Market.- Aichelin Group (Austria)
- SECO/WARWICK S.A. (Poland/USA)
- Tenova S.p.A. (Italy)
- Primetals Technologies (Japan/Germany)
- Ipsen USA (USA)
- IVA Schmetz GmbH (Germany)
- Surface Combustion, Ltd. (USA)
- ALD Vacuum Technologies GmbH (Germany)
- AFC-Holcroft (USA)
- Gasbarre Thermal Processing Systems (USA)
- ECM Technologies (France)
- Carbolite Gero (UK/Germany)
- Nabertherm GmbH (Germany)
- Centorr Vacuum Industries (USA)
- C.I. Hayes (USA)
- Kanthal (Sweden)
- Fives Group (France)
- Solar Manufacturing (USA)
- Siemens AG (Germany)
- Lindberg/MPH (USA)
- T-M Vacuum Products (USA)
- BTU International (USA)
- Bodycote PLC (UK)
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (Japan)
- Vesuvius plc (UK)
- Messer Group GmbH (Germany)
- Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. (USA)
- Linde plc (Ireland/UK)
- Danieli Group (Italy)
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Hydrogen Furnace market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary advantage of using a Hydrogen Furnace over a Natural Gas Furnace?
The primary advantage of using a Hydrogen Furnace is the near-zero direct carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions during combustion, as the main byproduct is water vapor (H2O). This critical benefit supports industrial decarbonization goals, unlike natural gas furnaces, which produce significant CO2. Furthermore, hydrogen often serves as a beneficial reducing atmosphere in metallurgical processes, enhancing material quality.
How does the safety profile of hydrogen furnaces compare to conventional industrial heating systems?
Hydrogen furnaces require significantly higher levels of safety monitoring due to the fuel’s low ignition energy and high flame speed. Modern systems employ advanced safety technologies, including sophisticated real-time hydrogen leak sensors, automated emergency shutdown systems, and robust ventilation protocols compliant with international standards (e.g., ATEX/IECEx). While complex, rigorous design and operational procedures ensure safe use equivalent to established hazardous industrial systems.
Which industrial sectors are the leading adopters of hydrogen furnace technology?
The leading adopters are the primary materials sectors facing intense pressure to decarbonize, particularly the iron and steel industry (for Direct Reduced Iron or H-DRI processes), specialized high-temperature metallurgy (aerospace, automotive component heat treatment), and the high-purity semiconductor manufacturing sector, which requires controlled, reducing atmospheres for sintering and annealing processes.
What are the main constraints hindering the widespread adoption of pure hydrogen furnaces?
The main constraints include the high cost and variable availability of certified green hydrogen, which significantly impacts operational expenditure compared to fossil fuels. Additionally, the substantial capital investment required for building new hydrogen storage and distribution infrastructure, along with the necessary retrofitting of existing furnace assets and adherence to complex new safety standards, slows mass adoption.
Are existing industrial furnaces able to be converted to run on hydrogen fuel, and is this cost-effective?
Many existing natural gas furnaces can be retrofitted to run on hydrogen blends (up to 20-50% H2) relatively cost-effectively by replacing burners and upgrading safety controls. However, conversion to pure hydrogen (100% H2) is significantly more complex, often requiring comprehensive material changes (refractory linings, piping alloys) and safety system overhauls, making the economic viability dependent on the furnace's age, design, and the local availability of subsidized green hydrogen.
What is the difference between a batch hydrogen furnace and a continuous hydrogen furnace?
A batch hydrogen furnace processes material in distinct cycles, heating a specific load before being unloaded, typically used for specialized, low-volume, high-value components (e.g., aerospace alloys). A continuous hydrogen furnace, conversely, uses a conveyor or roller hearth system to move material constantly through heating zones, designed for high-volume, consistent output, common in steel strip annealing or mass-produced automotive parts heat treatment.
How does government regulation impact the market growth of hydrogen furnaces?
Government regulation is the primary market driver. Policies such as carbon taxes, mandatory industrial decarbonization roadmaps (like the EU Green Deal), and significant production tax credits (like the US IRA 45V) directly enhance the economic competitiveness of hydrogen furnaces by penalizing CO2 emissions and subsidizing clean technology adoption, forcing industrial users to transition rapidly away from fossil fuel equipment.
What role does Artificial Intelligence play in optimizing hydrogen furnace performance?
AI plays a crucial role by using predictive algorithms to optimize combustion parameters, ensuring flame stability and thermal uniformity essential for high-quality output while minimizing expensive hydrogen consumption. AI also drives predictive maintenance, identifying component wear or potential safety risks in real-time before critical failure occurs, maximizing operational uptime and overall system integrity.
In which region is the demand for vacuum hydrogen furnaces highest, and why?
Demand for vacuum hydrogen furnaces is exceptionally high in the Asia Pacific region, specifically in South Korea, Taiwan, and Japan. This is driven by their world-leading position in semiconductor manufacturing and advanced electronics, where ultra-high purity annealing and sintering processes requiring tightly controlled hydrogen reducing atmospheres are mandatory for producing next-generation high-performance microchips and specialized technical ceramics.
What types of materials are required to build hydrogen-resistant refractory linings?
Hydrogen-resistant refractory linings often utilize specialized high-alumina, silicon carbide (SiC), or advanced ceramic fiber materials that possess low porosity and high resistance to chemical reaction and potential corrosion in a high-temperature, reducing hydrogen atmosphere. These materials must maintain structural stability and thermal insulation properties without suffering hydrogen embrittlement or degradation over extended operational lifecycles, contrasting with materials used in oxidizing environments.
How does the cost of a hydrogen furnace installation compare to a traditional gas furnace?
A new, purpose-built hydrogen furnace typically incurs a 20% to 50% higher capital expenditure (CAPEX) compared to an equivalent natural gas furnace, primarily due to the specialized, high-grade materials required for hydrogen resistance, the inclusion of sophisticated safety monitoring and control systems, and the increased costs associated with hydrogen storage and delivery infrastructure integration at the site level.
What is the concept of a dual-fuel hydrogen furnace, and why is it important?
A dual-fuel hydrogen furnace is designed to operate seamlessly using either natural gas, pure hydrogen, or any blend ratio between the two. This concept is crucial for market transition because it allows industrial users to begin decarbonization immediately by using blends, providing operational flexibility to switch to pure hydrogen only when the supply becomes reliable and economically competitive, mitigating energy supply risks during the infrastructure build-out phase.
How does hydrogen act as a reducing agent in furnace applications?
Hydrogen acts as a potent reducing agent, particularly beneficial in metallurgical processes like bright annealing or sintering. It chemically reacts with oxides present on the surface of metals, reducing them back to pure metal and producing water vapor. This process removes surface contamination, prevents scale formation, and maintains the brightness and purity of the treated material, which is superior to results achieved using inert or less reactive atmospheres.
What certifications and standards are required for operating hydrogen furnace equipment?
Operational hydrogen furnaces must comply with several critical certifications and standards, including local fire codes, national building codes, and specialized industrial gas safety regulations (e.g., ISO 14687 for fuel quality). Crucially, the equipment itself must meet hazardous area classification standards (like ATEX in Europe or NEC in the US) regarding explosion protection, necessitating intrinsically safe instrumentation and robust flame supervision systems.
What is the projected timeline for green hydrogen cost parity with natural gas, influencing furnace adoption?
Market analysts project that green hydrogen cost parity (or near parity) with natural gas, factoring in carbon pricing, may be achieved in major industrial clusters (such as parts of Europe and the US Gulf Coast) between 2030 and 2035. This timeline is heavily dependent on significant reductions in electrolyzer costs, large-scale deployment of renewable energy sources, and consistent government support through carbon taxes and production subsidies.
Beyond decarbonization, what material benefits does hydrogen processing offer?
In addition to zero-carbon processing, hydrogen atmospheres often improve the metallurgical properties of certain materials. For instance, in stainless steel heat treatment, hydrogen ensures a cleaner surface finish (bright annealing) and prevents undesirable oxidation layers. In powder metallurgy (sintering), the reducing environment helps consolidate high-performance metal powders more effectively, leading to improved density and mechanical strength in the final component.
How is the semiconductor industry utilizing advanced hydrogen furnace systems?
The semiconductor industry utilizes specialized ultra-high vacuum hydrogen furnaces for critical processes such as epitaxial growth, silicon wafer annealing, and high-purity sintering of interconnects. Hydrogen is used as a process gas to create an ultra-clean, reducing environment essential for preventing contamination and achieving the nanoscale precision required for advanced microprocessors and memory chips, where even trace oxidation can cause device failure.
What is the primary challenge related to hydrogen flame detection in high-temperature industrial environments?
The primary challenge is that hydrogen flames are inherently difficult to see (invisible or faint blue) in daylight or bright furnace environments due to the lack of soot or carbon particles typical of hydrocarbon fuels. This necessitates the use of specialized UV/IR flame detection sensors, which are designed to reliably detect the characteristic spectral output of the hydrogen flame, ensuring instantaneous and safe shutdown in case of combustion failure or flame-out.
What is the role of EPC firms in the hydrogen furnace market?
Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) firms play a vital role, especially for large industrial projects (like steel mills). They manage the complex integration of the hydrogen furnace system with the existing plant infrastructure, including handling the design, sourcing, and installation of the specialized gas delivery, storage, and safety systems. EPC expertise is essential for navigating the complex safety and regulatory requirements unique to hydrogen technology deployment.
How do Waste Heat Recovery (WHR) systems apply to hydrogen furnaces?
WHR systems are crucial for maximizing the energy efficiency of hydrogen furnaces. These systems capture the substantial heat from the furnace’s hot flue gases (which are primarily steam/water vapor) and use it to preheat combustion air or water for other plant processes. Optimizing WHR is even more critical for hydrogen furnaces to offset the potentially higher cost of hydrogen fuel compared to conventional fuels, significantly improving the overall thermal system economy.
Why is the automotive sector increasingly adopting hydrogen heat treatment technology?
The automotive sector, driven by the mass transition to electric vehicles (EVs) and demanding supply chain decarbonization targets, is adopting hydrogen heat treatment for critical components such as gears, bearing rings, and specialty alloys. Hydrogen furnaces offer the required precision and scale, while the zero-emission operation helps meet the stringent ESG compliance criteria imposed by major global automotive manufacturers on their entire supplier network.
What innovations are emerging in refractory material usage for hydrogen atmospheres?
Innovations are focused on developing low thermal mass (LTM) refractory materials and ceramic fiber modules that exhibit extreme resistance to hydrogen attack, specifically hydrogen embrittlement and chemical reaction at high temperatures. LTM materials allow the furnace to heat up and cool down faster, improving cycle times and energy efficiency, which is particularly beneficial in batch processing applications where quick turnaround is critical for productivity.
What is the financial impact of carbon pricing on the decision to adopt hydrogen furnaces?
Carbon pricing, through mechanisms like the European Union's Emissions Trading System (ETS) or similar national schemes, significantly increases the operating cost of natural gas and coal furnaces. As carbon prices rise, the zero-emission benefit of hydrogen furnaces becomes financially attractive, ultimately shifting the total cost of ownership (TCO) calculation in favor of hydrogen technology, accelerating investment decisions by large polluters seeking regulatory compliance and long-term cost stability.
How does the Hydrogen Furnace Market relate to the broader Green Hydrogen economy?
The Hydrogen Furnace Market is a crucial demand pillar for the broader Green Hydrogen economy. Industrial heating represents one of the largest potential off-takers of green hydrogen, providing essential, stable, large-scale demand required to justify and sustain the massive investment in electrolyzer production and renewable energy infrastructure, linking the supply side of the green hydrogen value chain directly to essential heavy industrial consumption.
What are the limitations of retrofitting an old natural gas furnace for pure hydrogen use?
Retrofitting older furnaces for 100% hydrogen use often faces critical limitations, including the unsuitability of existing piping and valves for hydrogen handling, the inadequate ventilation capacity for hydrogen venting, and the fundamental incompatibility of older refractory and metallic materials with high-temperature hydrogen atmospheres, which can lead to rapid degradation and safety hazards. Often, a complete replacement is safer and more economically sensible for maximizing pure hydrogen efficiency.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
