Metaverse Real Estate Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 439114 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 243 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Metaverse Real Estate Market Size
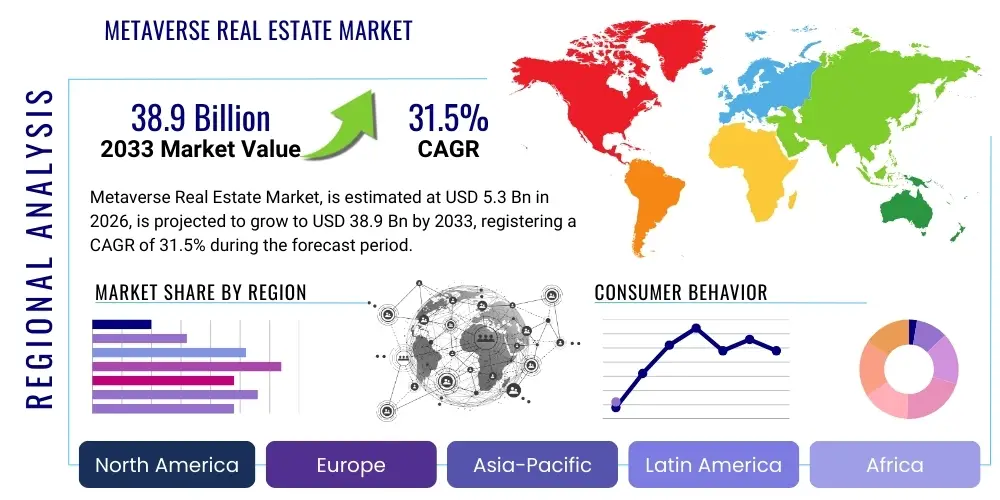
The Metaverse Real Estate Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 31.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at $5.3 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach $38.9 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033. This robust growth trajectory is underpinned by increasing corporate interest in establishing virtual presences, coupled with the rising adoption of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) as proof of digital asset ownership, making virtual land a highly sought-after investment vehicle globally. Furthermore, advancements in spatial computing and the enhancement of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies are significantly improving user immersion, thereby increasing the intrinsic and perceived value of digital property within these simulated environments.
Metaverse Real Estate Market introduction
The Metaverse Real Estate Market encompasses the transaction, development, and management of virtual land and property within persistent, shared, three-dimensional virtual environments (metaverses). These digital assets, often secured using blockchain technology and represented as NFTs, confer verifiable ownership rights to users, allowing them to build, monetize, and utilize their virtual spaces for purposes ranging from socializing and entertainment to e-commerce and professional collaboration. The product description fundamentally involves plots of digital land—finite resources within specific metaverse platforms like Decentraland or The Sandbox—which serve as foundational assets for the virtual economy. These properties are critical infrastructure supporting the burgeoning digital ecosystem, enabling the deployment of interactive experiences, virtual storefronts, and decentralized applications (dApps). The inherent scarcity enforced by platform design drives speculative investment and functional development.
Major applications of metaverse real estate are diversifying rapidly, moving beyond simple speculation. Enterprises are utilizing virtual land to host branded experiences, conduct virtual meetings, launch digital products, and establish permanent virtual headquarters, thereby enhancing customer engagement and reducing operational costs associated with physical infrastructure. Individual users leverage these spaces for passive income generation through virtual renting or advertising, creating personal art galleries, or establishing exclusive social clubs. The primary benefits include global accessibility, verifiable ownership through immutable blockchain records, and the ability to rapidly iterate and customize digital environments without the constraints of physical world logistics or zoning regulations. This flexibility fuels innovation in digital design and interaction models, attracting a wide demographic of investors and developers seeking early mover advantages in the Web 3.0 paradigm.
Driving factors propelling this market include the accelerating mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies and NFTs, which normalize the concept of digital ownership and value transfer. Significant investments by major technology conglomerates (such as Meta Platforms and Microsoft) validate the long-term potential of the metaverse, encouraging further venture capital inflow into underlying infrastructure and content creation tools. Additionally, the proliferation of high-speed internet and increasingly sophisticated consumer-grade VR/AR hardware lowers the barrier to entry for immersive experiences. The psychological shift, particularly among younger generations, viewing digital property as valuable and functional assets further stabilizes demand, ensuring continued market liquidity and development activity across diverse virtual worlds. Regulatory clarity, although nascent, is also expected to eventually enhance institutional confidence and participation.
Metaverse Real Estate Market Executive Summary
The Metaverse Real Estate Market is currently experiencing a transition from purely speculative investment to strategic functional development, driven by profound shifts in business trends. Major corporations, spanning sectors such as luxury retail, banking, entertainment, and professional services, are rapidly acquiring prime virtual land parcels to establish permanent digital footprints. This influx of institutional capital signals maturity, pushing valuation metrics beyond simple scarcity models toward utility-based assessments. Key business trends include the rise of virtual property management firms and dedicated Metaverse Real Estate Investment Trusts (MREITs) that facilitate fractional ownership and professional land development, democratizing access while ensuring sustainable development and maximizing return on investment (ROI) for both individual and institutional holders. Furthermore, cross-platform interoperability, though still challenging, is a central development focus, aiming to unlock greater liquidity and seamless user experience across distinct virtual environments.
Regional trends indicate North America and the Asia Pacific (APAC) as the leading centers of market activity and innovation. North America dominates in terms of transaction volume and the presence of foundational platform developers, benefiting from a robust venture capital ecosystem and high consumer awareness regarding Web 3.0 technologies. APAC, particularly South Korea, Japan, and Singapore, is rapidly gaining traction, fueled by strong government support for digital transformation initiatives and high metaverse adoption rates in the gaming and entertainment sectors. European markets are demonstrating cautious but steady growth, focusing on leveraging virtual spaces for digital art exhibitions, cultural heritage preservation, and professional education platforms. The maturity of regulatory frameworks concerning digital assets will be a primary determinant of differential regional growth over the forecast period, influencing institutional engagement and consumer trust across diverse geographies.
Segmentation trends highlight the increasing importance of Commercial Spaces within the Asset Type segment, reflecting the focus on monetization through e-commerce integration, advertising billboards, and experiential marketing setups. While Individual End-Users continue to drive the majority of unique transactions, the Enterprise segment is responsible for the largest aggregated capital inflow, dictating demand for large, strategically located land parcels suitable for complex virtual infrastructure. Within the Transaction Type, leasing and rental models are maturing, offering more accessible alternatives to outright purchase, thereby expanding the market to users seeking temporary operational bases or lower investment thresholds. Platform segmentation remains competitive, with established giants like The Sandbox and Decentraland facing robust challenges from emerging, niche metaverses specializing in specific functionalities, such as enterprise collaboration or hyper-realistic spatial experiences, leading to segmentation based on technological infrastructure and primary use case.
AI Impact Analysis on Metaverse Real Estate Market
Common user questions regarding AI's influence on Metaverse Real Estate center primarily on optimization, automation, and valuation accuracy. Users are keenly interested in how Artificial Intelligence can automate the tedious process of virtual property development, particularly concerning asset generation, architectural design, and environmental customization, asking: "Can AI design a functional virtual building faster and cheaper than a human developer?" Another significant area of concern revolves around AI's role in valuation and investment strategy, specifically querying the reliability and transparency of AI-driven pricing models for dynamic, non-fungible assets: "How accurate are AI algorithms in predicting future virtual land prices, given the speculative nature of the market?" Furthermore, users are exploring AI’s application in enhancing the utility and interactive nature of the properties, focusing on AI-powered Non-Player Characters (NPCs) and intelligent virtual assistants capable of managing virtual storefronts or providing personalized user experiences within the properties themselves, thereby fundamentally increasing the asset's functional value and operational efficiency, which is summarized as a shift towards intelligent virtual infrastructure.
AI is set to revolutionize the entire lifecycle of metaverse real estate, from initial design and construction to ongoing management and valuation. Generative AI tools are dramatically accelerating content creation, allowing developers to rapidly generate complex 3D models, textures, and spatial layouts based on simple textual prompts, thereby drastically reducing the time and cost associated with virtual property development. This capability democratizes the creation process, enabling a wider array of small developers and individual landowners to build sophisticated, high-utility properties. Furthermore, AI algorithms are being employed in predictive analytics to model market dynamics, assessing factors such as user traffic density, proximity to high-value social hubs, and historical price volatility to provide far more granular and informed valuation metrics than traditional methods, ultimately enhancing market transparency and attracting more risk-averse institutional investors seeking data-backed investment decisions in the highly volatile digital domain.
Beyond design and valuation, AI plays a crucial role in enhancing the functional utility and management of virtual assets. AI-powered virtual property managers can automate tasks such as leasing agreements, collecting virtual rent, managing advertising inventory, and ensuring regulatory compliance within the platform's terms of service. Moreover, the integration of intelligent NPCs and conversational AI within commercial metaverse properties enhances customer service capabilities and creates dynamic, engaging user experiences, effectively transforming static digital spaces into autonomous, functional virtual businesses. This operational efficiency drastically increases the ROI potential for commercial real estate parcels. However, the adoption necessitates significant advancements in decentralized AI training models and the establishment of clear ethical guidelines to prevent algorithmic bias in valuation or automated resource allocation, ensuring equitable access and fair market practices across diverse virtual platforms.
- AI-Driven Generative Design: Automating the creation of architectural blueprints, 3D assets, and interior layouts for rapid virtual construction.
- Predictive Valuation Models: Utilizing machine learning to analyze transaction data, user demographics, and utility metrics for accurate real-time land pricing.
- Intelligent Property Management: Deployment of AI agents for automated rental collection, virtual security, and managing operational aspects of commercial properties.
- Enhanced User Experience: Integration of sophisticated AI-powered NPCs and virtual assistants to improve interactivity and engagement within leased or owned spaces.
- Optimized Traffic Flow: Using AI to analyze and optimize user movement patterns within large virtual venues, maximizing visibility for commercial parcels.
- Fraud Detection: Employing machine learning algorithms to identify and mitigate sophisticated fraudulent activities and wash trading in NFT land marketplaces, enhancing market integrity.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Metaverse Real Estate Market
The Metaverse Real Estate Market is fundamentally shaped by a dynamic interplay of Drivers, Restraints, and Opportunities, which collectively constitute the primary Impact Forces determining its future trajectory. Key drivers center around the accelerating acceptance and utilization of blockchain technology and NFTs, which provide the essential framework for verifiable, immutable digital ownership, thereby establishing foundational trust in virtual assets. Concurrently, the increasing corporate adoption, where major global brands strategically invest in virtual land for marketing and customer engagement, injects substantial capital and credibility into the ecosystem. Restraints primarily involve regulatory uncertainty, as governments globally struggle to define the legal classification and taxation of virtual property, creating inherent risks for large-scale institutional investment. Furthermore, issues related to interoperability—the inability to seamlessly transfer assets or experiences between different metaverses—fragment the market and limit the overall utility of owned properties. The critical opportunities reside in the maturation of fractional ownership models and the expansion into enterprise-grade virtual collaboration spaces, which promise to unlock vast new demographics of buyers and use cases, transcending mere entertainment or speculative investment. These forces create a high-impact, high-volatility environment requiring agile strategic responses.
Drivers are exerting the strongest positive force on market growth. The increasing fidelity and accessibility of VR/AR hardware, coupled with continuous improvements in spatial computing, are making metaverse experiences more engaging and intuitive, driving sustained user engagement and increasing the demand for utility-focused digital land. Additionally, the proliferation of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) focused on virtual asset management and platform governance provides a robust, community-driven structure that instills confidence in the long-term viability of the underlying platforms. This decentralized approach contrasts sharply with traditional real estate models, appealing particularly to Web 3.0 native investors. The continuous flow of capital from venture capitalists and established tech firms into foundational metaverse infrastructure validates the market's long-term potential, creating a virtuous cycle where increased investment leads to better technology, which in turn attracts more users and further investment, significantly raising the baseline valuation of prime virtual assets across top-tier platforms.
While the market is driven by technological momentum, significant restraints impose friction on its expansion. High market volatility, fueled by speculative investment cycles and the influence of cryptocurrency price fluctuations, poses a risk to conservative investors and deters broad consumer adoption. The energy consumption associated with blockchain technologies, particularly proof-of-work mechanisms, presents environmental concerns that may trigger regulatory backlash or negatively impact public perception, necessitating a swift transition towards more sustainable protocols. Moreover, platform-specific risk, where the value of virtual land is intrinsically tied to the success and longevity of a single metaverse platform, introduces a unique form of technological dependency risk absent in physical real estate. Overcoming these restraints necessitates clear legal frameworks, the development of robust, platform-agnostic development standards, and sustained efforts towards making virtual environments more functionally indispensable across diverse professional and social applications, maximizing opportunity realization while mitigating inherent systemic risk factors.
Segmentation Analysis
The Metaverse Real Estate Market segmentation is crucial for understanding the diverse investment strategies and utility models prevalent across the ecosystem. The market is primarily segmented by Platform Type, Asset Type, End-User, and Transaction Type, reflecting the varied technological infrastructure and commercial applications inherent in different virtual worlds. Platform differentiation is vital, as the economic models, governance structures, and user bases vary significantly between major virtual environments, directly influencing the liquidity and intrinsic value of the land within them. Analyzing these segments provides strategic insights for developers seeking to optimize their virtual land acquisition portfolios and for businesses aiming to target specific demographics within specialized metaverses. The continued differentiation based on core utility—whether gaming, social, or enterprise focus—drives distinct valuation premiums across the various segmented categories, ensuring a complex, highly stratified market structure.
Asset Type segmentation reveals the evolving maturity of the virtual real estate economy, moving from simple land parcels to sophisticated, complex virtual structures. Commercial spaces, including virtual malls, advertising billboards, and office complexes, command the highest price premiums due to their direct monetization potential through virtual leasing and e-commerce integrations. Conversely, residential units, while experiencing steady demand from individual users seeking personalized social spaces, often exhibit lower transactional value but higher long-term community establishment potential. The End-User segmentation clearly delineates the driving forces behind capital allocation: Enterprises prioritize scale and functional utility for large-scale operations, while Individuals often seek prestige or speculative gains. Understanding these user motivations informs pricing strategies and development prioritization across platforms, ensuring that supply meets the distinct demands of both institutional and retail market participants effectively.
The Transaction Type segmentation highlights the shift towards more flexible ownership and usage models. Outright Purchase, often executed via cryptocurrency (like ETH or the native platform token), remains the primary method for long-term investment and speculative holding, conferring full ownership rights represented by an NFT. However, the rise of Lease agreements and Rental models is significantly lowering entry barriers for users and businesses who require temporary space for events, limited-time campaigns, or operational testing without committing to substantial capital outlay. This flexibility is essential for market scalability and ensures that the virtual real estate market becomes accessible not only to wealthy speculators but also to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and content creators who rely on operational agility. This maturation in transaction models signifies a robust movement towards established real-estate financial paradigms adapted for the digital domain, promising enhanced liquidity and more efficient capital deployment across the segmented market landscape.
- By Platform
- Decentraland (Focus on decentralized governance and events)
- The Sandbox (Focus on user-generated content and gaming experiences)
- Axie Infinity (Focus on play-to-earn gaming infrastructure)
- Upland (Focus on real-world mapped locations and property trading)
- Somnium Space (Focus on high-fidelity VR experiences)
- Cryptovoxels (Focus on artistic expression and building)
- By Asset Type
- Land Parcels (Undeveloped base assets)
- Commercial Spaces (Virtual stores, offices, advertising spaces)
- Residential Units (Private homes, apartments, customizable social spaces)
- Virtual Infrastructure (Roads, utilities, public plazas maintained by platform DAOs)
- By End-User
- Individuals (Speculators, content creators, consumers)
- Enterprises (Brands, corporations, virtual developers, educational institutions)
- Virtual Developers (Focused on building and selling turnkey virtual properties)
- Government/Public Sector (Virtual embassies, digital public services)
- By Transaction Type
- Purchase (Outright NFT ownership transfer)
- Lease/Rental (Temporary usage rights, often smart contract based)
- Fractional Ownership (Investment in shared property tokens)
Value Chain Analysis For Metaverse Real Estate Market
The value chain for the Metaverse Real Estate Market is fundamentally different from traditional real estate, being entirely digital and heavily reliant on technological infrastructure. The upstream segment involves the creation and maintenance of the core metaverse platforms, which is typically handled by centralized development teams or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). This phase includes developing the foundational blockchain layers, establishing the spatial computing engines, and defining the scarcity rules for virtual land issuance. Key activities upstream include smart contract auditing, 3D asset pipeline development, and server infrastructure scaling. The input resources are highly specialized software developers, blockchain architects, and significant computational power, underscoring the high technological barrier to entry for platform creation. The quality and longevity of this upstream infrastructure directly determine the intrinsic utility and stability of the downstream real estate assets, making platform governance a critical value determinant.
The midstream and downstream activities involve the actual real estate development, trading, and consumption. Midstream activities encompass virtual architecture (3D modeling, spatial design), utility development (integrating commerce tools, interactive dApps), and brokerage services. These services transform raw land parcels (NFTs) into usable, high-value assets. Downstream activities focus on the distribution channel, which is overwhelmingly digital and permissionless. Direct sales occur primarily through dedicated platform marketplaces (e.g., Decentraland Marketplace) where ownership is transferred instantly via smart contracts. Indirect channels involve external NFT aggregator marketplaces like OpenSea, which list virtual land alongside other digital collectibles, providing broader exposure and liquidity. Virtual property management services, which handle leasing and maintenance, also form a crucial part of the downstream value delivery, ensuring the continuous monetization of developed assets for owners who are not actively managing their virtual properties.
The efficiency of the distribution channel is heavily reliant on the seamless integration of blockchain technology and intuitive user interfaces. Direct channels offer lower transaction fees and streamlined platform-native experiences, favoring users highly integrated within the specific metaverse ecosystem. Indirect channels, while potentially incurring higher fees, benefit from massive user bases and superior liquidity due to cross-platform compatibility, acting as essential conduits for bringing new investors into the market. The entire value chain is optimized for speed and transparency, leveraging smart contracts to eliminate intermediaries in the transaction process (unlike traditional real estate). Maximizing value capture downstream requires developers to focus on creating assets with high functional utility and aesthetic appeal that can attract sustained user traffic, translating into tangible monetization opportunities through advertising, virtual events, or digital goods sales, effectively closing the loop between digital creation and economic realization.
Metaverse Real Estate Market Potential Customers
The customer base for Metaverse Real Estate is highly diversified, encompassing a broad spectrum of End-Users ranging from speculative investors and content creators to established multinational corporations and public institutions. The largest segment, in terms of transaction volume, remains the individual investor, often characterized by high risk tolerance and a foundational understanding of blockchain technology. These buyers are primarily motivated by the potential for high capital appreciation, viewing virtual land as an emergent asset class akin to early internet domain names. They typically acquire smaller, strategically located parcels with the intent to hold, flip, or engage in rudimentary development, leveraging their holdings for passive income through limited advertising or virtual renting. This demographic is crucial for maintaining market liquidity and volatility, providing the necessary trading activity to establish price floors and ceilings across different platforms.
The fastest-growing and highest-value customer segment is the Enterprise buyer. This includes global brands (e.g., Nike, Adidas, Gucci), financial institutions (e.g., JPMorgan), entertainment conglomerates (e.g., Warner Music Group), and large tech firms. Their motivation is not purely speculative but strategically utilitarian: establishing a permanent virtual presence to conduct marketing campaigns, launch digital products (NFTs), host virtual events, or establish collaboration hubs for remote workforces. Enterprise purchases typically involve acquiring larger land tracts or prime locations within established metaverse hubs, ensuring maximum visibility and user accessibility. These customers require complex, custom-built virtual infrastructure and often engage third-party virtual development agencies, significantly driving demand for high-end, utility-focused land development services and specialized virtual architecture talent, thereby increasing the overall functional value of the surrounding metaverse environment.
A third, emerging segment includes Virtual Developers and professional Metaverse Real Estate Investment Trusts (MREITs). These entities act as institutional intermediaries, acquiring undeveloped land in bulk, developing high-quality, functional properties (e.g., virtual office buildings or retail parks), and then monetizing them through long-term leases, fractional ownership schemes, or outright sales of completed structures. MREITs appeal to risk-averse institutional investors by offering diversified exposure to the market without the need for active management or deep technical expertise. Furthermore, content creators—including musicians, artists, and game developers—are vital customers, purchasing land specifically to host their digital creations, charge admission to virtual experiences, or sell bespoke digital assets. These customers enhance the cultural richness and functional utility of the metaverse, which in turn drives organic user traffic and increases the foundational appeal of the digital real estate assets, cementing their role as essential components of the market demand structure.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | $5.3 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | $38.9 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 31.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | The Sandbox, Decentraland, Axie Infinity, Republic Realm, Everyrealm, Meta Platforms, Roblox Corporation, Somnium Space, Uplandme, SuperWorld, Cryptovoxels, RFOX Games, OpenSea (as a marketplace facilitator), Animoca Brands, Microsoft (Mesh), Nvidia (Omniverse), Tokens.com, Decentral Games, LandVault. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Metaverse Real Estate Market Key Technology Landscape
The Metaverse Real Estate Market is entirely dependent on a sophisticated convergence of cutting-edge digital technologies, chief among them being Blockchain Technology and Spatial Computing. Blockchain, specifically implemented through decentralized ledgers like Ethereum and Polygon, serves as the immutable backbone, enabling the secure creation and transfer of virtual land assets represented as Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). This technology solves the fundamental problem of digital scarcity and verifiable ownership, providing the essential trust layer required for high-value transactions in a digital environment. Smart contracts, integral to blockchain, automate complex processes such as property transfer, rental agreements, and fractional ownership distribution, eliminating the need for traditional legal intermediaries and significantly streamlining the transaction lifecycle. The adoption of more efficient consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Stake, is also critical for addressing scalability issues and environmental concerns related to high transaction volumes, ensuring the long-term viability of the underlying digital infrastructure supporting the virtual real estate economy.
Complementary to blockchain are the core visualization and interaction technologies: Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). VR hardware provides the high-fidelity, immersive experience necessary for users to genuinely perceive the value and functionality of their virtual properties, driving deeper engagement and utilization of purchased land. AR and MR extend the metaverse real estate experience into the physical world, allowing users to overlay digital assets onto real-world environments, blurring the lines between physical and virtual property utilization, especially relevant for advertising and hyper-local commercial applications. Spatial computing, the underlying algorithmic framework that allows physical and virtual objects to interact logically within a 3D space, ensures the persistence and interactive capability of the built environment on owned virtual land. Advances in rendering pipelines (like those offered by Unreal Engine and Unity) and the rapid development of low-latency networking protocols (e.g., 5G) are continually improving the graphic realism and responsiveness, thereby enhancing the functional and aesthetic appeal of metaverse properties, which directly translates into higher market valuation premiums for well-developed land parcels.
Furthermore, the technology landscape includes advanced infrastructure tools for development and monetization. Cloud computing services provide the necessary scalability and distributed processing power to host vast, persistent virtual worlds that support millions of simultaneous users and complex architectural builds, ensuring high availability and minimal downtime for digital properties. AI and machine learning tools, as discussed previously, are becoming indispensable for automating the generation of high-quality 3D assets, optimizing the layout of virtual spaces based on user behavioral data, and providing robust valuation models for investment strategies. Finally, interoperability protocols, though still nascent, are crucial for future growth. Technologies that allow NFT assets or user avatars to move seamlessly between different metaverses (like platform bridges or generalized asset standards) will unlock the true potential of virtual land by expanding its utility beyond a single platform ecosystem, ensuring that investments in one metaverse remain valuable even if the primary platform declines or new, superior metaverses emerge, fundamentally protecting investor capital through technological abstraction.
Regional Highlights
- North America: Dominance in Innovation and Capital Investment
North America currently holds the largest share of the Metaverse Real Estate Market, primarily driven by the presence of key technology giants, pioneering metaverse platforms (e.g., Decentraland, The Sandbox creators), and a highly active venture capital ecosystem dedicated to Web 3.0 infrastructure. The region benefits from early consumer adoption of decentralized technologies and a cultural readiness to invest in digital assets. Corporate adoption is exceptionally high, with numerous Fortune 500 companies based in the US and Canada aggressively acquiring virtual land for strategic branding and virtual event hosting. Furthermore, a robust community of virtual developers and digital architects ensures continuous innovation in property development and utility creation, maintaining the region's lead in terms of transactional liquidity and high-value, large-scale virtual land sales. Regulatory discussions are advancing, albeit slowly, which, if streamlined, could significantly stabilize institutional interest and further accelerate market expansion across the continent.
Key drivers include substantial investment in foundational blockchain protocols and the established maturity of NFT marketplaces based in the region. The high density of skilled software engineers and 3D modeling experts further solidifies North America's position as the primary hub for both market activity and technological infrastructure development. Institutional players, including major banks and real estate firms, are actively exploring how to integrate virtual asset management into their traditional portfolios, lending credibility and professional structure to the nascent market. However, challenges related to energy consumption of legacy proof-of-work protocols and ensuring consumer protection against market manipulation remain pertinent areas requiring sustained focus to ensure long-term, sustainable regional growth.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Rapid Adoption and Gaming Integration
The APAC region is demonstrating the highest growth trajectory, fueled by massive user bases in gaming, strong governmental interest in digital transformation, and high smartphone penetration driving mobile-first metaverse adoption. Countries like South Korea, Japan, and Singapore are at the forefront, with South Korea, in particular, seeing significant municipal and national investment in creating public sector metaverses and supporting local metaverse development studios. The market in APAC is heavily integrated with the play-to-earn (P2E) gaming model, making virtual real estate (such as land in Axie Infinity or similar gaming metaverses) functionally valuable as infrastructure for economic activity within those platforms. This utility-driven approach contrasts slightly with the more speculative nature seen in parts of North America, resulting in a more sustained, user-centric demand for virtual properties.
The regulatory environment varies significantly across APAC nations, but positive signals from governments endorsing blockchain innovation are stimulating private sector investment. China, despite strict regulations on cryptocurrency, is seeing parallel development in government-controlled, centralized metaverses focusing on industrial and educational applications, demonstrating diverse regional models of digital land use. The vast and rapidly expanding digital consumer population provides a huge captive market for brands investing in virtual commercial spaces, ensuring that commercial metaverse real estate parcels in high-traffic zones within APAC-favored platforms will continue to see strong valuation growth. The focus on integrating virtual real estate with everyday applications, such as digital identity and educational services, is a distinctive regional characteristic driving fundamental demand.
- Europe: Focus on Cultural Heritage and Regulatory Clarity
Europe represents a mature market characterized by a slower, more deliberate adoption pace compared to North America or APAC, placing a significant emphasis on regulatory clarity and sustainable development. European activity often centers around utilizing the metaverse for cultural applications, such as digital preservation of historical sites, virtual art galleries, and hosting large-scale virtual music and cultural festivals. The region is actively working on establishing comprehensive legal frameworks, such as the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, which is expected to provide much-needed legal certainty for institutional investors regarding digital assets, including virtual land, potentially unlocking substantial investment flows previously held back by legal ambiguity.
Key countries like Germany, France, and the UK are seeing increasing corporate interest, particularly in the luxury retail and technology sectors, using metaverse land to extend their brand narratives and create exclusive digital experiences for European consumers. The focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria is also influencing European metaverse development, promoting platforms built on energy-efficient blockchain protocols. While transactional volumes may lag behind other regions currently, the anticipated clarity in digital asset regulation is projected to position Europe as a highly secure and predictable market for institutional investors entering the virtual real estate space, prioritizing stability over high volatility and offering a sustainable growth trajectory in the medium to long term, particularly for enterprise collaboration and high-fidelity social platforms.
- Latin America (LATAM) and Middle East & Africa (MEA): Emerging Hubs of Hypergrowth
LATAM and MEA are emerging as high-growth markets, driven by favorable demographics (young, digitally savvy populations), high inflation in local currencies leading to increased adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi), and a quest for alternative, inflation-resistant asset classes. In LATAM, countries like Brazil and Mexico show strong P2E gaming integration and high community engagement with decentralized platforms. The MEA region, particularly the UAE and Saudi Arabia, is making substantial strategic investments in metaverse technology as part of their national economic diversification efforts. Dubai, in particular, has launched significant government initiatives to promote the metaverse economy, aiming to become a global hub for digital assets, which directly stimulates demand and development of local metaverse real estate markets.
These regions demonstrate a high potential for leapfrogging traditional technology adoption cycles, leveraging mobile technology for metaverse access. Although initial market size is smaller compared to established regions, the compound growth rates are exceptionally high due to rapid integration of virtual assets into daily economic life. Challenges include securing adequate local high-speed internet infrastructure and overcoming currency conversion complexities for international transactions. However, government support, particularly in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations, coupled with high digital adoption rates among the youth, ensures that LATAM and MEA will become increasingly critical contributors to global metaverse real estate transaction volumes over the forecast period, focusing heavily on utility and localized cultural content within the virtual spaces they develop and occupy.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Metaverse Real Estate Market.- The Sandbox
- Decentraland
- Axie Infinity
- Republic Realm
- Everyrealm
- Meta Platforms
- Roblox Corporation
- Somnium Space
- Uplandme
- SuperWorld
- Cryptovoxels
- RFOX Games
- OpenSea (as a marketplace facilitator)
- Animoca Brands
- Microsoft (Mesh)
- Nvidia (Omniverse)
- Tokens.com
- Decentral Games
- LandVault
- Virtual Land Holdings
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Metaverse Real Estate market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What verifies ownership of Metaverse Real Estate?
Ownership of Metaverse Real Estate is primarily verified and secured using blockchain technology, specifically through Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). When a user purchases a piece of virtual land on a platform like Decentraland or The Sandbox, a unique NFT is minted and transferred to their digital wallet. This NFT acts as an immutable, verifiable, and cryptographic deed of title, proving the holder is the sole owner of that specific parcel within the metaverse ecosystem. This decentralized system ensures transparency and eliminates the reliance on a central authority for title verification, fundamentally distinguishing it from traditional digital asset ownership models.
How is the value of virtual land determined in the Metaverse?
The value of virtual land is determined by a complex interplay of scarcity, location, utility, and platform demand. Scarcity is inherent, as most metaverses limit the total number of land parcels. Location is critical, with properties near high-traffic hubs, popular community centers, or corporate headquarters fetching premium prices dueating the perceived value of physical world real estate. Utility, derived from the land's potential for monetization (e.g., hosting virtual stores, events, or advertising), is increasingly becoming the dominant value driver. Furthermore, the overall popularity, stability, and technological roadmap of the underlying metaverse platform directly influence investor confidence and, consequently, the land's valuation and long-term appreciation prospects.
Can Metaverse Real Estate be used to generate passive income?
Yes, Metaverse Real Estate offers multiple avenues for generating passive income, significantly enhancing its appeal as a functional asset class. Owners can rent or lease out their virtual properties to businesses or individual users for temporary use, utilizing smart contracts for automated revenue collection. Income can also be generated through virtual advertising by hosting digital billboards on high-traffic parcels. Additionally, developers can build functional virtual structures, such as entertainment venues or galleries, and charge admission fees or sell associated digital goods and services (e.g., virtual merchandise), thereby transforming the owned land into a direct and recurring revenue source within the platform's native economy, providing compelling returns on invested digital capital.
What are the primary regulatory risks facing the Metaverse Real Estate Market?
The primary regulatory risks center on ambiguity regarding the legal classification of virtual land and associated NFTs. Governments worldwide are debating whether these assets should be treated as commodities, securities, or property, leading to uncertainties regarding capital gains taxation, anti-money laundering compliance, and inheritance laws. Lack of clear international regulatory harmonization poses challenges for cross-border transactions and institutional participation. Furthermore, platform governance risks, consumer protection laws concerning fraudulent sales or platform shutdowns, and jurisdiction over decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) that manage some metaverse platforms are critical regulatory uncertainties that continue to deter certain institutional investors requiring high legal predictability.
What role does Artificial Intelligence (AI) play in virtual real estate development?
AI is transforming virtual real estate development by significantly enhancing efficiency and customization. Generative AI tools are now capable of automating the creation of high-fidelity 3D architectural designs and interior layouts based on simple text or image inputs, drastically reducing the time and specialized skill required for construction. Furthermore, AI is crucial for predictive market analysis, using machine learning to forecast demand, optimal pricing, and ideal virtual property location based on complex behavioral metrics. AI also powers intelligent Non-Player Characters (NPCs) and automated management systems, transforming static properties into dynamic, functional business venues that can autonomously manage tasks like customer service and rental agreements, ultimately increasing the utility and investment potential of the digital asset.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager