Microfinance Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 436673 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 245 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Microfinance Market Size
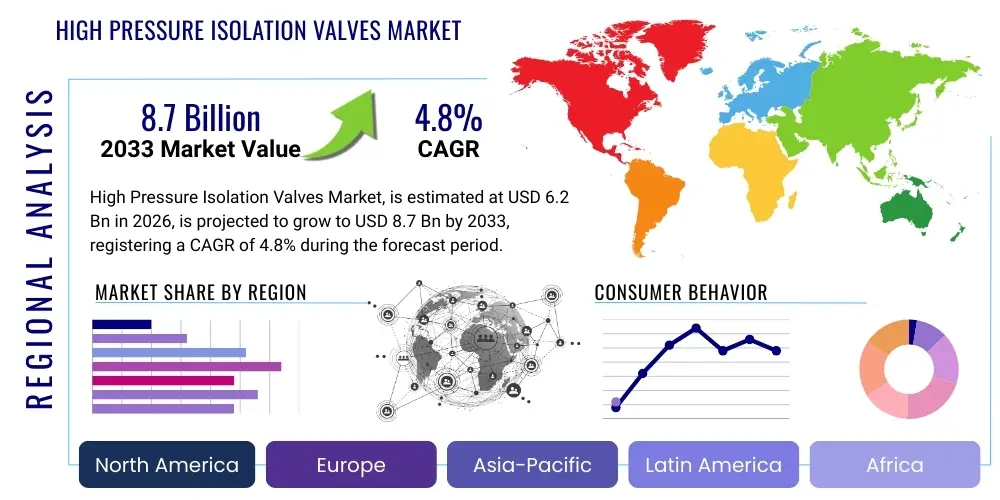
The Microfinance Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 250 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 565 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Microfinance Market introduction
The Microfinance Market encompasses a broad range of financial services, including microcredit, micro-savings, micro-insurance, and payment systems, specifically tailored to low-income clients, vulnerable populations, and micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) that lack access to conventional banking facilities. The core objective of microfinance institutions (MFIs) is poverty alleviation and fostering economic self-sufficiency by providing capital for income-generating activities. This sector has transitioned from a primarily non-profit, donor-driven model to a more commercialized and sustainable structure, driven by the realization that poor individuals are creditworthy and possess strong repayment ethics, particularly within group lending models.
Key applications of microfinance extend across diverse sectors such as agriculture, small-scale manufacturing, retail trade, and personal consumption needs, enabling beneficiaries to stabilize incomes and improve living standards. The products are designed to be flexible, often requiring minimal collateral, and utilize social collateral mechanisms. Benefits include enhanced financial inclusion, empowerment of women (who are often the primary clients), reduction of income inequality, and stimulation of local economic growth. The growing global commitment to sustainable development goals (SDGs) further cements the strategic importance of microfinance as a critical tool for equitable development.
Major driving factors fueling market expansion include supportive regulatory frameworks in developing economies that encourage MFI operations, the increasing penetration of digital technologies (FinTech) simplifying service delivery and reducing operational costs, and the high demand for collateral-free credit among the unbanked and underbanked populations globally. Furthermore, the rising interest from commercial investors and impact funds seeking social returns alongside financial returns is injecting significant capital into the ecosystem, professionalizing operations and expanding the reach of microfinance services across underserved geographies, particularly in Asia Pacific and Sub-Saharan Africa.
Microfinance Market Executive Summary
The Microfinance Market is experiencing robust expansion, characterized by a fundamental shift toward digital service delivery and portfolio diversification. Business trends indicate a strong move away from traditional brick-and-mortar operations toward mobile and agent banking models, which significantly lowers the cost-to-serve clients in remote areas. Commercial banks and specialized FinTech firms are increasingly entering the microfinance space, leveraging advanced data analytics for superior risk assessment and customized product development. This integration of commercial approaches is driving consolidation within the sector, pushing smaller, localized MFIs to either specialize or form strategic partnerships to compete effectively on scale and efficiency, focusing on hybrid models that balance social mission with financial sustainability.
Regionally, Asia Pacific maintains its dominance due to high population density, persistent income inequality, and strong governmental backing for financial inclusion mandates in countries like India, Bangladesh, and Indonesia. However, Latin America and Sub-Saharan Africa are exhibiting the fastest growth rates, catalyzed by rapid mobile penetration and a young, entrepreneurial population eager for financial resources. These regions are becoming testing grounds for innovative delivery channels, including pay-as-you-go models for essential services (e.g., solar power) funded through microfinance structures. The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, necessitating MFIs to navigate complex consumer protection and data privacy rules while maintaining operational agility.
In terms of segment trends, microcredit remains the largest segment, but micro-insurance and micro-savings are gaining traction as clients prioritize resilience against unexpected financial shocks, particularly post-pandemic. Technology-based lending platforms, powered by algorithms and alternative credit scoring, are rapidly displacing traditional group lending methodologies, especially in urban and peri-urban settings where individual financial data is more readily available. The focus on sustainability financing, particularly loans directed towards renewable energy, climate-resilient agriculture, and gender-lens investing, represents a high-growth opportunity segment that aligns with global impact investing standards, driving capital flow into socially and environmentally conscious microfinance portfolios.
AI Impact Analysis on Microfinance Market
Users frequently inquire whether Artificial Intelligence (AI) will fundamentally displace human loan officers or merely augment their capabilities within the microfinance sector. Common concerns revolve around AI's ability to accurately assess the creditworthiness of individuals lacking formal financial histories, the potential for algorithmic bias leading to exclusion of marginalized groups, and the infrastructure required for AI implementation in low-tech environments. Expectations are high regarding AI's potential to dramatically lower operating costs, accelerate loan disbursement, and improve portfolio quality through superior predictive analytics. Users seek confirmation on how AI, coupled with Big Data, can create personalized microfinance products that move beyond standard microcredit offerings, specifically addressing complex financial needs such as seasonal agricultural cycles or fluctuating market demand for small businesses, ensuring that technology scales inclusion rather than creating new barriers.
AI is set to revolutionize microfinance by providing sophisticated tools for risk modeling and customer segmentation. Machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of alternative data, including mobile phone usage, utility payments, and social network activity, to generate highly accurate credit scores for the unbanked population. This capability significantly reduces the reliance on traditional, slow, and expensive manual verification processes. Furthermore, AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are improving customer interaction, offering 24/7 support and personalized financial education, thereby enhancing client retention and overall service quality while freeing up human staff to focus on complex advisory roles and community relationship building.
The adoption of AI also impacts operational efficiency and compliance. AI tools are being deployed for automated fraud detection, monitoring transactional anomalies in real-time to safeguard MFI assets and client funds. In terms of portfolio management, predictive maintenance models powered by AI can forecast potential default rates based on economic indicators and client behavior patterns, allowing MFIs to implement proactive restructuring or collection strategies. While the integration presents challenges related to data privacy and regulatory compliance, the overall trajectory points toward AI becoming an essential operational layer that enables MFIs to scale outreach while maintaining profitability and social mission alignment.
- Automated Credit Scoring: Utilizing machine learning on alternative data sources (telco data, psychometrics) for rapid, bias-mitigated credit decisions.
- Enhanced Risk Modeling: Predictive analytics to anticipate portfolio delinquency and optimize loan pricing and maturity structures.
- Personalized Product Design: AI analyzes individual cash flow patterns to tailor loan repayment schedules and insurance products.
- Operational Efficiency: AI-powered chatbots handle routine client inquiries, streamlining customer service and reducing staff workload.
- Fraud and Compliance Monitoring: Real-time detection of suspicious transactions and automated regulatory reporting to ensure transparency.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Microfinance Market
The Microfinance Market is primarily driven by the imperative of financial inclusion mandated by global development goals, coupled with technological advancements that have drastically lowered the cost of financial service delivery. However, the sector faces significant headwinds from regulatory complexities, market saturation in certain urban areas, and the inherent credit risk associated with lending to low-income populations lacking formalized collateral. Opportunities abound in leveraging FinTech for scale, expanding into high-growth, underserved rural markets, and developing niche products such as climate finance or educational loans. These forces—Drivers, Restraints, and Opportunities—collectively shape the Impact Forces, defining the market's growth trajectory and influencing strategic decisions regarding commercial viability, social outreach, and operational resilience across diverse geographical landscapes.
Drivers: A primary driver is the large global population of unbanked adults, exceeding 1.7 billion, representing a massive latent demand for basic financial services. Governments and central banks across developing nations are actively promoting policies, such as national biometric identification systems and digital payment infrastructures, which create an enabling environment for MFIs to operate efficiently. Furthermore, the rising institutional interest from Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investors and philanthropic organizations provides steady access to capital. The success stories of microfinance in poverty reduction bolster investor confidence, establishing the sector as a proven mechanism for sustainable economic development, thus attracting further commercial funding and partnerships with larger financial entities.
Restraints: Significant restraints include the high operational costs associated with serving remote clients, often referred to as the 'last mile' problem, although digital solutions are mitigating this. Over-indebtedness among clients, stemming from multiple loan stacking or inadequate financial literacy, poses a systemic risk to portfolio quality and regulatory stability. Furthermore, interest rate caps imposed by some governments, intended to protect consumers, often constrain the profitability and sustainability of MFIs, particularly those operating in high-risk zones. The lack of reliable historical data and robust credit bureaus in many target markets makes accurate risk assessment challenging, increasing default probability compared to conventional banking portfolios.
Opportunities: Major opportunities reside in harnessing the power of mobile technology and blockchain for transparent and secure transaction processing, reducing transaction costs and increasing client trust. The development of specialized insurance products—particularly health and crop insurance—that cater specifically to the volatility faced by low-income households presents a lucrative growth avenue. Expanding into cross-border microfinance, facilitating remittances and small trade financing for micro-entrepreneurs involved in global value chains, offers another high-potential area. Finally, strategic collaborations with telecommunications companies and technology providers allow MFIs to quickly bypass infrastructure deficits and rapidly onboard new customers, accelerating market penetration in regions previously deemed inaccessible.
Segmentation Analysis
The Microfinance Market is comprehensively segmented based on three critical axes: services offered (which dictates revenue streams and client resilience tools), delivery channel (which determines operational efficiency and reach), and borrower type (which shapes risk profiles and product tailoring). Analyzing these segments provides strategic insights into which areas exhibit the highest scalability and potential for profitability versus those requiring deep social investment. The shift towards diversified product portfolios, moving beyond simple credit to include savings and insurance, reflects a maturing market focused on comprehensive client welfare and long-term financial health. The accelerating transition to digital and mobile-based channels is redefining accessibility, particularly benefiting rural and underserved populations.
Segmentation by Services includes Microcredit (the largest segment), Micro-savings, Micro-insurance, and Remittance/Payment Services. Microcredit dominates but Micro-insurance is the fastest-growing segment, driven by the need for financial buffers against environmental and health shocks. Segmentation by Delivery Channel distinguishes between traditional Branch-Based Lending and modern Non-Branch Based methods (such as mobile banking, agent networks, and online platforms), with the latter segment experiencing exponential growth due to lower infrastructure costs and improved accessibility. Segmentation by Borrower Type differentiates between Group Lending (social collateral model) and Individual Lending, with Individual Lending gaining prominence in technologically advanced settings where proprietary credit scoring enables personalized assessment.
- By Service Type:
- Microcredit
- Micro-savings
- Micro-insurance
- Remittance and Money Transfer Services
- By Delivery Channel:
- Non-Branch Based (Mobile Banking, Agent Banking, Digital Platforms)
- Branch-Based (Traditional Physical Offices)
- By Borrower Type:
- Group-Based Loans
- Individual Loans
- By End-Use Sector:
- Agriculture and Rural Finance
- Trade and Retail (Micro-enterprises)
- Housing and Home Improvement
- Education and Health
Value Chain Analysis For Microfinance Market
The microfinance value chain begins with upstream activities focused on securing capital, which involves fundraising from impact investors, government grants, commercial banks, and capital markets. Upstream efficiency dictates the operational cost of funds and the subsequent lending rates offered to clients. Key activities here include rigorous due diligence of investors, structuring financial instruments (such as social bonds), and managing liquidity risk to ensure adequate funds are available for disbursement. Strong capital mobilization capabilities are essential for scaling operations and achieving stability, influencing the overall pricing structure and competitive position of the MFI in the lending market.
The core value addition occurs in the operational stage, encompassing loan origination, client assessment, disbursement, and portfolio management. Distribution channels form a critical part of this middle stage, encompassing direct engagement via field officers and indirect engagement through mobile platforms or partnership networks (e.g., utility companies or retail agents). The adoption of digital technologies is rapidly transforming this stage, moving away from labor-intensive manual processes to highly automated underwriting and collection systems. Effective portfolio monitoring, including timely repayment tracking and default management, determines the quality and sustainability of the MFI's lending practices.
Downstream analysis focuses on the final interaction with the client and the long-term impact realized. This involves loan utilization monitoring, offering ongoing financial literacy training, and providing additional supportive services (like micro-insurance or business mentorship). Both direct distribution, via local branches and loan officers who maintain critical social connections, and indirect distribution, through automated digital platforms that offer convenience and speed, play essential roles. The ultimate value delivery is measured not only by repayment rates but also by improvements in client income, asset accumulation, and resilience, which reinforces the MFI's social mission and justifies external investment.
Microfinance Market Potential Customers
The primary potential customers in the Microfinance Market are typically the working poor, individuals and households operating in the informal economy who lack documentation or collateral required by conventional banking institutions. This demographic includes micro-entrepreneurs—market vendors, small farmers, and artisans—who require small injections of capital to purchase inventory, upgrade equipment, or manage cash flow volatility associated with their businesses. A substantial segment comprises rural populations who are geographically marginalized and rely heavily on agriculture, needing seasonal loans for planting and harvesting inputs to secure their livelihoods.
A particularly vital segment of potential customers consists of women entrepreneurs. Historically, women have demonstrated higher repayment rates and tend to utilize loans more effectively for household welfare and business growth. MFIs often prioritize lending to women, leveraging group lending models that foster social accountability and support. Beyond micro-entrepreneurs, potential customers also include low-income wage earners seeking housing loans or finance for essential expenditure like education and healthcare, where traditional banks often deem the loan sizes too small or the risk profiles too high.
Furthermore, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) that have outgrown traditional microfinance but are still too small or risky for large commercial banks represent a growing customer base for specialized "meso-finance" products. This segment, requiring loans slightly larger than typical microcredit, is crucial for job creation and economic diversification. The expansion of digital microfinance channels is opening access to urban youth who are digitally native but financially underserved, offering tailored products like consumption loans or short-term emergency credit accessible entirely via mobile applications.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 250 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 565 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR 12.5% |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Grameen Bank, Compartamos Banco, SKS Microfinance (Bharat Financial Inclusion), BRAC, ASA International, Bandhan Bank, CreditAccess Grameen, FINCA International, Accion International, Kiva, One Acre Fund, MFIC, Opportunity International, ProCredit Holding, Amret Microfinance Institution, Fundación WWB Colombia, ECLOF International, Al Amana Microfinance, BPI Globe BanKo, Equity Bank Group |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Microfinance Market Key Technology Landscape
The Microfinance Market is rapidly adopting digital transformation tools, centralizing around mobile financial services (MFS) as the foundational technology for outreach and transaction execution. MFS allows MFIs to bypass the prohibitive costs of establishing physical branches in remote areas, enabling direct interaction with clients via basic feature phones or smartphones. This shift relies heavily on robust integration with mobile network operators (MNOs) and the use of agent networks for cash in/cash out services. Additionally, cloud computing solutions are crucial for MFIs to manage large client databases efficiently, ensuring data security and scalability without significant upfront capital investment in proprietary hardware. The ability of these platforms to handle massive volumes of micro-transactions securely defines the operational efficiency of modern microfinance.
Beyond basic mobile platforms, advanced analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are the next frontier in the technological landscape. MFIs are leveraging Big Data analytics to process alternative data sources, such as geospatial data, psychometric testing results, and digital footprints, to create proprietary credit scoring models that effectively assess risk for clients with no formal financial history. This AI-driven underwriting process not only accelerates loan approval but also minimizes human bias and standardizes decision-making, significantly enhancing portfolio quality. Furthermore, the incorporation of biometric technology (fingerprint or iris scanning) is increasingly being used for client identification and transaction authentication, particularly in regions with high illiteracy rates, improving security and reducing identity fraud.
The use of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) or blockchain is beginning to emerge as a key technology for improving transparency and efficiency in the microfinance supply chain. Blockchain can provide an immutable record of transactions, reducing operational fraud and facilitating faster, cheaper cross-border transfers and remittances, which are vital for many microfinance clients. Specific technology applications also include specialized software for Field Management Systems (FMS), which allows loan officers to input data, track repayments, and manage client visits in real-time using tablets, thereby streamlining the "last mile" delivery process. This comprehensive digital ecosystem—combining mobile access, cloud storage, AI decisioning, and secure ledger systems—is essential for sustaining the high-growth trajectory of the market.
Regional Highlights
- Asia Pacific (APAC): APAC remains the epicenter of the global microfinance market, dominating in terms of both client outreach and portfolio value. Countries like India, Bangladesh, Indonesia, and the Philippines have deeply entrenched microfinance ecosystems supported by favorable regulatory policies and high levels of entrepreneurship in the informal sector. India, specifically, has witnessed rapid growth driven by the commercialization of MFIs and their transformation into Small Finance Banks (SFBs), leveraging extensive digital infrastructure (e.g., Aadhaar and UPI). The region is characterized by intensive competition and high density of clients, pushing MFIs to continuously innovate in digital channels and rural penetration strategies.
- Latin America (LATAM): The LATAM region, particularly Mexico, Peru, Colombia, and Brazil, presents a highly commercialized microfinance environment. MFIs here often operate with a focus on individual lending and have successfully transitioned to utilizing sophisticated financial technologies, sometimes outpacing other regions in implementing complex credit scoring models. High urbanization rates and significant informal economies drive demand. Challenges include political instability and volatility in local currencies, which necessitate robust risk hedging strategies and diversified funding sources to maintain stability and profitability.
- Africa (Sub-Saharan Africa - SSA): SSA is projected to be the fastest-growing region, driven primarily by exponential mobile money adoption, which provides a ready-made platform for digital microfinance services. Key markets include Kenya, Nigeria, and Tanzania, where collaborations between MFIs and MNOs are standard practice. The focus is heavily skewed towards innovative delivery models, including linking microcredit to productive assets (like solar energy systems or farm equipment) through pay-as-you-go systems. The region struggles with significant infrastructure gaps and lower financial literacy, necessitating greater investment in educational outreach alongside credit disbursement.
- North America and Europe: While not core operational hubs for traditional microcredit focused on extreme poverty, these regions feature niche microfinance markets focused on economic inclusion and social entrepreneurship within developed economies. Services often target immigrants, low-income urban communities, and small businesses requiring seed capital not accessible through conventional banks. The operational models here are highly regulated and often rely on hybrid funding structures, combining government grants, philanthropic donations, and targeted social impact investments, focusing on high-impact local projects rather than mass-market penetration.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): The MEA market is highly diverse. While SSA drives growth, the Middle East segment focuses more on Sharia-compliant microfinance (Islamic microfinance), requiring specialized product structures (such as Murabaha and Musharaka) that adhere to Islamic banking principles prohibiting interest (riba). These institutions emphasize partnership and profit-sharing models. Regulatory harmonization remains a challenge across the heterogeneous MEA landscape, but demand remains high, particularly in post-conflict or economically vulnerable states, making microfinance a crucial tool for reconstruction and stability.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Microfinance Market.- Grameen Bank
- Compartamos Banco
- SKS Microfinance (Bharat Financial Inclusion)
- BRAC
- ASA International
- Bandhan Bank
- CreditAccess Grameen
- FINCA International
- Accion International
- Kiva
- One Acre Fund
- MFIC
- Opportunity International
- ProCredit Holding
- Amret Microfinance Institution
- Fundación WWB Colombia
- ECLOF International
- Al Amana Microfinance
- BPI Globe BanKo
- Equity Bank Group
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Microfinance market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary difference between microfinance and traditional commercial banking?
Microfinance specifically targets low-income, unbanked individuals and micro-entrepreneurs who lack collateral, offering small, customized loans often using social collateral, whereas traditional banking serves clients with established financial histories and collateral requirements.
How is technology currently transforming the delivery channels in microfinance?
Technology, particularly mobile banking and agent networks, is replacing expensive physical branches, enabling MFIs to reach remote populations, reduce operational costs, and utilize digital platforms for faster loan disbursement and collection tracking.
What is the biggest risk facing the sustainability of microfinance institutions (MFIs)?
The primary systemic risk is client over-indebtedness, often caused by poor financial literacy or multiple simultaneous borrowing, which threatens portfolio quality and repayment rates, potentially leading to regulatory intervention.
Which geographical region dominates the global microfinance market share?
Asia Pacific (APAC) holds the dominant share of the microfinance market, driven by high client volumes in nations like India, Bangladesh, and Indonesia, coupled with extensive government support for financial inclusion initiatives.
Are interest rates in microfinance higher than conventional bank loans, and why?
Yes, microfinance interest rates are often higher due to the high operational costs associated with administering very small loans, managing credit risk for uncollateralized borrowers, and serving geographically dispersed, remote clientele.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager