Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 432470 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 248 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market Size
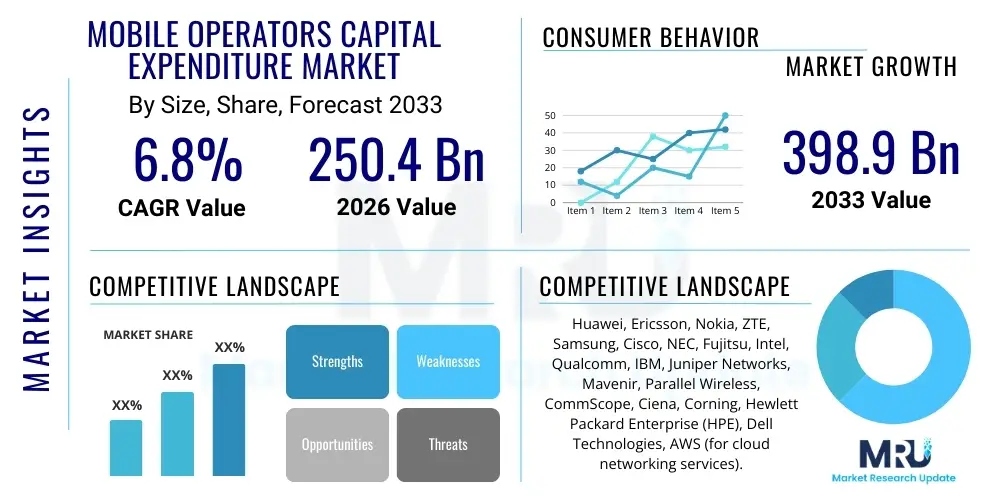
The Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.8% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 250.4 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 398.9 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market introduction
The Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure (CapEx) market encompasses the investments made by cellular network providers globally into physical assets required for the operation and expansion of their networks. This includes spending on infrastructure such as radio access network (RAN) equipment, core network infrastructure, fiber optic backbone, data centers, and specialized software platforms necessary for network orchestration and management. The primary function of CapEx is to enhance network capacity, improve coverage, and deploy new technologies, crucially enabling the transition from 4G/LTE to 5G and future generations, while also supporting the rapidly escalating demand for mobile data traffic stemming from increasing device penetration and widespread adoption of bandwidth-intensive applications.
Major applications driving this CapEx include the large-scale deployment of 5G infrastructure, modernization of existing legacy networks, expansion into underserved rural areas, and investments in cloud-native core architectures that offer greater flexibility and efficiency. These investments are non-negotiable for mobile operators aiming to maintain competitive advantage, improve customer experience, and support emerging enterprise services such as IoT, massive machine-type communications (mMTC), and enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB). Furthermore, the shift towards network virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN) requires significant initial CapEx allocation, paving the way for lower long-term operational expenditures (OpEx).
The principal benefits derived from robust CapEx investment include superior network quality, reduced latency, and higher data throughput, which directly translate into improved customer satisfaction and opportunities for premium service offerings. Key driving factors accelerating market growth include governmental initiatives promoting digital inclusion, increasing competition among service providers necessitating constant technological upgrades, and the structural necessity to handle exponential data growth driven by video streaming, cloud gaming, and industrial automation applications. This continuous cycle of investment ensures that mobile networks remain the foundational platform for global digital transformation.
Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market Executive Summary
The Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure market is defined by aggressive infrastructure expansion, primarily fueled by the global rollout of 5G technology and the strategic pivot toward cloud-native network architectures. Business trends indicate a focus on network sharing agreements (RAN sharing and MOCN) to optimize CapEx efficiency, particularly in mature markets where competitive saturation is high. Furthermore, there is a discernible trend toward Open RAN adoption, aiming to diversify vendor landscapes and reduce reliance on proprietary equipment, though this transition demands substantial initial investment in integration and validation capabilities. Operators are increasingly prioritizing investments in fixed mobile convergence (FMC) assets, blurring the lines between wireline and wireless infrastructure to offer seamless connectivity packages to consumers and businesses.
Regional trends demonstrate distinct investment velocities. Asia Pacific, specifically China, India, and Southeast Asia, dominates CapEx spending due to massive population density, governmental mandates for digital infrastructure build-out, and the aggressive push for 5G industrial applications. North America and Europe maintain high CapEx levels focused on densification, fiber expansion to support small cell backhaul, and the deployment of mid-band and millimeter-wave 5G spectrum. Meanwhile, emerging regions like Latin America and MEA are accelerating investments, often bypassing older generations (2G/3G) to jump directly into 4G and introductory 5G phases, supported by regulatory incentives aimed at closing the digital divide.
Segment trends reveal that spending is heavily concentrated in the Radio Access Network (RAN) segment, which constitutes the largest portion of overall CapEx, driven by the need for new 5G base stations (gNBs) and antenna systems. Following RAN, core network investments are rapidly growing, specifically in software and virtualization infrastructure necessary to manage the complexity and scale of 5G standalone (SA) deployments. Technology-wise, 5G remains the dominant driver, demanding capital allocation not just for physical hardware but also for spectrum acquisition and crucial network planning and optimization tools. This summary underscores a market where CapEx is fundamentally linked to technological evolution and operational efficiency improvements.
AI Impact Analysis on Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market
Common user questions regarding AI's influence on the Mobile Operators CapEx Market frequently center on efficiency gains, predictive maintenance, and the necessary CapEx investment for AI infrastructure itself. Users are primarily concerned with whether AI tools can significantly reduce network planning CapEx by optimizing site selection and spectrum utilization, and if AI-driven operations can decrease future operational spend (OpEx) related to fault detection and network optimization. Key themes revolve around the trade-off: the initial capital outlay required for AI-capable hardware, data lakes, and software licenses versus the long-term benefits derived from proactive network management and reduced physical equipment replacement cycles. The consensus expectation is that AI will shift CapEx allocation away from brute-force physical expansion toward intelligent, software-defined infrastructure.
- AI-driven Network Planning: Optimization algorithms reduce redundant cell site construction, potentially lowering overall RAN CapEx by ensuring optimal coverage and capacity allocation based on real-time data analysis.
- Predictive Maintenance Savings: AI enables proactive identification of equipment failure, minimizing costly emergency replacements and extending the lifespan of existing hardware, thereby optimizing replacement CapEx cycles.
- Software-Defined Network Investment: Significant CapEx shift towards AI software, computational platforms (GPUs/specialized hardware), and data infrastructure required to run complex AI/ML models for network automation and orchestration.
- Enhanced Spectrum Utilization: AI tools maximize spectral efficiency, potentially deferring the need for expensive additional spectrum acquisition or physical network densification, acting as a soft CapEx saver.
- Automation of Core Network Functions: AI simplifies complex core network management and provisioning, leading to CapEx savings on manual labor and specialized proprietary hardware configurations.
- Security Infrastructure CapEx: Increased investment in AI-powered security solutions is required to protect sophisticated, decentralized 5G and IoT networks from advanced cyber threats.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market
The Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure market is primarily driven by the imperative to deploy next-generation wireless technologies, particularly 5G, which necessitates vast investments in new spectrum, infrastructure densification, and core network modernization. Restraints often manifest as regulatory hurdles regarding site acquisition and environmental permissions, high initial costs associated with fiber backhaul deployment, and increasing market pressure from competitors and content providers to reduce connectivity charges, which limits operators' profitability and available capital for reinvestment. Opportunities abound in emerging economies where greenfield network construction is needed, and in specialized enterprise segments (e.g., private 5G networks, smart factory automation) that demand tailored high-performance infrastructure. Impact forces center on the economic cyclicality of technology upgrades, the competitive intensity among equipment vendors, and the critical influence of government policies regarding spectrum allocation and rural broadband mandates.
Segmentation Analysis
The Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market is broadly segmented based on the type of network components acquired, the technology generation being deployed, and the application area within the operator's network architecture. Analyzing these segments provides strategic insights into investment priorities. The Type segmentation distinguishes between physical infrastructure investments, such as active and passive RAN components, and crucial associated services, including network planning, maintenance, and integration services. The Technology segmentation is vital, charting the massive CapEx flow into 5G ecosystems, including mid-band and mmWave infrastructure, compared to sustaining investments in 4G/LTE assets. Lastly, the Application segmentation details where the capital is physically utilized, primarily across the Radio Access Network (RAN), the high-capacity backhaul infrastructure, and the virtualized Core Network responsible for traffic management and control plane functions.
- By Type:
- Infrastructure (Hardware and Software)
- Services (Planning, Optimization, Maintenance)
- By Technology:
- 5G
- 4G/LTE
- Others (Legacy 2G/3G, Fixed Broadband Infrastructure)
- By Application:
- Radio Access Network (RAN)
- Core Network
- Backhaul and Transport
Value Chain Analysis For Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market
The value chain for the Mobile Operators CapEx market begins significantly upstream with component manufacturers, semiconductor fabricators, and specialized software developers who provide the foundational elements like chipsets, antennas, and virtualization software. This upstream segment dictates the pace of innovation and the cost structure of network equipment. Moving mid-stream, the value chain involves major network equipment providers (NEPs) such as Ericsson, Huawei, and Nokia, who integrate these components into fully functional, deployable hardware and software solutions (RAN, core, transport). These NEPs are crucial as they offer not only the physical products but also the comprehensive integration and testing services that precede network rollout.
The core of the market activity resides at the mobile operator level (the customer/buyer), who utilizes direct and indirect distribution channels to acquire the CapEx assets. Direct channels involve large-scale, long-term procurement agreements negotiated directly between the operator and the major NEPs for multi-year network build-out projects. Indirect channels include local system integrators, distributors, and specialized consulting firms, particularly for smaller projects, specialized testing equipment, or regional network upgrades. The choice between direct and indirect channels often hinges on project scale, vendor relationships, and the complexity of the deployment.
Downstream, the impact of CapEx investment is realized by end-users (consumers and enterprises) who benefit from improved services. However, the value chain also extends to managed services providers who take over the ongoing optimization and maintenance (often OpEx rather than CapEx, but intrinsically linked to the initial investment) of the deployed infrastructure. The increasing emphasis on Open RAN shifts some value chain power toward software specialists and away from integrated hardware providers, driving operators to engage more deeply with independent software vendors (ISVs) and hyperscalers for network orchestration and cloud-native functions.
Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market Potential Customers
The primary customers and end-users of the products and services within the Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure market are globally distributed Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs) who are investing in their own physical infrastructure. These customers range from Tier 1 global operators (e.g., Vodafone, AT&T, China Mobile) focusing on large-scale national rollouts and densification projects to smaller regional carriers mandated to cover specific geographical areas. Additionally, governmental telecommunications agencies and state-owned enterprises often act as major purchasers, particularly in developing nations, where infrastructure build-out is a matter of national strategic importance and digital inclusion policy.
A rapidly growing segment of potential customers includes large enterprises and industrial entities focused on deploying Private 5G networks. These private network operators, often in sectors like manufacturing, logistics, mining, and healthcare, are deploying dedicated, localized network infrastructure, requiring CapEx similar to traditional MNOs, albeit on a smaller, highly customized scale. Furthermore, specialized utility companies, smart city initiatives, and transportation authorities (e.g., railways) are increasingly investing capital in network infrastructure tailored for IoT and mission-critical communications, expanding the traditional customer base beyond consumer-facing cellular providers.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 250.4 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 398.9 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR 6.8% |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, Samsung, Cisco, NEC, Fujitsu, Intel, Qualcomm, IBM, Juniper Networks, Mavenir, Parallel Wireless, CommScope, Ciena, Corning, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), Dell Technologies, AWS (for cloud networking services). |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market Key Technology Landscape
The technology landscape governing Mobile Operators CapEx is highly dynamic and characterized by the transition toward software-centric, cloud-native network architectures. The most critical technology investment is in 5G New Radio (NR) equipment, encompassing massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (mMIMO) antennas and small cells that facilitate network densification and high capacity. Operators are heavily investing in millimeter-wave (mmWave) technology in urban centers to deliver multi-gigabit speeds, while sub-6 GHz spectrum dominates wider coverage areas. Crucially, the move from Non-Standalone (NSA) to Standalone (SA) 5G requires significant capital investment in virtualized 5G Core (5GC) components, which rely heavily on Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN) technologies to enable network slicing and ultra-low latency services.
Beyond traditional hardware, a pivotal technology shift driving CapEx is the rise of Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN). Open RAN aims to disaggregate hardware and software components, fostering vendor interoperability and potentially lowering the overall cost of ownership in the long term, although initial integration CapEx is substantial. This transition requires operators to invest capital in specialized servers, cloud infrastructure, and advanced orchestration software. Furthermore, fiber optic backhaul remains foundational; operators allocate considerable CapEx to expanding high-capacity fiber infrastructure necessary to connect 5G small cells and macro sites to the core network, ensuring the massive data generated by 5G can be efficiently transported.
Investment also extends to technologies supporting operational intelligence and security. This includes advanced analytics platforms and Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools integrated into the network management system to automate fault detection, optimize energy consumption, and manage resource allocation dynamically. Security CapEx is focused on robust zero-trust architecture implementations and advanced threat detection systems necessary to secure the increasingly distributed and virtualized 5G network topology. The confluence of these technologies demands higher computational capability within the network, often leading operators to partner or invest capital in edge computing facilities and cloud provider infrastructure integration.
Regional Highlights
Regional variations in CapEx spending reflect differences in technological maturity, regulatory environments, and data consumption rates. Asia Pacific (APAC) stands out as the global leader in CapEx investment, driven primarily by China, which has the world's largest 5G network, and by aggressive rollouts in South Korea, Japan, and increasingly, India, where massive subscriber bases and government impetus for digitalization fuel infrastructure spend. The primary focus in APAC is on rapid 5G coverage expansion, network densification, and integrating 5G into industrial verticals.
North America (NA) represents a mature, high-value market where CapEx is highly concentrated on network densification in metropolitan areas, the deployment of mid-band (C-Band) spectrum, and expanding fiber footprint to support residential broadband and fixed wireless access (FWA). Regulatory auctions for spectrum necessitate significant capital allocation, and leading operators are focusing on deploying sophisticated virtualized cores (5G SA) and experimenting with Open RAN technologies to future-proof their networks.
Europe’s CapEx landscape is characterized by slower, more fragmented rollouts due to varying national spectrum policies and lower market consolidation compared to the US and China. However, investments are accelerating, focused on mandated rural coverage targets and modernization of existing 4G networks while slowly transitioning core components to 5G SA. Regulatory pressure often necessitates joint infrastructure agreements, influencing how and where CapEx is deployed for efficiency.
Latin America (LATAM) and the Middle East and Africa (MEA) are emerging regions experiencing robust CapEx growth. LATAM countries are prioritizing 4G upgrades and initial 5G launches, often focusing on greenfield build-outs. MEA markets, particularly the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations, are leading advanced 5G deployments for smart cities and high-density use cases, while Sub-Saharan Africa is focused on maximizing 4G coverage and investing capital in affordable fixed broadband alternatives to address connectivity gaps.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Highest CapEx growth; driven by China, India, and Southeast Asia; focus on rapid 5G build-out, especially industrial IoT applications, and massive subscriber density management.
- North America: High per-subscriber CapEx; concentrated on mid-band 5G deployment (C-Band), extensive fiber integration for FWA, and sophisticated network virtualization (5G SA).
- Europe: Moderate, accelerating investment; driven by mandatory coverage obligations and infrastructure sharing; increasing focus on network slicing and gradual adoption of Open RAN standards.
- Latin America (LATAM): Growing market; priorities include bridging the rural digital divide, upgrading older infrastructure to 4G/5G, and strategic fiber deployment for backhaul connectivity.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): High growth in GCC countries focusing on cutting-edge 5G services (smart cities); Sub-Saharan Africa CapEx focuses on maximizing 4G reach and establishing foundational backbone networks.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure Market.- Huawei
- Ericsson
- Nokia
- ZTE
- Samsung
- Cisco
- NEC
- Fujitsu
- Intel
- Qualcomm
- IBM
- Juniper Networks
- Mavenir
- Parallel Wireless
- CommScope
- Ciena
- Corning
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
- Dell Technologies
- AWS (for cloud networking services)
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary factor driving current Mobile Operators CapEx spending?
The primary driver is the pervasive, worldwide necessity to deploy and densify 5G networks, requiring extensive capital investment in new Radio Access Network (RAN) equipment, securing valuable spectrum licenses, and upgrading core network infrastructure to support 5G Standalone (SA) capabilities.
How does Open RAN affect the future capital expenditure strategies of MNOs?
Open RAN adoption is expected to flatten long-term CapEx by introducing competition and component modularity. While initial integration and testing require substantial capital outlay, the technology promises reduced vendor lock-in and lower ongoing equipment procurement costs over the network's lifespan, shifting CapEx towards software and integration services.
Which geographical region accounts for the highest Mobile Operators CapEx investment?
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region currently holds the largest share of global Mobile Operators CapEx, primarily driven by massive, state-backed 5G deployments in China and rapid, necessary infrastructure expansion to serve vast populations in markets such as India and Southeast Asia.
What role does virtualization play in influencing CapEx allocation?
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN) compel a shift in CapEx away from proprietary, specialized hardware toward commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) server hardware, virtualization software, and cloud-native platforms, enabling greater flexibility and faster service deployment at the edge and core network.
Are fiber infrastructure investments included in Mobile Operators CapEx, and why are they critical?
Yes, significant CapEx is allocated to fiber optic infrastructure. Fiber is critical as it serves as the high-capacity backhaul connecting 5G macro and small cells to the core network, ensuring the ultra-high speeds and low latency promised by 5G technology can be fully delivered to end-users.
Mobile Operators CapEx Segmentation By Type: Infrastructure vs. Services
The segmentation of Mobile Operators Capital Expenditure by type clearly delineates investment into physical assets (Infrastructure) and non-physical technical expertise required for deployment and integration (Services). The Infrastructure segment typically commands the majority of the CapEx budget. This category encompasses all hardware components essential for network operation, including base stations (gNBs), antennas, switches, routers, transmission equipment, fiber optic cables, and the physical servers required for cloud-native core deployment. Investments in infrastructure are capital intensive and often necessitate large, multi-year procurement contracts with major network equipment providers. The current trend shows a substantial infrastructure CapEx allocation towards densification efforts, requiring a higher volume of smaller cells and dedicated indoor coverage solutions in high-traffic areas.
The Services segment, while often a smaller percentage of the total CapEx compared to hardware, is growing rapidly in complexity and value, especially with the introduction of Open RAN and virtualization. Services CapEx covers crucial activities such as network planning and design, complex systems integration, spectrum harmonization studies, software testing and validation for new core platforms, and professional services required to transition from legacy networks to virtualized architectures. As networks become software-defined and disaggregated, the expertise needed to integrate components from multiple vendors necessitates specialized consulting and implementation services, boosting CapEx in this area. Operators prefer to allocate CapEx to services that accelerate time-to-market for new technologies and ensure optimal performance from expensive infrastructure assets.
The balance between Infrastructure and Services CapEx is dynamic; periods of major technological transition, like the 5G rollout, typically see a concurrent increase in both categories. High Infrastructure spending is required to acquire the hardware (e.g., Massive MIMO antennas), while increased Services spending is necessary for the sophisticated software integration and optimization required to run these highly complex, software-centric networks. Furthermore, operators are increasingly allocating CapEx to secure specialized software licenses for network automation, performance management, and security platforms, which are classified within the Infrastructure/Software component.
- Infrastructure (Hardware and Software) Dominance:
- Includes physical RAN, Core, and Transport hardware.
- Covers virtualization software licenses and specialized servers (COTS).
- Largest CapEx component, driven by 5G equipment procurement volumes.
- Services (Planning, Optimization, Maintenance) Growth:
- Essential for successful 5G and Open RAN deployment, focusing on complex multi-vendor integration.
- Includes project management, network design consultancy, and site acquisition services.
- Rising value due to the need for expert configuration of virtualized and cloud-native networks.
Mobile Operators CapEx Segmentation By Technology: 5G, 4G/LTE, Others
The segmentation by technology vividly illustrates the directional shift in global CapEx priorities. 5G deployment is unequivocally the single largest driver of capital expenditure in the current market forecast period. Investments in 5G span across all necessary assets, including the acquisition of new high-frequency spectrum (mmWave and mid-band), the physical deployment of massive MIMO radios and small cell sites required for density, and the overhaul of the core network to enable 5G Standalone (SA) architecture. This segment of CapEx is characterized by high upfront costs and reflects the operators' competitive need to offer advanced services such as ultra-low latency, enhanced mobile broadband, and dedicated network slicing capabilities for enterprise customers, which are only achievable through native 5G infrastructure.
While 5G dominates headlines, sustaining and upgrading 4G/LTE networks (including LTE-Advanced and Pro) remains a crucial component of CapEx, particularly in regions where 5G penetration is still nascent or geographically limited. Operators must continue to invest capital in 4G infrastructure for two key reasons: capacity augmentation in areas not yet covered by 5G, and as a foundational layer for Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G deployments, where the 4G core still anchors the service. CapEx in this segment focuses on software upgrades to maximize spectral efficiency (e.g., higher-order MIMO for LTE) and tactical small cell deployments to offload congested macro sites, ensuring a smooth transition for the vast majority of subscribers who still rely on 4G-capable devices.
The "Others" segment encompasses investments in legacy technologies (2G/3G) necessary for maintaining basic service obligations in remote areas, though this CapEx is rapidly declining as sunsetting programs are implemented globally. More importantly, this segment also includes significant capital investment in fixed network infrastructure, particularly high-speed Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) and cable infrastructure. Many mobile operators are adopting Fixed Mobile Convergence (FMC) strategies, requiring CapEx to build or acquire fixed network assets to offer bundled services, ensuring robust backhaul for their mobile sites and providing competitive high-speed residential broadband services, thereby diversifying their revenue streams and maximizing asset utilization.
- 5G Dominance:
- Highest investment priority, covering new spectrum licenses, massive MIMO, small cells, and virtualization of the 5G Core.
- Critical for delivering advanced enterprise services (network slicing, IoT).
- Focus shifted from Non-Standalone (NSA) to capital-intensive Standalone (SA) deployments.
- 4G/LTE Maintenance and Upgrade:
- Necessary CapEx for capacity management and coverage sustainment.
- Focuses on LTE-Advanced Pro upgrades and efficient spectrum use.
- Serves as the foundational layer during the transition to complete 5G coverage.
- Others (Fixed/Legacy):
- Declining CapEx for 2G/3G sunsetting programs.
- Crucial CapEx investment in Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) infrastructure supporting Fixed Mobile Convergence (FMC).
- Includes specialized transport and microwave links for challenging geographies.
Mobile Operators CapEx Segmentation By Application: RAN, Core, Backhaul
The segmentation of CapEx by application reveals the physical distribution of capital expenditure within the network architecture. The Radio Access Network (RAN) consistently absorbs the largest share of mobile operator CapEx. The RAN segment includes everything from macro cell towers and base transceiver stations (BTS) to antennas, remote radio units (RRUs), and the specialized software used for signal processing. The enormous expenditure in RAN is driven by the physical requirement to install new equipment for every new generation (5G NR) and the ongoing need for network densification—placing more cells closer together—to handle exponentially increasing data traffic, particularly in dense urban and suburban environments. As networks become software-defined, the CapEx includes investment in Centralized Unit (CU) and Distributed Unit (DU) hardware and virtualization platforms required for vRAN/Open RAN implementations.
The Core Network segment, while historically smaller than RAN CapEx, is experiencing rapid acceleration due to the shift to 5G Standalone (SA). The Core Network is the brain of the mobile network, managing subscriber authentication, mobility, and internet gateway functions. Current CapEx here is largely focused on deploying cloud-native 5GC architectures, requiring significant investment in virtualization infrastructure, containerization platforms (Kubernetes), high-capacity servers, and specialized security gateways. This investment is crucial for enabling features like network slicing and edge computing, which are vital for attracting high-value enterprise clients. The transition to a cloud-native core often requires upfront capital investment in partnerships with hyperscale cloud providers or building private cloud infrastructure.
Backhaul and Transport CapEx links the RAN (cell sites) to the Core Network. This segment includes investment in fiber optic cabling, microwave transmission links, and high-capacity routing equipment. The demand for massive 5G data throughput necessitates extremely high-capacity, low-latency backhaul, making fiber expansion a non-negotiable CapEx item. Operators are spending considerable capital extending the fiber footprint deep into their networks to support not just existing macro sites but also thousands of new small cell deployments that require multi-gigabit connectivity. In challenging or sparsely populated areas, CapEx in high-capacity microwave systems acts as a crucial alternative transport mechanism, ensuring connectivity where fiber deployment is economically unfeasible. Effective backhaul CapEx is foundational to maximizing the performance of both RAN and Core investments.
- Radio Access Network (RAN) Dominance:
- Constitutes the highest percentage of CapEx due to 5G mass deployment and densification requirements (Massive MIMO, Small Cells).
- Includes hardware (antennas, RRUs, basebands) and software licensing for centralized RAN functions.
- Investment in vRAN/Open RAN COTS hardware is a growing CapEx sub-segment.
- Core Network Investment Spike:
- Focus on 5G Core (5GC) modernization, requiring capital for NFV/SDN software and cloud-native server infrastructure.
- Critical for future-proofing services like network slicing and Mobile Edge Computing (MEC).
- Includes security and identity management systems necessary for the decentralized core.
- Backhaul and Transport Foundation:
- Essential CapEx for extending high-capacity fiber optic networks to all 5G sites.
- Includes routers, switches, and microwave links necessary for aggregating and transporting massive data volumes between the RAN and the Core.
- Investment driven by the necessity for low-latency transmission for advanced 5G applications.
The continuous evolution of network technology dictates that mobile operators must maintain a significant CapEx pipeline to remain competitive and meet regulatory demands for coverage and quality. The market demonstrates a shift away from simple hardware acquisition towards sophisticated, software-enabled systems that require specialized integration services. This necessitates a strategic reallocation of capital, favoring modular, efficient, and AI-optimized solutions that can manage the increasing complexity of 5G and future network generations, thereby safeguarding long-term OpEx efficiency through aggressive upfront CapEx investment.
In summary, the Mobile Operators CapEx market is highly inelastic, driven by essential technological cycles (5G deployment) and structural demand growth (data consumption). Operators leverage these capital investments not just for connectivity, but to establish platforms for future revenue streams in areas like private networks, automotive connectivity, and industrial automation. Regional disparities reflect economic capacity and spectrum availability, while segmentation analysis highlights the overwhelming priority placed on the physical and software components of the Radio Access Network and the vital transport infrastructure supporting it.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
