mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 437265 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 246 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market Size
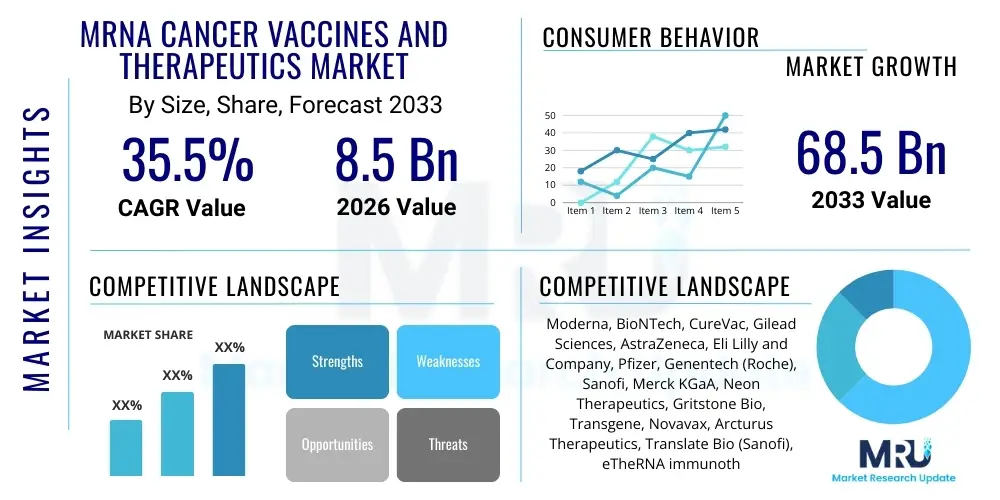
The mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 35.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at $8.5 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach $68.5 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market introduction
The mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market represents a paradigm shift in oncology, moving away from traditional treatments toward highly specific, immune-modulating approaches. Messenger RNA (mRNA) technologies leverage the body’s cellular machinery to produce specific tumor antigens, thereby activating a robust and targeted cytotoxic T-cell response against cancer cells. These therapies are broadly categorized into prophylactic (preventative, often targeting viruses linked to cancer) and therapeutic (treatment-oriented, targeting existing tumors). The inherent flexibility and speed of development associated with mRNA platforms—as validated during the recent global health crisis—make them exceptionally well-suited for personalized oncology, where treatments must rapidly adapt to individual patient tumor profiles and neoantigens.
Major applications of mRNA cancer vaccines span solid tumors, hematological malignancies, and increasingly, minimal residual disease (MRD) settings. These applications benefit immensely from the platform’s capacity to encode multiple antigens simultaneously, creating a multi-pronged attack that helps overcome tumor heterogeneity and escape mechanisms. Furthermore, the technology enables the rapid manufacturing of individualized treatments, a crucial capability for neoantigen-specific vaccines. Unlike DNA vaccines or protein-based immunotherapies, mRNA bypasses the need for nuclear entry, reducing concerns regarding genomic integration and enhancing the overall safety profile, driving higher adoption rates in critical patient populations globally.
Driving factors for this accelerated market expansion include the sustained high incidence of various cancer types globally, coupled with significant advancements in bioinformatics and sequencing technologies that enable precise neoantigen identification. Pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms are investing heavily in improving delivery systems, primarily lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), to enhance the stability, efficacy, and targeted delivery of the mRNA payloads to dendritic cells and lymph nodes. The clinical success of early-stage trials, particularly in melanoma and pancreatic cancer, is generating substantial momentum, prompting increased regulatory fast-tracking and venture capital funding into the ecosystem, positioning mRNA therapeutics as foundational to the future standard of care in oncology.
mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market Executive Summary
The mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market is poised for exponential growth, driven by unprecedented technological maturation and a strong investment pipeline focused on personalized medicine. Current business trends indicate a critical shift toward strategic partnerships between large pharmaceutical entities experienced in clinical development and nimble biotech firms specializing in proprietary mRNA formulation and delivery technologies, particularly around enhanced LNP systems and novel adjuvant designs. The operational focus remains heavily centered on optimizing thermostability to overcome existing cold chain logistics restraints, which currently pose significant hurdles to widespread global accessibility, particularly in developing economies. Furthermore, companies are prioritizing Phase II and Phase III trials combining mRNA vaccines with established checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs), seeking synergistic effects that promise significantly improved patient outcomes compared to monotherapies.
Regional trends highlight North America, specifically the United States, as the dominant market leader, accounting for the largest share due to robust infrastructure, extensive R&D spending, and a favorable regulatory environment that supports rapid clinical translation. Europe follows closely, benefiting from strong academic research institutions and public health initiatives promoting innovative cancer treatments. However, the Asia Pacific region is anticipated to demonstrate the highest CAGR, primarily fueled by massive, untapped patient populations, improving healthcare spending, and emerging local manufacturing capabilities seeking to replicate the success of Western platforms. Regulatory harmonization across key global regions remains a critical determinant of successful, rapid commercialization and market penetration.
Segmentation trends reveal that therapeutic vaccines targeting solid tumors—such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), breast cancer, and colorectal cancer—dominate the application segment, reflecting the high prevalence and significant unmet need in these areas. By product type, personalized neoantigen vaccines, while highly complex and costly, are expected to command premium pricing and significant growth due to their superior specificity and potential for long-term durable responses. Conversely, off-the-shelf or shared-antigen vaccines offer a scalable solution for broader patient populations and represent a crucial component of future accessible oncology care. The end-user segment is highly concentrated, with specialized oncology centers and hospitals being the primary purchasing entities, requiring substantial specialized infrastructure for administration and monitoring.
AI Impact Analysis on mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market
User queries regarding the intersection of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the mRNA Cancer Vaccines market frequently center on how AI can accelerate target identification, optimize manufacturing processes, and personalize treatment protocols. Users are primarily concerned with whether AI can reliably predict the immunogenicity and specificity of neoantigens derived from complex tumor mutational data, thereby dramatically reducing the failure rate and development timelines of novel candidates. There is also significant interest in AI's role in refining the physical chemistry of the vaccine formulation, specifically optimizing the design of Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) for better stability, targeted delivery, and lower systemic toxicity. Key expectations involve leveraging machine learning to analyze vast patient databases and genomic profiles to identify biomarkers predictive of treatment response, ensuring maximum therapeutic benefit for specific patient subgroups.
The application of AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, is revolutionizing the preclinical phase of mRNA vaccine development. By processing high-throughput sequencing data and comparing patient tumor profiles against healthy tissue, AI tools can rapidly and accurately sift through thousands of potential targets to nominate the most immunogenic neoantigens for inclusion in a personalized vaccine construct. This computational efficiency reduces the experimental burden and substantially decreases the time required to progress from biopsy to manufactured drug. Furthermore, AI contributes significantly to predicting potential off-target effects and assessing the stability of the transcribed mRNA sequence, leading to higher quality, safer, and more effective vaccine candidates entering clinical trials.
Beyond discovery, AI is proving transformative in streamlining complex manufacturing processes governed by strict regulatory standards. Predictive maintenance models minimize downtime in the advanced bioreactors used for in vitro transcription (IVT) and LNP encapsulation. Additionally, generative AI can optimize the coding sequence of the mRNA itself—codon optimization—to maximize protein expression within the host cell, thereby boosting the therapeutic payload without increasing the overall dosage. The integration of AI into clinical trial design, managing patient recruitment based on predicted response profiles, and analyzing real-world evidence data sets are critical steps that will drive down the cost and shorten the duration of the regulatory approval pathway for future mRNA cancer therapeutics, solidifying its role as an indispensable tool in the market.
- AI accelerates neoantigen identification and prioritization based on predicted immunogenicity and specificity.
- Machine learning optimizes mRNA sequence design for enhanced protein expression and stability (codon optimization).
- Deep learning models facilitate the rational design and optimization of Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems.
- AI enhances clinical trial efficiency by predicting patient responders and optimizing inclusion criteria based on genomic data.
- Predictive analytics are used for quality control and process optimization in advanced biomanufacturing facilities.
DRO & Impact Forces Of mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market
The market trajectory is primarily propelled by strong Drivers (D) related to therapeutic potential, while facing significant Restraints (R) concerning logistics and cost, leading to compelling Opportunities (O) in combination therapies and manufacturing innovation. The primary driver is the demonstrable speed and flexibility of the mRNA platform, allowing for rapid development cycles essential for personalized cancer treatments where time is often life-critical. Complementary drivers include substantial public and private funding directed toward oncology research and the increasing regulatory support, including breakthrough designations and fast-track approvals granted by agencies such as the FDA and EMA. The high unmet medical need in advanced or treatment-refractory cancers further accelerates the adoption of these innovative therapies, as existing standards of care often yield insufficient durable responses. This potent combination of technological readiness and clinical demand creates a strong upward pressure on market valuation and growth.
Significant restraints challenge the immediate and widespread commercial viability of mRNA cancer vaccines. The primary bottleneck is the requirement for stringent ultra-low temperature storage and distribution (cold chain logistics), necessary to maintain the integrity of the fragile mRNA molecule and its LNP delivery vehicle. This limits accessibility, particularly in regions with underdeveloped infrastructure, escalating operational costs significantly. Furthermore, the high initial cost of production for personalized neoantigen vaccines, stemming from individualized sequencing, synthesis, and manufacturing processes, restricts broad patient access and places economic pressure on healthcare systems. Regulatory complexity, particularly the evolving guidelines for novel delivery systems and combination products, also presents hurdles, requiring continuous adaptation by developers.
These challenges simultaneously create vital opportunities for strategic market growth and innovation. The most significant opportunity lies in the synergistic potential of combining mRNA vaccines with established immunotherapies, such as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, which often converts "cold" tumors into "hot" tumors receptive to immune attack. Investment in advanced formulation technologies (e.g., lyophilization, novel buffer systems) offers a chance to mitigate cold chain dependence, expanding geographic reach. Impact Forces shaping the competitive landscape include intense intellectual property disputes over foundational LNP technology, necessitating careful licensing and partnership strategies. Additionally, public perception and trust, heavily influenced by the success of infectious disease vaccines, exert a positive impact force, supporting broader patient acceptance and clinical trial enrollment for oncology applications, pushing the industry towards sustained innovation and market maturity.
Segmentation Analysis
The mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market is intricately segmented based on several critical parameters, providing granularity into the evolving product mix and end-user adoption patterns. Key segmentation criteria include the type of vaccine (personalized vs. off-the-shelf), the application (various cancer types), and the end-user setting (hospitals, research institutes). Understanding these segments is crucial for strategic planning, as personalized neoantigen vaccines, while currently representing a smaller volume, command the highest average selling price and require specialized manufacturing infrastructure, contrasting sharply with the scalability potential of shared-antigen, off-the-shelf products targeting broader populations. The predominance of therapeutic vaccines over prophylactic vaccines currently defines the landscape, although prophylactic segments targeting HPV or Hepatitis B-related cancers show growing promise.
The application segmentation is particularly dynamic, with strong growth observed in segments related to solid tumors that exhibit high tumor mutational burden (TMB), making them excellent candidates for neoantigen targeting. Melanoma, recognized for its sensitivity to immunotherapy and its high mutational load, currently leads the application segment, serving as a critical testing ground for the newest personalized vaccine candidates. However, significant R&D efforts are rapidly shifting focus toward prevalent and highly challenging tumors like pancreatic, ovarian, and colorectal cancers, where existing treatments are often ineffective, promising substantial future market displacement. The ability of the mRNA platform to rapidly prototype and test new antigen combinations allows for accelerated exploration across numerous cancer types simultaneously.
Further analysis of the end-user segmentation reveals a market heavily concentrated within specialized clinical settings. Academic research institutions and Comprehensive Cancer Centers (CCCs) are major early adopters due to their capacity for complex genomic sequencing, access to advanced manufacturing capabilities, and expertise in managing complex immunotherapy regimens. While large hospitals and private clinics constitute the largest overall volume of patient treatments, the early stage of the market means that the majority of clinical experience and infrastructural investment remains centralized. Future market expansion depends heavily on the successful decentralization of administration and the establishment of robust, standardized clinical guidelines across various oncology care providers, facilitating smoother integration into standard treatment protocols.
- Type:
- Personalized Neoantigen Vaccines
- Off-the-Shelf (Shared Antigen) Vaccines
- Application:
- Solid Tumors (Melanoma, NSCLC, Colorectal Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Others)
- Hematological Malignancies (Leukemia, Lymphoma)
- End-User:
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Academic & Research Institutions
- Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies
Value Chain Analysis For mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market
The value chain for mRNA cancer vaccines is complex and highly specialized, beginning with intensive upstream activities focused on drug design and material sourcing. The initial stage involves bioinformatics and genomic sequencing for personalized approaches, or extensive target validation for shared-antigen vaccines, followed by the procurement of critical raw materials. Key upstream components include high-purity DNA templates for in vitro transcription (IVT), specialized enzymes (e.g., T7 RNA polymerase), and critically, highly defined lipid components necessary for the formulation of stable and effective Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs). The quality and consistency of these upstream inputs directly dictate the stability, yield, and immunogenicity of the final therapeutic product, necessitating stringent quality assurance protocols and reliance on a limited number of specialized suppliers.
The central phase of the value chain is characterized by highly technical manufacturing and formulation processes. This involves the enzymatic synthesis of the mRNA molecules via IVT, followed immediately by the precise encapsulation of the fragile mRNA payload within the LNP delivery vehicle, typically through microfluidic mixing techniques. This manufacturing step is capital-intensive and requires specialized Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) facilities designed to handle sterile, high-purity biological products, often operating under ultra-low temperature constraints. Quality control testing, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency in terms of potency, purity, and particle size, consumes a significant portion of this central phase, reflecting the novel and sensitive nature of the drug substance and drug product.
Downstream activities focus heavily on distribution, logistics, and patient administration. Given the mandatory ultra-cold storage requirements, the distribution channel relies on highly specialized logistics partners equipped with robust cold chain management systems capable of maintaining temperatures typically ranging from -60°C to -80°C until the point of care. Direct distribution models, where the manufacturer controls the supply chain to maintain integrity, are common. The indirect distribution channel involves specialized distributors authorized to handle temperature-sensitive therapeutics. Ultimately, the product reaches the end-user, primarily specialized oncology centers, where highly trained clinical staff are required for handling, thawing, and administering the vaccine, concluding the complex journey from gene sequence to therapeutic intervention.
mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market Potential Customers
The primary customer base for mRNA cancer vaccines and therapeutics consists of specialized oncology centers and large, integrated hospital systems that possess the necessary infrastructure and expertise to deploy advanced immunotherapy treatments. These institutions are the direct purchasers of the therapeutic product and require significant investment in ultra-low temperature freezers and specialized pharmacy handling protocols. Their purchase decisions are heavily influenced by clinical efficacy data from Phase III trials, regulatory approval status, and the financial viability of integrating high-cost personalized therapies into their existing treatment pathways. Comprehensive Cancer Centers (CCCs), especially those affiliated with academic institutions, are early and high-volume adopters due to their involvement in clinical research and access to specialized patient populations suitable for cutting-edge treatments.
Secondary but highly influential customers include governmental health agencies and third-party payers, which ultimately determine market access and patient reimbursement rates. While not the direct users of the product, their purchasing power, particularly in nationalized healthcare systems (like in Europe), dictates the commercial success and volume uptake of the vaccines. Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies themselves act as significant customers when acquiring intellectual property, manufacturing capabilities, or when engaging in research collaborations, specifically purchasing reagents, manufacturing services, and analytical technologies related to mRNA and LNP production. This highlights a B2B component within the customer ecosystem focused on enabling future development.
Furthermore, specialized research institutes and academic laboratories focused on immunology and tumor microenvironment studies constitute a niche, yet critical, customer segment. These entities purchase small volumes of investigational or non-GMP grade mRNA constructs and LNPs for preclinical research, mechanism-of-action studies, and platform optimization. The clinical research segment, encompassing Contract Research Organizations (CROs) managing large-scale trials, also represents a temporary customer base, driving demand for clinical-grade material production. However, the sustainable, long-term market valuation is predominantly anchored to the successful integration and routine deployment of approved vaccines within mainstream hospital and specialized oncology practices globally.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | $8.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | $68.5 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR 35.5% |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Moderna, BioNTech, CureVac, Gilead Sciences, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly and Company, Pfizer, Genentech (Roche), Sanofi, Merck KGaA, Neon Therapeutics, Gritstone Bio, Transgene, Novavax, Arcturus Therapeutics, Translate Bio (Sanofi), eTheRNA immunotherapies, Argos Therapeutics, VaxEquity, Tiba Biotechnology |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market Key Technology Landscape
The technological backbone of the mRNA Cancer Vaccines market is centered around optimizing the three core components: the mRNA molecule itself, the delivery vehicle, and the manufacturing process. Advanced technologies for sequence design and optimization, specifically Codon Optimization Algorithms, are critical for maximizing the expression level and duration of the encoded antigen within the patient’s cells, ensuring a potent immune response. Furthermore, the incorporation of modified nucleosides (e.g., N1-methylpseudouridine) is a foundational technological advancement used to suppress innate immune recognition of the foreign RNA, thereby reducing inflammation and increasing translational efficiency. These molecular modifications are essential for enhancing the therapeutic index and ensuring the safety profile of the vaccine products currently under clinical investigation.
The most defining technological challenge and area of intense innovation is the delivery system, predominantly relying on Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs). Current LNP technology involves sophisticated formulations that protect the fragile mRNA from enzymatic degradation in the bloodstream and facilitate targeted uptake by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), especially dendritic cells, in the lymph nodes. Continuous advancements are focusing on engineering novel ionizable lipids that offer improved endosomal escape—a critical step for the mRNA to reach the cytoplasm and initiate protein synthesis—without inducing high systemic toxicity. Emerging delivery modalities, such as polymer-based nanoparticles, exosomes, and self-amplifying RNA (saRNA) systems, are also gaining traction, promising lower dosing requirements and potentially greater thermostability compared to standard LNP formulations, thereby addressing key logistical constraints.
In terms of manufacturing, the key technological focus is the transition from batch production to continuous manufacturing systems utilizing microfluidics. Microfluidic mixing ensures highly reproducible and precisely controlled encapsulation of the mRNA into LNPs, which is vital for maintaining uniformity and stability across large commercial batches. Advanced quality control technologies, including high-throughput sequencing and automated analytical methods, are required to rapidly verify the integrity and purity of the synthetic mRNA and the LNP structure. Overall, the market's progression is inextricably linked to success in engineering more stable, highly expressible, and efficiently targeted mRNA constructs that can withstand the rigors of commercial logistics and reliably activate the patient’s immune system upon administration.
Regional Highlights
North America maintains its position as the dominant region in the mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market, primarily driven by the United States. This dominance is attributable to the presence of leading biotechnology hubs (e.g., Boston, San Diego), massive governmental and private investment in oncological research, and a highly competitive ecosystem fostering rapid innovation. The region benefits from a streamlined regulatory pathway for innovative therapies, such as the FDA’s regenerative medicine advanced therapy (RMAT) designation, facilitating accelerated clinical trials and market access for promising candidates. High healthcare expenditure and sophisticated patient infrastructure capable of handling personalized medicine protocols further solidify North America's market leadership and R&D concentration.
Europe represents the second-largest market, characterized by strong academic foundations in immunology and genomics, particularly in Germany, the UK, and Switzerland. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) actively supports advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs), providing regulatory clarity that encourages development and commercialization. However, market penetration can be slower than in the US due to fragmented national reimbursement systems and stringent health technology assessment (HTA) requirements focused on cost-effectiveness. Despite these hurdles, strategic public-private partnerships, often involving European biotech firms that pioneered mRNA technology, ensure Europe remains a critical location for both clinical trials and advanced manufacturing capabilities.
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region is projected to register the fastest growth, driven by an increasing incidence of cancer across densely populated countries like China, Japan, and India, coupled with rapidly modernizing healthcare infrastructure and increasing affordability. While currently dependent on Western technologies, several APAC nations are heavily investing in localized mRNA production capacity and actively seeking collaborations for technology transfer, aiming to serve their vast patient populations and reduce reliance on expensive imports. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa (MEA) currently hold smaller market shares, but increasing awareness, improved health equity initiatives, and strategic partnerships aiming to overcome cold chain limitations present promising, long-term expansion opportunities in these emerging markets.
- North America: Dominant market share due to high R&D investment, leading biotech presence, and favorable FDA regulatory pathways for personalized therapies. The U.S. is the primary innovation driver.
- Europe: Second-largest market, supported by strong academic research (Germany, UK) and foundational mRNA technology expertise. Focus on establishing accessible reimbursement models.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Highest projected CAGR, fueled by rising cancer prevalence, increasing healthcare infrastructure spending, and growing local manufacturing capacity in China and Japan.
- Latin America (LATAM) & Middle East and Africa (MEA): Emerging markets facing logistical constraints but showing increasing demand and strategic government investments aimed at improving access to advanced oncology treatments.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics Market.- Moderna, Inc.
- BioNTech SE
- CureVac N.V.
- Gritstone Bio, Inc.
- Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- AstraZeneca PLC
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Pfizer Inc.
- Genentech (Roche Group)
- Sanofi S.A.
- Merck KGaA
- Neon Therapeutics (a subsidiary of BioNTech)
- Transgene SA
- Novavax, Inc.
- Arcturus Therapeutics Holdings Inc.
- Translate Bio (Sanofi)
- eTheRNA immunotherapies NV
- Argenx SE
- VaxEquity
- Tiba Biotechnology
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the mRNA Cancer Vaccines and Therapeutics market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What differentiates personalized mRNA cancer vaccines from off-the-shelf versions?
Personalized vaccines are custom-made for an individual patient based on sequencing their unique tumor mutations (neoantigens), requiring rapid, complex manufacturing. Off-the-shelf vaccines target shared, common tumor antigens expressed across many patients, offering greater scalability and accessibility but potentially less specific immune activation.
What role do Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) play in mRNA cancer therapy delivery?
LNPs are critical delivery vehicles that encapsulate and protect the fragile mRNA molecule from degradation in the bloodstream. They facilitate the targeted uptake by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and ensure efficient release of the mRNA into the cytoplasm, which is necessary for the subsequent production of the targeted tumor antigen.
How significant are cold chain logistics as a constraint for this market?
Cold chain logistics represent a major market restraint, requiring mandatory ultra-low temperature storage (often -80°C) to maintain the integrity of the mRNA and LNP formulation. This requirement significantly increases distribution complexity and cost, limiting accessibility in regions lacking specialized infrastructure, although stabilization technologies are rapidly emerging.
Which cancer type is currently leading the development and clinical trials for mRNA vaccines?
Melanoma currently leads the application segment in clinical trials for mRNA cancer vaccines. Melanoma's high tumor mutational burden (TMB) makes it particularly susceptible to neoantigen-targeted immunotherapy, demonstrating strong initial efficacy and serving as a proof-of-concept for personalized mRNA therapeutic platforms.
How does the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) benefit mRNA vaccine development?
AI significantly enhances development by rapidly identifying and prioritizing the most effective neoantigens from complex genomic data, optimizing the mRNA sequence for maximum protein expression (codon optimization), and accelerating the rational design of improved LNP delivery systems, thereby shortening the discovery-to-clinic timeline.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
