Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 432759 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 253 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market Size
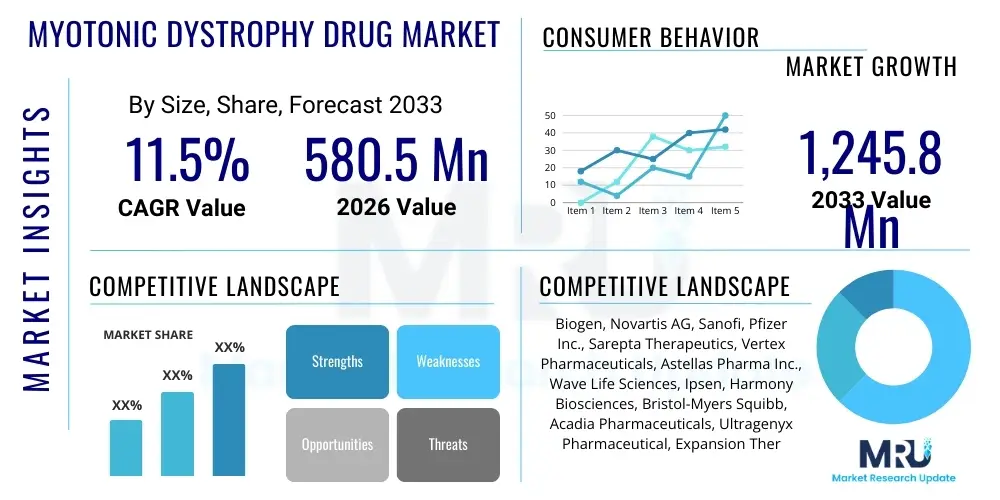
The Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at $580.5 Million in 2026 and is projected to reach $1,245.8 Million by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market introduction
The Myotonic Dystrophy (DM) Drug Market encompasses therapeutic agents aimed at treating Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1) and Type 2 (DM2), which are debilitating, multi-systemic genetic disorders characterized by progressive muscle wasting, weakness, myotonia, and various non-muscular complications including cardiac defects, cataracts, and cognitive impairment. DM1, caused by the expansion of CTG trinucleotide repeats in the DMPK gene, is the most prevalent adult-onset muscular dystrophy, driving significant demand for effective disease-modifying treatments. Current palliative care largely focuses on symptom management, utilizing medications like mexiletine for myotonia or cardiac drugs for associated arrhythmias, but the critical unmet need lies in developing therapies that target the underlying genetic defect, specifically the toxic RNA gain-of-function mechanism. The market is transitioning from symptomatic treatments toward innovative therapeutic modalities, particularly those involving genetic and oligonucleotide-based technologies.
The core products currently driving market revenue are focused on managing the severe phenotypic manifestations of the disease, such as excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and myotonia. However, the market structure is rapidly evolving due to robust investment in preclinical and clinical-stage development focusing on targeted disease modification. This shift is primarily centered around antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and small molecules designed to interfere with the toxic CUG or CCUG repeat expansions responsible for sequestering critical splicing factors, leading to widespread downstream effects. The therapeutic pipeline includes agents aimed at restoring normal splicing patterns (e.g., targeting MBNL protein release) or directly degrading the toxic RNA transcripts. The inherent complexity of DM, involving multi-organ system deterioration and variable onset and severity, necessitates diverse therapeutic approaches, fueling significant R&D spending by pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms specializing in rare diseases.
Major applications for Myotonic Dystrophy drugs extend beyond mere muscle function improvement, encompassing crucial domains such as cognitive support, cardiac stability, and endocrine management, reflecting the systemic nature of the disease. The driving factors for market acceleration include a growing understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of DM, successful preclinical validation of targeted gene therapies, increasing patient advocacy demanding definitive treatments, and favorable regulatory pathways (such as Orphan Drug Designation) that expedite the development and approval of treatments for rare diseases. Furthermore, the rising global prevalence of DM, coupled with improved diagnostic capabilities leading to earlier identification, is expanding the addressable patient population, making this niche market increasingly attractive for high-value drug development investments, particularly in genetically targeted treatments designed to halt or reverse disease progression.
Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market Executive Summary
The Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market is currently characterized by intense pipeline innovation, shifting focus from generalized symptomatic relief to targeted, disease-modifying mechanisms, primarily utilizing advanced genetic technologies. Key business trends indicate strong partnership formation between large pharmaceutical companies and specialized biotech firms possessing expertise in antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) and small molecule splicing modulation platforms. The competitive landscape is heating up as several candidates progress through late-stage clinical trials, with commercialization success hinging on demonstrated efficacy in slowing or reversing key clinical endpoints like muscle strength and function, fatigue, and cardiac conduction abnormalities. Furthermore, valuation models in this rare disease sector heavily rely on peak sales projections driven by ultra-premium pricing strategies justified by the high unmet need and orphan status, leading to substantial investment despite the relatively small patient pool compared to common chronic diseases.
Regionally, North America, particularly the United States, maintains market dominance, driven by robust funding for rare disease research, a high concentration of specialized clinical trial centers, expedited FDA regulatory processes (including Fast Track and Breakthrough Therapy Designations), and high willingness-to-pay among sophisticated payer systems for innovative genetic therapies. Europe follows as a crucial market, though regulatory hurdles and pricing negotiations across different member states, managed by agencies like the European Medicines Agency (EMA), often lead to slower market access compared to the US. Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, stimulated by increasing awareness, improving healthcare infrastructure, and the recognition of the need to address the prevalence of DM in populous nations, though the commercial success here will depend significantly on local manufacturing capabilities and insurance coverage expansion.
Segment trends reveal that the Disease-Modifying Agent segment, especially those leveraging Oligonucleotides and Gene Therapy, is poised for explosive growth and is expected to overtake traditional symptomatic treatments in market share post-approval of the first targeted therapeutic. Within the Indication segment, DM Type 1 (DM1) dominates development efforts due to its higher prevalence and severity, receiving the lion's share of research funding. However, increased understanding of the distinct, though mechanistically similar, molecular pathology of DM Type 2 (DM2) is starting to attract focused development efforts. Distribution channel optimization is also becoming critical, with hospital pharmacies and specialized infusion centers being essential for the delivery of anticipated biologic and genetic therapies, contrasting with the retail pharmacy pathway used for existing small molecule symptom management drugs.
AI Impact Analysis on Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market
User queries regarding the impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market frequently revolve around accelerating drug discovery, optimizing clinical trial design, and personalizing treatment approaches for this genetically complex disease. Key themes emerging from these inquiries include the potential for AI algorithms to quickly sift through vast genomic and transcriptomic datasets to identify novel therapeutic targets, particularly focusing on the toxic RNA mechanism and associated downstream pathways that lead to multi-systemic pathology. Concerns often touch upon the validation and interpretability of AI-generated insights, ensuring that models accurately predict patient response given the heterogeneity of DM presentation (variable age of onset, severity of myotonia vs. fatigue), and managing the high computational cost required for handling large-scale patient registry and deep phenotyping data necessary for robust machine learning applications in a rare disease context.
AI is already demonstrating immense value in the early stages of drug development by streamlining the hit-to-lead process. Machine learning models can predict the binding affinity and toxicity of small molecules or the efficacy and stability of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) targeting the expanded CUG repeats in the DMPK gene. This capability drastically reduces the time and expense associated with traditional wet lab screening, accelerating the identification of promising candidates that can selectively engage the toxic RNA species without causing significant off-target effects. Furthermore, natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLMs) are being deployed to analyze disparate biomedical literature, patents, and internal research data to uncover previously unrecognized mechanistic connections between the genetic mutation and the systemic symptoms (e.g., cardiac defects or insulin resistance), thereby illuminating new, highly specific drug targets beyond the primary splicing defects.
In clinical development and patient management, AI promises to revolutionize trial execution and diagnostic speed. Computational tools are being used to analyze complex biomarkers, such as quantitative muscle strength measures, MRI muscle fat fraction analysis, and electrophysiological readings, enabling researchers to define more sensitive and objective endpoints that capture meaningful clinical change, a persistent challenge in DM trials. Moreover, AI-driven predictive modeling can optimize patient stratification for clinical trials, ensuring that the right patient subpopulation receives the appropriate experimental therapy, thereby increasing statistical power and reducing overall trial duration. Ultimately, the application of AI, coupled with remote monitoring technologies, is paving the way for personalized medicine in Myotonic Dystrophy, allowing clinicians to adjust dosing or therapeutic strategy based on real-time, AI-interpreted data reflecting individual disease progression and response patterns.
- Accelerated identification of small molecule modulators targeting CUG repeat toxicity via deep learning algorithms.
- Optimization of antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) design parameters (e.g., backbone chemistry, target binding site selection) using predictive AI models.
- Enhanced interpretation of multi-omics data (genomics, proteomics, transcriptomics) to elucidate secondary disease pathways in DM1 and DM2.
- Improved diagnostic accuracy and speed through automated analysis of muscle biopsies, MRI scans, and electromyography (EMG) data.
- AI-driven selection of optimal clinical trial sites and identification of eligible patients based on predictive models derived from patient registries and Electronic Health Records (EHRs).
- Development of digital biomarkers and predictive tools to monitor disease progression and treatment response remotely, enhancing trial efficiency and patient care.
- Refinement of personalized dosing strategies based on genetic background and real-time pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) data interpretation using machine learning.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market
The dynamics of the Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market are shaped by powerful Drivers, inherent Restraints, and significant Opportunities, which together constitute the primary Impact Forces determining market trajectory. A major Driver is the critically high unmet medical need, as currently available treatments are purely symptomatic, failing to address the fundamental genetic pathology of the disease, leading to devastating long-term outcomes for patients. This critical gap incentivizes substantial investment in high-risk, high-reward disease-modifying therapies, particularly in the oligonucleotide and gene therapy space. The increasing global awareness of rare diseases, coupled with robust financial and regulatory support from major governmental bodies (e.g., FDA, EMA) via mechanisms like Orphan Drug Designation and priority review, significantly reduces commercialization risk and accelerates development timelines, acting as a powerful market catalyst. Furthermore, the elucidation of the molecular mechanism—the toxic RNA gain-of-function—provides clear, druggable targets, inspiring confidence among developers.
However, the market faces considerable Restraints that moderate growth. The foremost restraint is the technical complexity and high cost associated with developing and delivering gene-based therapies, which require specialized manufacturing capabilities and often high-cost administration pathways (e.g., intrathecal or systemic delivery of ASOs). Furthermore, Myotonic Dystrophy is highly heterogeneous in its clinical presentation and progression, posing a significant challenge in designing clinical trials with unified, quantifiable endpoints that accurately reflect meaningful patient benefit across diverse phenotypes. The small patient population inherent to a rare disease limits the scope for economies of scale, leading to extremely high drug pricing, which, despite payer willingness, can create reimbursement challenges, particularly in developing and emerging markets. Moreover, potential long-term safety concerns associated with novel genetic therapies, such as off-target effects or immunogenicity, necessitate prolonged and rigorous post-marketing surveillance, adding to regulatory complexity.
Significant Opportunities exist that promise to unlock substantial future value. The discovery of biomarkers that accurately track disease progression and therapeutic response (e.g., analysis of splicing products like chloride channel mRNA—CLCN1) provides a crucial opportunity to de-risk clinical trials and accelerate regulatory approval. Expansion into combination therapies, addressing both the underlying genetic defect and the secondary muscular and cardiac complications, presents a pathway to comprehensive patient care and enhanced market penetration. Furthermore, leveraging advanced diagnostic techniques, particularly genetic screening, to identify asymptomatic or mildly affected individuals (especially in congenital DM cases) creates an opportunity for early intervention, potentially offering the highest therapeutic benefit and expanding the future addressable market. The advancement of non-invasive or easily administered delivery systems for nucleic acid therapeutics (e.g., oral formulations or subcutaneous injections) would also drastically improve patient compliance and market accessibility, solidifying the long-term growth potential.
Segmentation Analysis
The Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market segmentation provides a granular view of therapeutic approaches, underlying mechanisms, and commercial distribution channels currently influencing market dynamics. Analysis by Drug Type highlights the crucial transition from traditional small molecules, which are typically utilized for symptomatic relief, toward advanced biological and genetic modalities, particularly antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and gene therapy vectors. This shift underscores the industry's commitment to developing curative or disease-modifying treatments that address the root cause of the disease—the toxic CUG repeat expansion. Segmentation by Mechanism of Action (MoA) differentiates drugs based on whether they enhance muscle function, modulate the RNA splicing machinery, or directly target the toxic RNA transcript, offering insights into the focus areas of current R&D pipelines.
Further breakdown by Indication (DM1 and DM2) reveals a heavy concentration of clinical research and financial investment directed toward DM Type 1, which is the more common and often more severe form, although targeted efforts for DM2 are gaining momentum as the market matures and translational research bridges the gap between the two types. The final layer of segmentation, by Distribution Channel, reflects the anticipated logistical requirements for future market-leading drugs. Symptomatic oral treatments are easily managed through retail and online pharmacies, but complex, often infusion-based, disease-modifying therapies are expected to be predominantly distributed through specialized hospital pharmacies and infusion centers, demanding high-level cold chain management and professional administration services.
Understanding these segments is essential for strategic planning, enabling companies to allocate R&D resources effectively, forecast logistical needs, and tailor commercial strategies to specific patient populations (DM1 vs. DM2) and product types (genetic therapies vs. symptomatic drugs). The dominance of the Oligonucleotide segment within the Drug Type category illustrates the highest area of future potential, as ASOs offer a highly specific, tunable mechanism to disrupt the toxic RNA mechanism, positioning this segment for rapid revenue growth pending regulatory approvals in the latter half of the forecast period.
- By Drug Type:
- Small Molecules
- Biologics (Antibodies, Recombinant Proteins)
- Oligonucleotides (Antisense Oligonucleotides, SiRNA)
- Gene Therapy
- By Mechanism of Action:
- Splicing Modulators (Targeting MBNL Sequestration)
- Muscle Function Enhancers (Addressing Myotonia and Weakness)
- Disease Modifying Agents (Directly targeting the toxic RNA)
- Ion Channel Modulators
- By Indication:
- Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1)
- Myotonic Dystrophy Type 2 (DM2)
- By Distribution Channel:
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Specialty Infusion Centers
Value Chain Analysis For Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market
The Value Chain for the Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market is intensely specialized, commencing with extensive Upstream Analysis focused on fundamental genomic and proteomic research into the pathophysiology of DM, primarily the role of the toxic RNA expansion and the subsequent mis-splicing cascade. This initial stage involves university research labs, specialized rare disease institutes, and biotech firms conducting target identification and validation, particularly focusing on identifying sequences amenable to ASO binding or small molecule modulation. Drug substance manufacturing, especially for highly complex biologics and nucleic acid therapeutics, represents a crucial high-cost element, requiring stringent quality control (QC) and high-yield synthesis capabilities to produce clinical and commercial-grade materials. The successful transition from raw materials to active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in the gene therapy space also requires specialized viral vector (e.g., AAV) manufacturing, which is often outsourced to highly specialized contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs).
The midstream process involves clinical development, regulatory affairs, and large-scale formulation and packaging. Due to the rarity and complexity of DM, clinical trial recruitment is often challenging, necessitating strong collaboration with patient advocacy groups and specialized clinical centers. The regulatory phase is supported by orphan drug incentives, which, while beneficial, demand comprehensive data demonstrating significant clinical benefit over existing care standards. Distribution channels fall into two primary categories: Direct and Indirect. Direct distribution is common for high-value, newly approved specialty drugs, where pharmaceutical companies maintain direct control over inventory, often distributing through closed systems or specialty pharmacies to manage the complex logistics, temperature requirements, and patient support programs associated with novel treatments like ASOs or gene therapies, ensuring traceability and safe handling.
The Downstream Analysis involves the final delivery to the end-user, patient monitoring, and post-market surveillance. For established symptomatic treatments (e.g., small molecules), indirect distribution via traditional wholesalers and retail pharmacies remains the standard. However, the anticipated disease-modifying treatments will rely heavily on specialized hospital and infusion centers, constituting the primary channel for patient administration. The final stage of the value chain is critical in the rare disease space, involving continuous data collection (pharmacovigilance) to monitor long-term safety and efficacy, often facilitated by robust patient registry programs and tailored patient support services (e.g., assistance with insurance verification, co-pay assistance, and nurse navigators) provided directly by the manufacturer, ensuring market access and adherence, which is vital for maintaining the premium valuation of these life-changing therapies.
Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market Potential Customers
The primary potential customers and end-users of Myotonic Dystrophy drug products are individuals formally diagnosed with Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1) or Type 2 (DM2) across all stages of disease progression, from congenital and juvenile onset to adult-onset patients. Within this group, customers are often identified and managed through specialized neurological centers and muscular dystrophy clinics, indicating that the purchasing decisions are highly influenced by expert neurologists, geneticists, and cardiologists who specialize in managing the multi-systemic complications of DM. A critical segment of the customer base consists of patients requiring advanced disease modification, particularly those with rapidly progressing muscle weakness or severe, debilitating myotonia that is refractory to current symptomatic care. These patients, along with their caregivers, actively seek out clinical trials and are highly motivated early adopters of novel, FDA-approved, disease-modifying agents that promise to stabilize or reverse the progression of their condition, reflecting a deep, urgent demand for effective solutions.
Institutional customers form another major segment, comprising hospital systems, specialized infusion centers, and government health agencies responsible for funding and administering high-cost specialty pharmaceuticals. For the anticipated genetic and oligonucleotide therapies, the procurement decision is often centralized within hospital pharmacy committees or formulary managers who evaluate the clinical and economic value proposition based on evidence generated during clinical trials and comparative effectiveness research. Since many DM patients require ongoing management for co-morbidities (cardiac, respiratory, endocrine), large tertiary care centers that aggregate multidisciplinary expertise represent key purchasing hubs. Furthermore, government programs and major private insurance payers act as indirect but powerful customers, as their coverage decisions fundamentally determine patient access and market volume. Manufacturers must therefore dedicate significant resources to health economics and outcomes research (HEOR) to justify the ultra-premium pricing models characteristic of rare disease drugs to these powerful institutional purchasers.
The evolving customer base also includes patients diagnosed early via genetic screening who may be asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic, particularly in families with known histories of DM. As gene therapies advance toward potential curative status, preventative or pre-symptomatic treatment becomes a viable and highly sought-after option, representing a potential expansion of the addressable market, provided robust long-term safety data supports intervention prior to clinical manifestations. Thus, the target customer ranges from severely affected individuals seeking immediate relief and disease reversal, to institutional bodies managing complex care pathways, and potentially to pre-symptomatic individuals seeking prophylactic genetic interventions, all of whom share the underlying need for treatments that address the core genetic and molecular pathology of Myotonic Dystrophy.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | $580.5 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | $1,245.8 Million |
| Growth Rate | 11.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Biogen, Novartis AG, Sanofi, Pfizer Inc., Sarepta Therapeutics, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Astellas Pharma Inc., Wave Life Sciences, Ipsen, Harmony Biosciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical, Expansion Therapeutics, Audentes Therapeutics (now Astellas Gene Therapies), Dyne Therapeutics, PepGen, Evox Therapeutics, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Scholar Rock. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market Key Technology Landscape
The technological landscape of the Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market is currently dominated by advancements in nucleic acid therapeutics, specifically Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which represent the most mature platforms for targeted disease modification. ASOs are single-stranded synthetic nucleic acids designed to bind directly to the toxic CUG repeat expansion in the DMPK mRNA, thereby inhibiting the toxic gain-of-function mechanism, preventing the sequestration of MBNL proteins, and ultimately restoring normal splicing patterns. Key technological developments in this area focus on optimizing ASO chemistry, such as using phosphorothioate backbones and 2'-O-methoxyethyl (MOE) modifications, to improve stability, increase binding affinity, and enhance cellular uptake, particularly into muscle tissue and the central nervous system (CNS), which are crucial for treating the systemic manifestations of DM.
A secondary, but rapidly advancing, technological focus involves Gene Therapy, typically utilizing Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) vectors. These therapies aim to deliver functional components that either degrade the toxic RNA or express factors that counteract the toxicity, providing a potentially long-lasting or even curative effect after a single administration. Technological hurdles being addressed include optimizing AAV serotypes (e.g., AAV9 or novel capsids) to achieve broad and effective transduction of skeletal muscle, cardiac tissue, and CNS neurons, ensuring robust and sustained therapeutic gene expression without triggering significant immune responses. Furthermore, advancements in specialized delivery mechanisms, such as those employing transferrin receptors or other ligand-mediated approaches (like the muscle-targeting antibody conjugation used by Dyne Therapeutics), are crucial for overcoming the inherent difficulty of systemically delivering large therapeutic molecules specifically to muscle cells.
Small molecule drug development technology remains relevant, concentrating on high-throughput screening of chemical libraries to identify orally bioavailable compounds that can either disrupt the RNA-protein interaction (e.g., MBNL-CUG repeats) or modulate downstream effectors, such such as ion channels involved in myotonia. Technologies like fragment-based drug design and computational molecular modeling are heavily leveraged to engineer small molecules with improved specificity, reduced off-target effects, and enhanced permeability across biological barriers, particularly the blood-brain barrier. The convergence of these technologies—ASO optimization for tissue specificity, advanced AAV vector engineering for systemic delivery, and computationally guided small molecule design—characterizes the cutting-edge R&D environment, offering diverse pathways to potentially address the multi-faceted pathophysiology of Myotonic Dystrophy.
Regional Highlights
- North America (United States and Canada): North America is projected to maintain its position as the largest and most dominant market for Myotonic Dystrophy drugs throughout the forecast period. This dominance is intrinsically linked to the region’s robust biopharmaceutical R&D ecosystem, which includes the highest concentration of specialized biotechnology firms focused on rare and genetic diseases, such as those pioneering ASO and gene therapy platforms. The United States market benefits significantly from the highly developed regulatory framework provided by the FDA, which facilitates accelerated development pathways (e.g., Fast Track, Breakthrough Therapy, Orphan Drug Designation), offering strong market exclusivity incentives that justify the high cost of specialized rare disease research. Furthermore, high per capita healthcare spending and a supportive reimbursement environment, where private insurance and government programs (Medicare/Medicaid) generally cover high-cost specialty drugs, ensure rapid market uptake upon approval. The substantial presence of Myotonic Dystrophy clinical trial sites and patient registries in major US cities also enables efficient patient recruitment and robust clinical data generation, solidifying its leading role in global drug development and commercialization. The high level of patient advocacy and awareness further drives demand for novel therapies.
- Europe (Germany, France, UK, Italy, Spain, Rest of Europe): Europe represents the second-largest market, characterized by a significant patient population and advanced healthcare systems capable of managing complex genetic disorders. Market growth in this region is stimulated by national initiatives focused on rare diseases and the centralized review process via the European Medicines Agency (EMA), which streamlines regulatory approval across member states. However, market access and pricing negotiations post-approval present a complex challenge, as individual national health technology assessment (HTA) bodies (e.g., NICE in the UK, HAS in France) scrutinize the cost-effectiveness of premium-priced therapies, potentially leading to varied availability and adoption rates across the continent. Germany and the UK, with their strong research base and sophisticated healthcare infrastructure, are expected to be primary growth engines. Increasing collaboration between European academic centers and industry partners to improve diagnostic protocols and genetic counseling is essential for expanding the addressable patient base and facilitating the adoption of future disease-modifying treatments. The implementation of harmonized clinical guidelines for DM management across the European Union is anticipated to further standardize care and increase therapeutic market penetration.
- Asia Pacific (APAC) (Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia): The Asia Pacific region is forecast to exhibit the fastest growth rate, fueled by improving healthcare access, increasing governmental focus on non-communicable and rare diseases, and a growing recognition of the genetic prevalence of DM in countries like Japan and South Korea, which have highly advanced biomedical research capabilities. Japan, with its strong emphasis on regenerative medicine and genetic research, is often a key early adopter market outside of North America. China and India, while presenting enormous patient pools, face challenges related to fragmented healthcare systems, lower per capita healthcare expenditure, and complex local regulatory requirements, meaning market entry and scale-up for ultra-expensive genetic therapies will be gradual but ultimately significant. Investment in domestic clinical trial infrastructure and the establishment of local patient registries are necessary precursors for widespread commercial success in this diverse region. Strategic partnerships between Western developers and local pharmaceutical distributors are critical for navigating the diverse regulatory and logistical landscape of APAC.
- Latin America (LATAM) and Middle East & Africa (MEA): These regions currently represent smaller market shares but hold substantial long-term growth potential, particularly for symptomatic and less expensive small molecule treatments. Market expansion is constrained by factors such as limited centralized diagnostic capabilities for genetic disorders, lower levels of health insurance coverage for high-cost specialty drugs, and political and economic volatility affecting healthcare investment. Within LATAM, countries like Brazil and Mexico, possessing relatively more mature private healthcare sectors, are likely to be initial targets for specialized drug launches. In the MEA, nations with significant oil wealth and investments in specialized medical infrastructure, such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia, are expected to lead regional adoption of novel therapies. For both regions, market success hinges on strategic public-private partnerships aimed at subsidizing treatment costs and improving access to specialized medical expertise required for the diagnosis and comprehensive management of Myotonic Dystrophy.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market.- Biogen
- Novartis AG
- Sanofi
- Pfizer Inc.
- Sarepta Therapeutics
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals
- Astellas Pharma Inc.
- Wave Life Sciences
- Ipsen
- Harmony Biosciences
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Acadia Pharmaceuticals
- Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical
- Expansion Therapeutics
- Audentes Therapeutics (now Astellas Gene Therapies)
- Dyne Therapeutics
- PepGen
- Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals
- Scholar Rock
- Evox Therapeutics
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Myotonic Dystrophy Drug market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary mechanism of action for novel Myotonic Dystrophy drugs currently in development?
The primary mechanism focuses on disease modification by targeting the toxic RNA gain-of-function caused by the expanded trinucleotide repeats (CUG or CCUG). Novel therapies, particularly Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) and small molecules, aim to bind to this toxic RNA, preventing the sequestration of MBNL proteins and restoring normal RNA splicing patterns essential for muscle and organ function.
Which segment, DM1 or DM2, is receiving the most research and development investment?
Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1) currently receives the vast majority of research and development investment. This is due to its higher global prevalence, generally more severe clinical presentation, including congenital onset, and the greater clarity regarding its molecular mechanism, making it the dominant target for high-value disease-modifying therapies.
How are advancements in gene therapy technology impacting the Myotonic Dystrophy drug pipeline?
Gene therapy, primarily using AAV vectors, is crucial as it offers the potential for a single-dose, curative treatment by delivering genetic material that degrades the toxic RNA or restores MBNL function. Technological advancements focus on optimizing AAV serotypes and specialized delivery systems to ensure effective, systemic transduction of key affected tissues like muscle and the central nervous system.
What is the largest restraint affecting the commercialization of new DM therapies?
The largest restraint is the high technical complexity and immense cost of manufacturing and delivering advanced genetic therapies, coupled with the need to justify ultra-premium pricing models for a rare disease. This often leads to significant reimbursement challenges and variable market access across different global healthcare systems, despite the high unmet medical need.
Which geographical region dominates the Myotonic Dystrophy Drug Market?
North America, specifically the United States, dominates the market due to its high concentration of specialized biotech research, favorable regulatory incentives (Orphan Drug Designation), established patient advocacy networks, and a robust payer system supporting the adoption and coverage of high-cost, innovative rare disease therapeutics.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
