Small Satellite Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2025 to 2032 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 429714 | Date : Nov, 2025 | Pages : 249 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Small Satellite Market Size
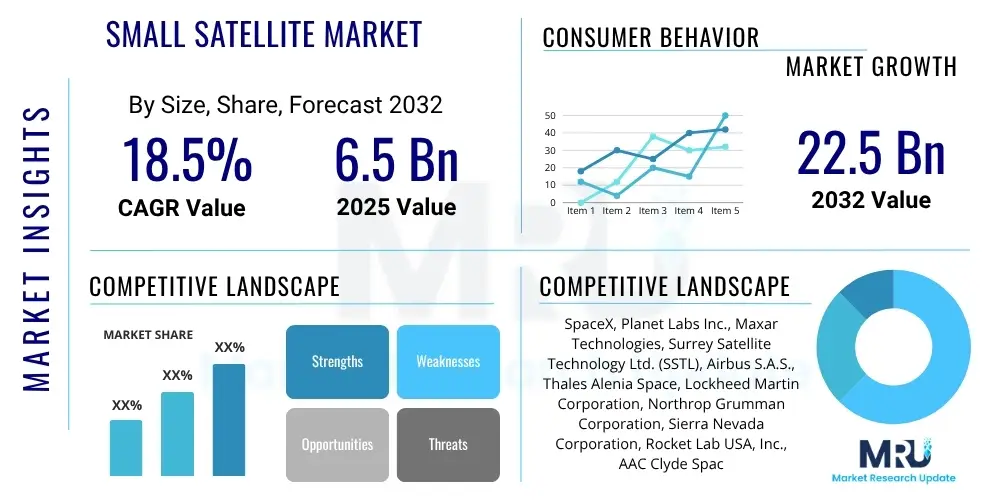
The Small Satellite Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 18.5% between 2025 and 2032. The market is estimated at USD 6.5 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 22.5 billion by the end of the forecast period in 2032.
Small Satellite Market introduction
The Small Satellite Market encompasses the design, manufacturing, launch, and operation of satellites typically weighing less than 500 kg, including categories such as nanosatellites (1-10 kg), microsatellites (10-100 kg), and mini-satellites (100-500 kg). These compact and often cost-effective spacecraft are transforming the space industry by democratizing access to space and enabling a multitude of applications that were previously restricted to larger, more expensive platforms. The primary applications for small satellites span across Earth observation, global communication networks, Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, scientific research, technology demonstration, and defense and intelligence gathering. Their inherent benefits include reduced development and launch costs, faster deployment times, greater flexibility for mission design, and the ability to operate in large constellations for enhanced coverage and resilience.
The proliferation of small satellites is fundamentally driven by several key factors. Technological advancements in miniaturization have allowed for powerful payloads and robust subsystems to be packed into smaller form factors, significantly enhancing their capabilities. Concurrently, the emergence of dedicated small satellite launch vehicles and ride-sharing opportunities on larger rockets has drastically lowered the cost of reaching orbit, making space more accessible to a wider array of commercial and governmental entities. Furthermore, the escalating global demand for high-resolution imagery, real-time data, pervasive internet access, and precise navigation services is fueling the deployment of extensive small satellite constellations. These factors collectively contribute to the robust expansion and diversification of the small satellite ecosystem, positioning it as a pivotal segment within the broader space economy.
Small Satellite Market Executive Summary
The Small Satellite Market is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by a confluence of technological innovation and increasing commercialization of space. Business trends indicate a strong shift towards large-scale constellation deployment, particularly for communication and Earth observation, fostering a competitive landscape where both established aerospace giants and agile startups are thriving. Significant investment from venture capital and private equity firms is propelling new business models centered around satellite-as-a-service, in-orbit manufacturing, and advanced data analytics, making space data more accessible and valuable across various industries. The drive for miniaturization and cost reduction continues to lower barriers to entry, while the development of more efficient launch solutions, including dedicated small satellite launchers and robust ride-share options, is accelerating mission deployment schedules. This dynamic environment is fostering rapid innovation, enhancing satellite capabilities, and diversifying market applications beyond traditional government and defense use cases.
Regional trends highlight North America and Europe as leading innovators and investors, with a mature ecosystem of technology developers, manufacturers, and service providers. The Asia Pacific region is rapidly emerging as a significant market, propelled by substantial government investments in space programs, increasing demand for satellite-based services in developing economies, and the rise of local players across countries like China, India, and Japan. Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are also showing growing interest, particularly for remote sensing, telecommunications, and national security applications, often leveraging international partnerships and technology transfers. In terms of segment trends, communication satellites, especially those supporting global broadband and IoT, are projected to dominate market share due to the insatiable demand for ubiquitous connectivity. Earth observation and remote sensing applications also represent a substantial and growing segment, driven by needs in environmental monitoring, agriculture, urban planning, and disaster management. Furthermore, technology demonstration and scientific research missions continue to be crucial for advancing capabilities and validating new concepts for future commercial and defense deployments.
AI Impact Analysis on Small Satellite Market
Users frequently inquire about how artificial intelligence is transforming small satellite operations, seeking to understand its role in data processing, autonomous functionality, and mission optimization. There is a strong interest in AI's ability to enhance the efficiency and intelligence of satellite constellations, particularly concerning the massive volumes of data generated and the need for real-time decision-making. Common concerns revolve around the reliability and security of AI systems in space, the ethical implications of autonomous operations, and the potential for AI to streamline or even automate tasks currently performed by human operators. Users anticipate that AI will significantly improve mission success rates, reduce operational costs, and unlock novel capabilities for small satellites, ranging from advanced onboard analytics to adaptive mission planning and autonomous anomaly detection, ultimately making satellite systems more resilient and responsive.
The integration of artificial intelligence across the small satellite lifecycle is fundamentally reshaping the capabilities and operational paradigms of these compact spacecraft. AI algorithms enable onboard processing of raw satellite data, allowing for intelligent filtering, compression, and analysis before transmission to Earth, thereby reducing downlink bandwidth requirements and latency. This capability is critical for applications requiring immediate insights, such as disaster response, maritime surveillance, or real-time agricultural monitoring. Furthermore, AI contributes significantly to the autonomy of small satellites, enabling them to make independent decisions regarding orbital maneuvers, resource management, and payload tasking, which is essential for managing large, complex constellations with minimal human intervention. AI-driven systems also enhance the resilience and longevity of missions by detecting and diagnosing anomalies in real-time, predicting component failures, and initiating recovery procedures, moving towards a more self-aware and adaptive satellite architecture. These advancements are not merely incremental but represent a paradigm shift towards truly intelligent and efficient space operations, maximizing the utility of each small satellite deployed.
- Enhanced Onboard Data Processing: AI processes sensor data directly on the satellite, reducing downlink needs and latency for actionable insights.
- Autonomous Mission Management: AI enables satellites to make independent decisions for orbital maneuvers, task scheduling, and resource optimization.
- Predictive Maintenance and Anomaly Detection: Machine learning identifies potential system failures and unusual behavior, improving mission reliability and lifespan.
- Adaptive Payload Operations: AI dynamically adjusts sensor parameters and data collection strategies based on environmental conditions and mission objectives.
- Optimized Constellation Management: AI algorithms facilitate efficient routing, resource allocation, and collision avoidance for large satellite swarms.
- Improved Image and Signal Analysis: Deep learning models enhance the accuracy and speed of interpreting Earth observation imagery and communication signals.
- Cybersecurity Enhancements: AI-powered systems detect and mitigate cyber threats targeting satellite infrastructure and data links.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Small Satellite Market
The Small Satellite Market is propelled by a robust set of drivers, primarily the continuous reduction in launch costs and the rapid advancement in miniaturization technologies, which make space access and satellite deployment more economically viable for a broader range of entities. The escalating demand for high-resolution Earth observation data, ubiquitous communication services, and global IoT connectivity further fuels market expansion, as small satellites offer scalable and flexible solutions. However, the market faces significant restraints, including the growing concern over space debris, which poses collision risks and complicates orbital operations, as well as complex international regulatory frameworks that govern satellite deployment and spectrum usage. Opportunities abound in emerging applications such as in-orbit servicing, space tourism support, and advanced scientific research missions, while impact forces like geopolitical dynamics, environmental considerations, and the high capital intensity of developing new space technologies continuously shape market trajectory and innovation incentives.
A primary driver for the Small Satellite Market is the increasing affordability of space access. Innovations in launch vehicle technology, coupled with the growing availability of ride-share options and dedicated small satellite launchers, have drastically reduced the cost per kilogram to orbit. This cost efficiency allows more startups, research institutions, and developing nations to deploy their own satellite missions. Concurrently, rapid advancements in microelectronics, sensor technology, and manufacturing processes have led to significant miniaturization of satellite components without compromising performance. This enables a wider range of sophisticated payloads and capabilities to be integrated into smaller, lighter, and more cost-effective platforms. The burgeoning demand for applications such as real-time Earth monitoring for climate change, precision agriculture, maritime surveillance, and the establishment of global broadband internet and IoT networks via satellite constellations are critical demand-side drivers, ensuring a continuous pipeline of projects and investments into the sector.
Despite these powerful drivers, several restraints pose challenges to sustained growth. The exponential increase in satellite launches, particularly small satellites forming large constellations, exacerbates the issue of space debris. This creates a more congested orbital environment, raising the risk of collisions and necessitating advanced tracking and mitigation strategies. Additionally, the fragmented and often slow-moving regulatory landscape across different national and international bodies can impede rapid deployment, particularly concerning frequency allocation, orbital slot assignments, and licensing requirements for commercial operations. The relatively short lifespan of many small satellites compared to their larger counterparts necessitates frequent replenishment, adding to operational complexity and costs. Furthermore, the reliance on advanced, often proprietary technologies introduces supply chain vulnerabilities and intellectual property challenges, potentially stifling broader market adoption and competition for certain high-end components.
- Drivers:
- Decreasing Launch Costs: Cheaper access to space through ride-shares and dedicated small launch vehicles.
- Technological Miniaturization: Advancements enabling powerful capabilities in smaller, lighter satellites.
- Rising Demand for Satellite Data: Increased need for Earth observation, communication, and IoT connectivity.
- Government and Defense Initiatives: Increased investment in space-based assets for national security and scientific research.
- Commercialization of Space: Growing private sector involvement and innovative business models.
- Restraints:
- Space Debris Concerns: Risk of collisions and orbital congestion from growing satellite numbers.
- Regulatory and Licensing Hurdles: Complex national and international regulations for spectrum and orbital slots.
- Limited Bandwidth and Power: Constraints on data transmission and energy for smaller platforms.
- High Initial Investment: Significant upfront capital required for constellation development and ground infrastructure.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Vulnerabilities of satellite systems to cyber attacks.
- Opportunities:
- IoT and 5G Integration: Expanding connectivity solutions for underserved and remote areas.
- In-Orbit Servicing and Manufacturing: Development of capabilities for satellite repair, refueling, and assembly in space.
- Advanced Remote Sensing: Enhanced capabilities for environmental monitoring, disaster management, and resource mapping.
- Deep Space Exploration: Small satellites for cost-effective planetary missions and scientific probes.
- Data Analytics and AI Integration: Value-added services from processing vast amounts of satellite data.
Segmentation Analysis
The Small Satellite Market is comprehensively segmented across various dimensions to provide a detailed understanding of its complex structure and diverse applications. These segments include satellite type, application area, end-user industry, orbital deployment, and subsystem components, each reflecting distinct technological requirements, operational models, and market demand drivers. This granular segmentation allows for a precise analysis of market dynamics, identifying key growth areas, competitive advantages, and technological innovations specific to each category. Understanding these segments is crucial for stakeholders to strategize effectively, allocate resources efficiently, and capitalize on the multifaceted opportunities within this rapidly evolving space sector. The interplay between these segments often dictates the pace of technological adoption and the evolution of new satellite services.
The segmentation by satellite type, for instance, distinguishes between nanosatellites, microsatellites, and mini-satellites, each offering a unique balance of cost, capability, and mission suitability. Application-based segmentation highlights the primary uses such as Earth observation, communication, and scientific research, showcasing how small satellites serve a broad spectrum of global needs. End-user categories differentiate between commercial, government, defense, and academic sectors, revealing varied procurement processes and operational requirements. Furthermore, orbital segmentation, typically Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), and Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO), emphasizes the distinct technical challenges and service advantages associated with each orbital regime. Finally, subsystem segmentation delves into the critical components that comprise a small satellite, from propulsion and power systems to payloads and on-board computers, reflecting the technological intricacies and supply chain dynamics of the market. This detailed breakdown facilitates a holistic view of the market's current state and future trajectory.
- By Type
- Nanosatellite (1-10 kg)
- Microsatellite (10-100 kg)
- Minisatellite (100-500 kg)
- By Application
- Earth Observation and Remote Sensing
- Communication and M2M/IoT
- Scientific Research and Exploration
- Technology Demonstration and Verification
- Navigation and Global Positioning System (GPS) Augmentation
- Space Situational Awareness (SSA)
- By End User
- Commercial
- Government and Military
- Civil and Academia
- By Orbit
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
- Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO)
- By Subsystem
- Payload
- Structure
- Electrical Power System (EPS)
- Propulsion System
- On-Board Computer (OBC)
- Attitude Determination and Control System (ADCS)
- Telemetry, Tracking, and Command (TT&C) System
Value Chain Analysis For Small Satellite Market
The value chain of the Small Satellite Market is a complex ecosystem encompassing various stages from conceptualization to end-user service delivery, characterized by numerous specialized actors. The upstream segment involves critical activities such as research and development, satellite design, and the manufacturing of intricate components and subsystems like propulsion units, power systems, sensors, and structural elements. Key players in this stage include specialized component suppliers, advanced materials providers, and satellite integrators who assemble these components into a functioning spacecraft. This phase is heavily reliant on technological innovation, precision engineering, and adherence to rigorous quality standards, often involving collaborations between academic institutions and private enterprises to push the boundaries of miniaturization and capability. The effectiveness and efficiency of this upstream segment directly influence the cost, performance, and reliability of the final small satellite product.
Moving further along the value chain, the midstream segment primarily focuses on the crucial aspect of launch services. This involves securing orbital access through dedicated small satellite launchers, ride-sharing opportunities on larger rockets, or specialized orbital transfer vehicles. Companies providing launch services play a pivotal role in delivering small satellites to their intended orbits efficiently and reliably, greatly impacting mission success and overall project timelines. The downstream segment of the value chain is dedicated to post-launch operations, including ground segment development, which comprises ground stations for communication, tracking, and control, as well as software for mission management and data processing. Crucially, this stage also involves the provision of various end-user services derived from satellite data, such as Earth observation imagery analysis, environmental monitoring, telecommunications, and IoT connectivity solutions. The distribution channel for these services can be direct, through contracts with end-users, or indirect, via partnerships with value-added resellers and data analytics firms, highlighting the diverse ways small satellite capabilities reach their ultimate beneficiaries and generate economic value.
The direct distribution channels typically involve prime contractors engaging directly with government agencies, defense organizations, or large commercial clients for bespoke satellite solutions or dedicated constellation services. This often includes long-term contracts for satellite procurement, launch, and ongoing operational support. Indirect channels, on the other hand, leverage a network of distributors, system integrators, and software developers who add value by integrating satellite data into broader service offerings, customizing applications, and reaching a wider customer base, particularly in commercial sectors like agriculture, logistics, and resource management. These indirect channels are vital for democratizing access to satellite-derived information and services, converting raw data into actionable intelligence for diverse industries. The evolution of this distribution landscape is increasingly influenced by online marketplaces for satellite imagery and data, facilitating easier access for smaller businesses and academic researchers, thereby expanding the overall market reach and impact of small satellite technology.
Small Satellite Market Potential Customers
The Small Satellite Market serves a diverse and expanding base of potential customers, spanning across various sectors that leverage the unique capabilities and cost-effectiveness of these compact spacecraft. Predominantly, governments and defense agencies represent significant end-users, utilizing small satellites for critical national security applications such as intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), secure communications, border monitoring, and disaster management. These entities prioritize reliability, data security, and rapid deployment capabilities to enhance situational awareness and operational efficiency. The commercial sector, however, is rapidly becoming the largest and fastest-growing customer segment, driven by companies specializing in telecommunications, Earth observation, and the burgeoning Internet of Things (IoT). These commercial buyers seek scalable solutions for global connectivity, high-resolution imagery for commercial analytics, and pervasive machine-to-machine communication, often through large constellations designed for continuous service delivery.
Beyond traditional government and commercial applications, the Small Satellite Market attracts a wide array of other end-users. Academic and research institutions frequently acquire small satellites, particularly CubeSats, for scientific experiments, technology validation, and educational purposes, benefiting from lower costs and easier access to space for innovative projects. Emerging markets and developing economies are also becoming increasingly important customers, as small satellites offer affordable means to address critical infrastructure gaps in telecommunications, remote sensing for agricultural planning, and environmental monitoring where traditional terrestrial infrastructure is lacking or cost-prohibitive. Furthermore, specialized industries like maritime, aviation, and resource management (mining, oil & gas) are adopting small satellite data for optimizing logistics, tracking assets, and monitoring environmental compliance. The versatility and evolving capabilities of small satellites continue to broaden their appeal, creating new market niches and attracting novel applications from a growing global customer base seeking cost-effective and agile space-based solutions.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 6.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 22.5 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR 18.5% |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2032 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | SpaceX, Planet Labs Inc., Maxar Technologies, Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd. (SSTL), Airbus S.A.S., Thales Alenia Space, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Sierra Nevada Corporation, Rocket Lab USA, Inc., AAC Clyde Space, GomSpace A/S, ICEYE, BlackSky Global LLC, Swarm Technologies (SpaceX Subsidiary), LEO Aerospace, OHB SE, QinetiQ, Astro Digital |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Small Satellite Market Key Technology Landscape
The Small Satellite Market's impressive growth is inextricably linked to continuous advancements in its underlying technology landscape, which enables greater capabilities within ever-smaller packages. Key technological drivers include the development of highly efficient propulsion systems, such as electric propulsion (e.g., Hall effect thrusters, ion engines) and compact chemical propulsion systems, critical for orbital maneuvering, constellation maintenance, and extended mission lifespans. Significant progress in advanced materials, including lightweight composites and additive manufacturing (3D printing), allows for the creation of robust yet mass-optimized satellite structures, reducing launch mass and cost. The integration of advanced power solutions, such as high-efficiency solar panels and compact, high-density batteries, ensures sustained operation and supports increasingly power-hungry payloads. These innovations collectively contribute to enhancing the performance, durability, and operational flexibility of small satellites, pushing the boundaries of what is achievable with limited size and weight constraints.
Another pivotal aspect of the technology landscape is the sophistication of payloads and onboard electronics. Miniaturized, high-resolution optical and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) sensors are now capable of delivering imagery comparable to larger satellites, enabling applications like precision agriculture, environmental monitoring, and persistent surveillance. The burgeoning field of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) is profoundly impacting small satellites, facilitating onboard data processing and analysis, autonomous decision-making for mission operations, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Furthermore, advancements in inter-satellite communication links and mesh networking technologies are enabling the creation of highly resilient and interconnected satellite constellations, improving data relay speeds and overall system responsiveness. Software-defined radios and reconfigurable payloads offer unprecedented flexibility, allowing missions to adapt to changing requirements post-launch. These technological leaps are not only expanding the range of applications for small satellites but are also fundamentally altering how space-based services are delivered and consumed globally.
The continuous evolution in ground segment technologies also plays a crucial role in maximizing the utility of small satellites. This includes the development of more efficient and automated ground stations capable of managing large constellations and processing massive data volumes. Cloud-based ground segment services are becoming prevalent, offering scalable and flexible solutions for mission control, data reception, and distribution without the need for extensive upfront infrastructure investment by satellite operators. Furthermore, enhanced data security measures and cybersecurity protocols are increasingly integrated into both space and ground segments to protect sensitive satellite data and control systems from malicious attacks. The confluence of these hardware and software innovations, combined with evolving operational methodologies, underpins the robust technological foundation of the small satellite market, promising even more transformative capabilities in the years to come.
Regional Highlights
The global Small Satellite Market exhibits distinct regional dynamics, influenced by varying levels of technological advancement, government investment, and commercial activity. North America stands as a dominant force, driven by substantial government expenditure from agencies like NASA and the Department of Defense, a thriving private space sector led by companies like SpaceX and Rocket Lab, and a robust ecosystem of technology providers and startups. The region benefits from significant R&D investments, fostering innovation in satellite design, manufacturing, and launch services, particularly for commercial constellations in LEO. Europe also presents a strong market, supported by initiatives from the European Space Agency (ESA) and national space programs, with a focus on Earth observation, scientific research, and secure communications. European companies are known for their expertise in precision engineering and high-quality satellite components, contributing to numerous global small satellite missions.
The Asia Pacific region is rapidly emerging as a critical growth hub for small satellites, propelled by increasing government investments in space infrastructure, a growing demand for satellite-based services in telecommunications and remote sensing, and the rise of local manufacturing capabilities, particularly in countries like China, India, and Japan. These nations are expanding their domestic space programs and fostering commercial entities, often with an emphasis on national security, disaster monitoring, and bridging digital divides. Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa (LAMEA) represent burgeoning markets with significant potential. While smaller in scale, these regions are increasingly leveraging small satellites for essential services such as agricultural monitoring, natural resource management, and improving connectivity in remote areas, often through international collaborations and technology transfers aimed at economic development and regional stability. This global distribution underscores the widespread recognition of small satellites as versatile tools for addressing diverse socio-economic and strategic objectives.
- North America: Leading market with extensive government and private investment, strong R&D, and a high concentration of key players in satellite manufacturing and launch services. Focus on commercial constellations and defense applications.
- Europe: Robust market supported by ESA and national programs, strong emphasis on scientific research, Earth observation, and secure communications. Key players in satellite technology and integration.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Fastest-growing region due to increasing government spending, burgeoning commercial space sector, and rising demand for communication and remote sensing services from countries like China, India, and Japan.
- Latin America: Emerging market with growing interest in small satellites for agricultural monitoring, environmental protection, and basic communication infrastructure. Collaborative projects often drive growth.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): Developing market leveraging small satellites for national security, resource management, and telecommunications connectivity in underserved areas. Increasing governmental initiatives and partnerships are key growth factors.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Small Satellite Market.- SpaceX
- Planet Labs Inc.
- Maxar Technologies
- Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd. (SSTL)
- Airbus S.A.S.
- Thales Alenia Space
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Sierra Nevada Corporation
- Rocket Lab USA, Inc.
- AAC Clyde Space
- GomSpace A/S
- ICEYE
- BlackSky Global LLC
- Swarm Technologies (SpaceX Subsidiary)
- LEO Aerospace
- OHB SE
- QinetiQ
- Astro Digital
- Exolaunch
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a small satellite and how does it differ from traditional satellites?
A small satellite typically weighs less than 500 kilograms, encompassing categories such as nanosatellites (1-10 kg), microsatellites (10-100 kg), and minisatellites (100-500 kg). They differ from traditional, larger satellites primarily in their reduced size, lower cost, quicker development and deployment times, and greater flexibility for mission-specific applications or large constellation formations.
What are the primary applications driving the growth of the Small Satellite Market?
The primary applications driving market growth include Earth observation and remote sensing for environmental monitoring, agriculture, and disaster management; global communication networks and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity; scientific research and technology demonstration; and defense and intelligence gathering. These versatile uses benefit from the cost-effectiveness and rapid deployability of small satellites.
What is the projected growth rate for the Small Satellite Market?
The Small Satellite Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 18.5% between 2025 and 2032. This robust growth is attributed to decreasing launch costs, technological miniaturization, and increasing demand for satellite-derived data and services across various sectors.
How is AI impacting the Small Satellite Market?
AI is significantly impacting the Small Satellite Market by enabling enhanced onboard data processing, autonomous mission management, predictive maintenance, and optimized constellation operations. It allows for faster insights, reduces reliance on ground control, improves mission longevity, and boosts overall system efficiency and resilience, despite ongoing considerations regarding security and ethical implications.
What are the key challenges faced by the Small Satellite Market?
Key challenges include the growing concern over space debris and orbital congestion, complex regulatory and licensing hurdles for satellite deployment and spectrum use, limitations in bandwidth and power for smaller platforms, and the high initial investment required for developing and launching constellations. Cybersecurity risks also pose a significant concern for satellite operators.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
- Small Satellite Market Statistics 2025 Analysis By Application (National Security, Science & Environment, Commerce), By Type (Microsatellite, Nanosatellite), and By Region (North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, and Africa) - Size, Share, Outlook, and Forecast 2025 to 2032
- Small Satellite Market Size, Share, Trends, & Covid-19 Impact Analysis By Type (Nanosatellite, Microsatellite, Minisatellite), By Application (National Defense, Civil, Commercial), By Region - North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, and Africa | In-depth Analysis of all factors and Forecast 2023-2030
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
