Online Food Delivery Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 438090 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 248 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
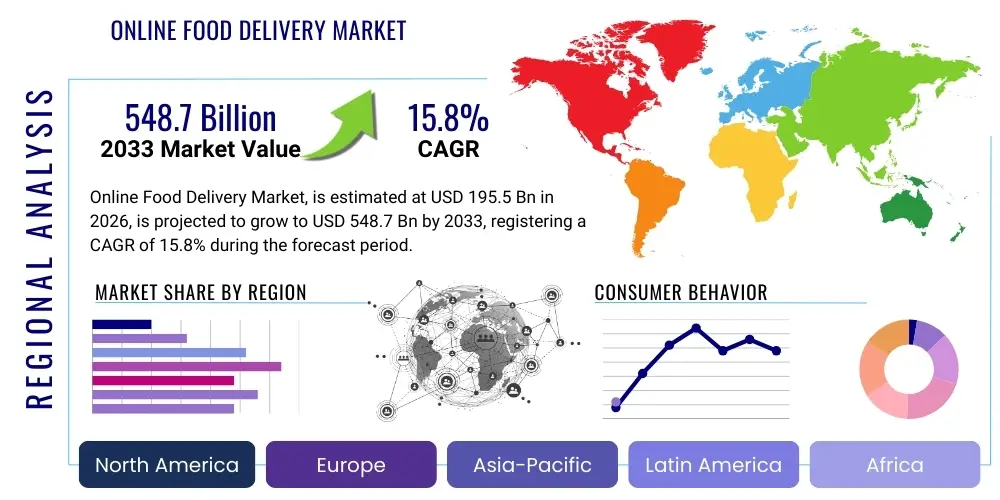
Online Food Delivery Market Size
The Online Food Delivery Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 15.8% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 195.5 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 548.7 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
This robust expansion is primarily fueled by accelerated digitalization, shifting consumer preferences toward convenience, and high urban density across developing economies. The pandemic significantly accelerated the adoption curve globally, embedding online food ordering as a habitual convenience rather than a sporadic luxury. Consequently, market participants are heavily investing in technological infrastructure, including advanced logistics management systems and personalized user interfaces, to handle escalating order volumes and maintain competitive delivery speeds.
Furthermore, the market's size calculation considers both the Platform-to-Consumer (P2C) model, dominated by aggregators like DoorDash and Uber Eats, and the Restaurant-to-Consumer (R2C) model, encompassing large restaurant chains utilizing their proprietary delivery fleets. Future growth projections are underpinned by the expansion into non-food essentials (quick commerce) and the integration of sophisticated AI algorithms for dynamic pricing and route optimization, ensuring that the market capitalization continues its upward trajectory well beyond the current forecast horizon.
Online Food Delivery Market introduction
The Online Food Delivery Market encompasses digital platforms and services facilitating the ordering and distribution of prepared meals from restaurants directly to consumers. Key components include mobile applications and websites offering menus, payment gateways, and real-time tracking. Major applications span quick-service restaurants, fine dining establishments, and virtual ghost kitchens. Benefits include unparalleled consumer convenience, expanded reach for restaurants, and creation of new employment opportunities in the gig economy. Driving factors involve rising internet penetration, increasing disposable incomes, and the persistent urbanization trend that prioritizes time efficiency over traditional meal preparation.
The core functionality of the online food delivery ecosystem revolves around seamlessly connecting three primary stakeholders: the consumer, the restaurant partner, and the independent delivery driver. This complex logistical network requires sophisticated operational management to ensure efficiency, quality control, and customer satisfaction. The operational model has evolved significantly, moving beyond simple order aggregation to encompass comprehensive services such as marketing support, data analytics for menu optimization, and financial services tailored for small and medium-sized restaurant enterprises (SMEs). This expansion of services positions delivery platforms as integral partners rather than mere transactional facilitators, deepening their market penetration and justifying their substantial commission rates.
A major defining characteristic of the modern market is the relentless pursuit of speed and geographical coverage. Platforms are constantly optimizing algorithms to reduce 'last-mile' delivery times, particularly in dense metropolitan areas where consumer expectations are highest. Furthermore, the entry of major grocery and quick commerce players into the prepared meal space is blurring traditional market boundaries, forcing pure-play food delivery operators to innovate rapidly. The market is intrinsically tied to technological advancements, leveraging cloud computing, geolocation services, and predictive modeling to anticipate demand spikes and allocate resources effectively, driving operational improvements and profitability across the supply chain.
Online Food Delivery Market Executive Summary
The Online Food Delivery Market Executive Summary highlights strong business trends driven by the maturation of platform economies and strategic diversification. Regionally, Asia Pacific maintains dominance due to dense populations and early mobile adoption, while North America and Europe focus on consolidation and integrating quick commerce. Segment trends show a clear shift towards convenience-focused models, including subscription services and virtual kitchens (ghost kitchens), capitalizing on optimized operational costs and flexible menu offerings to meet persistent consumer demand for immediacy and variety.
Key business trends indicate a global pivot towards achieving profitability after years of aggressive expansion focused solely on market share. Companies are utilizing advanced data analytics to refine operating models, selectively increasing commission structures, and diversifying revenue streams through advertising placements, fulfillment services for non-food items, and leveraging financial technology (FinTech) solutions tailored for their restaurant partners. Mergers and acquisitions remain a crucial strategy for eliminating competition and consolidating regional strength, ensuring that the market transitions from a high-growth, high-burn phase to a mature, sustainable structure driven by operational leverage.
In terms of regional divergence, emerging markets in Southeast Asia and Latin America represent significant untapped potential, characterized by increasing smartphone penetration and a young, digitally native population eager to adopt convenience technologies. Conversely, mature markets like the United States and Western Europe are characterized by intense competition and efforts to build customer loyalty through exclusive restaurant partnerships and superior service quality, including specialized offerings like drone or robotic delivery trials in select urban areas. Segment-wise, the growth of the ghost kitchen concept is particularly transformative, allowing businesses to rapidly scale their offerings without the overhead associated with traditional dine-in establishments, effectively utilizing the delivery infrastructure built by third-party platforms.
AI Impact Analysis on Online Food Delivery Market
Common user questions regarding AI's impact typically center on three core themes: 'Will AI take away delivery driver jobs?' (Job displacement concern), 'How does AI make my food cheaper or faster?' (Efficiency and pricing expectation), and 'How secure is my data when AI personalizes my recommendations?' (Privacy and personalization concern). Users are seeking assurance that AI implementation will primarily enhance service quality, improve logistics transparency, and drive down costs without compromising data security or fairness for gig workers. The summarized key theme is the expectation of hyper-optimized, friction-less service delivery driven by predictive intelligence, balanced against the ethical considerations of labor force displacement and data governance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are fundamentally reshaping the operational backbone of the Online Food Delivery Market, moving far beyond simple recommendation engines. These technologies are critical for real-time demand forecasting, enabling platforms to accurately predict peak hours, geographical hotspots, and specific menu item popularity. This predictive capability allows for proactive resource allocation, ensuring that the necessary number of delivery personnel are available precisely when and where they are needed, dramatically reducing customer wait times and optimizing driver earnings through minimized idle time. Furthermore, AI models are continuously fed transactional data, geospatial information, and external variables like weather patterns to refine their accuracy, leading to a dynamic operational environment that maximizes throughput efficiency.
The application of AI extends significantly into customer experience and platform profitability. Through advanced natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision, platforms are enhancing customer service chatbots and improving quality control of uploaded restaurant menus. Crucially, AI powers sophisticated dynamic pricing models for both menu items and delivery fees, balancing marketplace liquidity, driver availability, and consumer price sensitivity to maximize total transaction value. In the context of the supply chain, AI is instrumental in developing highly granular, multi-stop route optimization algorithms that account for traffic congestion, delivery sequence priority, and temperature control requirements, ensuring that complex logistics are managed efficiently across highly fragmented urban landscapes.
Addressing the concern of labor impact, while AI enhances operational efficiency, it is primarily focused on automating decision-making and optimization tasks rather than completely replacing human drivers in the foreseeable future. However, AI is central to the development of autonomous last-mile delivery solutions, including ground robots and drones. These pilot programs, though currently limited, rely on sophisticated computer vision, sensor fusion, and reinforcement learning to navigate complex urban environments autonomously. As these technologies mature, AI will transition from merely an optimization tool to a core component of the delivery infrastructure, offering supplementary capacity, especially for high-density, short-distance deliveries.
- AI-driven Dynamic Pricing: Optimizing delivery fees and menu prices based on real-time demand, driver supply, and congestion levels.
- Predictive Demand Forecasting: Utilizing machine learning to anticipate order volume spikes based on historical data, weather, and local events.
- Hyper-Personalized Recommendations: Enhancing customer retention and order value by suggesting meals based on past behavior, dietary restrictions, and time of day.
- Route Optimization Engines: Minimizing delivery mileage and time through complex algorithms considering multiple stops and real-time traffic updates.
- Automated Customer Support: Deployment of NLP-powered chatbots for instantaneous resolution of common issues related to order status and payments.
- Ghost Kitchen Efficiency: Using ML to determine optimal ghost kitchen locations and menu configurations based on localized demand analytics.
- Fraud Detection and Security: Employing AI to monitor suspicious transaction patterns, enhancing payment security for both customers and restaurant partners.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Online Food Delivery Market
The market is predominantly driven by increasing consumer demand for convenience and accelerated digital transformation, while facing restraints related to high commission rates and the inherent operational complexities of managing a decentralized delivery fleet. Opportunities emerge from the expansion of ghost kitchens and the integration of quick commerce, offsetting the impact forces dominated by competitive pressure and evolving regulatory scrutiny over labor practices. These elements combine to create a highly dynamic and intensely competitive market environment where technological superiority and robust logistical infrastructure are paramount to achieving sustainable market share and profitability.
Drivers: A primary driver is the pervasive lifestyle shift favoring convenience, especially among urban millennials and Generation Z, who prioritize time savings over traditional cooking methods. Coupled with this is the continuous improvement in mobile technology and ubiquitous internet access, making ordering frictionless and accessible across socioeconomic strata. Furthermore, the extensive selection offered by platforms—connecting users to diverse culinary options that may not be available locally—signifies a massive improvement over traditional takeout methods. This convenience factor, underpinned by high service reliability and user interface improvements, solidifies online delivery as a necessary utility in modern urban life, rather than a luxury service.
Restraints: Significant restraints include the escalating cost structure for both consumers and restaurant operators. High commission fees levied by third-party platforms often reduce restaurant profitability, leading to friction and encouraging operators to seek direct ordering alternatives or raise menu prices. Operationally, maintaining consistent quality and food temperature during transit remains a logistical challenge, particularly over long distances or during periods of extreme weather. Moreover, regulatory uncertainty surrounding the employment status of gig workers poses a continuous financial risk, as mandated benefits or fixed wages could severely undermine the highly flexible and cost-efficient contractor model currently prevalent in the industry.
Opportunities: The market offers substantial opportunities, particularly in geographical expansion into Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities across Asia and Latin America, where digital adoption is accelerating. The proliferation of ghost kitchens represents a cost-effective scaling mechanism, allowing rapid menu experimentation and market penetration without significant real estate investments. Strategic partnerships with major grocery and retail chains for quick commerce delivery broaden the platform utility, mitigating dependence solely on prepared meals. Additionally, leveraging subscription models (e.g., membership programs offering reduced delivery fees) enhances customer loyalty and provides predictable, recurring revenue streams, stabilizing financial performance.
Impact Forces: The most significant impact force is intense, sustained competition, driving continuous investment in marketing, technology, and driver subsidies, often eroding margins. Secondly, shifting consumer loyalty is a constant threat; customers frequently utilize multiple apps, forcing platforms to compete aggressively on price and speed. Regulatory changes, especially concerning data privacy (GDPR, CCPA) and labor rights, exert considerable pressure on operational compliance and cost management. Finally, the environmental impact of single-use plastics and high traffic volumes generated by delivery fleets is attracting public scrutiny, pushing companies towards sustainable packaging and electric vehicle adoption.
Segmentation Analysis
Segmentation of the Online Food Delivery Market is primarily categorized by Platform Type (Platform-to-Consumer, Restaurant-to-Consumer), Model (Order Only, Order and Delivery), Cuisine Type (Fast Food, Fine Dining, Casual), and Payment Method (Online Payment, Cash on Delivery). This granular categorization allows stakeholders to analyze specific competitive landscapes, identify high-growth niches, and tailor investment strategies. The market is increasingly defined by the distinction between integrated logistics solutions and aggregation services, with operational efficiency serving as the key differentiator across all segments.
The Platform Type segmentation is crucial for understanding market dynamics, distinguishing between third-party aggregators (P2C) that provide broad marketplace visibility and logistics, and proprietary in-house systems (R2C) preferred by large chains like Domino’s or McDonald’s for maintaining control over brand experience and data. While P2C dominates the overall market volume due to scale and variety, R2C models offer higher margins for the restaurant operator. The convergence of these models, where platforms offer white-label delivery services to R2C operators, highlights the fluid nature of the competitive landscape.
Segmentation by Model reveals the evolving depth of platform involvement. The "Order Only" model focuses purely on providing the digital storefront and processing payments, leaving logistics to the restaurant. The dominant "Order and Delivery" model, however, involves the platform managing the end-to-end process, including dispatching, tracking, and customer service. The shift toward the latter is accelerating market growth, as consumers increasingly demand fully integrated, hassle-free service. Furthermore, segmentation by Cuisine Type demonstrates consumer preferences, with fast food and casual dining continuing to hold the largest shares, though the demand for healthy and specialty food options is growing rapidly, prompting platforms to onboard diverse and niche culinary partners.
- By Platform Type:
- Platform-to-Consumer (P2C)
- Restaurant-to-Consumer (R2C)
- By Model:
- Order Only (Marketplace)
- Order and Delivery (Logistics Integration)
- By Cuisine Type:
- Fast Food
- Casual Dining
- Fine Dining
- Specialty/Healthy Food
- By Payment Method:
- Online Payment (Credit/Debit Card, Digital Wallets)
- Cash on Delivery (COD)
- By End-User:
- Residential
- Corporate
- By Geographical Region:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific (APAC)
- Latin America (LATAM)
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
Value Chain Analysis For Online Food Delivery Market
The Value Chain for Online Food Delivery spans upstream activities involving restaurant onboarding and menu management, critical midstream logistics and technology provision, and downstream operations focused on final mile delivery and customer support. The distribution channel is predominantly characterized by the direct-to-consumer model facilitated by indirect service providers (the delivery platforms). Efficiency is derived from streamlining the information flow between consumers, platforms, and restaurants, minimizing friction at every transaction point, while revenue generation is highly dependent on high volume throughput across dense urban areas.
Upstream Analysis: The upstream segment is dominated by content aggregation and partnership management. This involves securing relationships with restaurants, integrating their point-of-sale (POS) systems with the platform's ordering infrastructure, and ensuring accurate menu digitization and pricing. Quality control at this stage is vital, as misinformation or delays in menu updates directly impact consumer trust. Platforms leverage sophisticated data science to identify potential restaurant partners in underserved areas, using predictive modeling to ensure the variety of cuisine meets local consumer demand profiles. The efficiency of the onboarding process is a critical factor in rapidly expanding a platform's reach and density within a competitive region.
Downstream Analysis and Distribution Channels: The downstream portion focuses intensely on the 'last mile' delivery process and post-sale customer relationship management. The primary distribution channel is the digital platform (app/website) which enables the direct flow of goods (food) to the consumer's location. This channel is indirect in the sense that the consumer does not interact directly with the restaurant's proprietary logistics but rather through the platform's aggregated fleet. Excellence in this segment requires robust real-time tracking, rapid issue resolution (e.g., missing items, late arrival), and efficient driver remuneration systems. The drive toward sustainability and reducing the carbon footprint is also becoming a key downstream consideration, influencing the selection of delivery vehicles and packaging materials.
The interplay between technology and logistics defines the value creation. The platform technology itself acts as the core integrator, reducing search costs for consumers and marketing costs for restaurants. Value is captured by the platform through commission fees (from restaurants), delivery fees (from consumers), and increasingly, advertising revenue. Optimization across the entire chain—from automated order injection into the restaurant system to AI-optimized route assignment—is essential for converting high transaction volume into profitable operations, ensuring the sustainable growth of the overall ecosystem.
Online Food Delivery Market Potential Customers
The primary end-users, or potential customers, of the Online Food Delivery Market are residential consumers, particularly working professionals and nuclear families seeking convenience, and increasingly, corporate entities requiring catering or large-scale meal provision for employees. These buyers are characterized by high digital literacy, disposable income, and a willingness to pay a premium for expedited service and variety. The market is continuously expanding its demographic base by offering specialized services catering to health-conscious individuals and those with specific dietary needs, widening the overall addressable market.
The largest segment of potential customers comprises urban residents, typically aged 25 to 45, who value time efficiency over the cost associated with delivery fees. These consumers are habituated to digital convenience and often live in areas with high restaurant density, facilitating fast delivery times. Their purchasing behavior is often influenced by factors such as promotions, loyalty programs, and the breadth of restaurant choice available on a single platform. Marketing efforts are heavily concentrated on maintaining stickiness with this cohort through personalized offers and subscription benefits, ensuring repeat transactional engagement which is vital for platform profitability.
A rapidly growing segment includes suburban and peri-urban dwellers whose local restaurant options might be limited, making the aggregated variety offered by platforms highly attractive. Furthermore, the corporate segment represents significant bulk ordering potential, especially post-pandemic, as many companies provide subsidized or catered meals as an employee benefit. Platforms are developing dedicated corporate accounts and invoicing systems to capture this institutional demand. Identifying potential customers also involves understanding the shift in meal occasions—extending beyond dinner to include lunch, breakfast, and late-night snacks—thereby maximizing the utilization rate of the delivery fleet across all operating hours.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 195.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 548.7 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 15.8% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Uber Eats, DoorDash, Deliveroo, Meituan, Just Eat Takeaway.com, Delivery Hero, Zomato, GrabFood, Swiggy, Rappi, Takeaway.com, Foodpanda, Postmates, Grubhub, Talabat, Wolt, Ele.me, Glovo, SkipTheDishes, Oda |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Online Food Delivery Market Key Technology Landscape
The technological landscape of the Online Food Delivery Market is characterized by heavy reliance on mobile application development, sophisticated geolocation and GIS mapping systems, and advanced cloud computing infrastructure to handle massive transaction volumes. Key technologies include real-time data streaming for instantaneous order processing, artificial intelligence for predictive logistics and dynamic pricing, and robust cybersecurity frameworks necessary to protect sensitive consumer payment data. The successful deployment of these technologies is instrumental in scaling operations efficiently and maintaining competitive delivery times across diverse urban environments.
One critical area of technological innovation is the adoption of advanced Geolocation and Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Platforms utilize precise GPS tracking, often combined with proprietary mapping data, to optimize driver routes, provide highly accurate estimated arrival times (ETAs) to customers, and define optimal delivery zones for restaurant partners. This technology minimizes ‘dead mileage’ and maximizes the number of orders a single driver can complete per hour, directly impacting the operational leverage of the entire business model. Furthermore, the integration of 5G networks is expected to further enhance data transmission speeds, facilitating even more precise real-time communication between the platform, the driver, and the customer, reducing latency critical for timely service updates.
Another transformative technological pillar is the backend infrastructure, built almost entirely on highly scalable cloud platforms (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure). This scalability is essential to manage extreme fluctuations in demand, such as those occurring during major sporting events or holidays, without service degradation. Beyond core ordering and payment processing, FinTech integrations are growing in importance, enabling instant, transparent payments to delivery personnel and streamlined financial reporting for restaurant partners. Looking ahead, robotic process automation (RPA) is being increasingly deployed within ghost kitchen operations to manage inventory and streamline food preparation processes, marking a comprehensive technological penetration across the entire value chain.
Finally, emerging technologies focused on automation, specifically autonomous vehicle delivery and drone trials, represent the next frontier. While fully autonomous delivery remains subject to regulatory and safety hurdles, platforms are heavily investing in Computer Vision and Sensor Fusion technologies required for these systems. These advancements, combined with personalized marketing leveraging advanced data mining techniques, ensure that technology remains the core competitive moat protecting leading market players from disruption.
Regional Highlights
The global Online Food Delivery Market displays significant regional divergence driven by regulatory environments, population density, and technological adoption rates. Asia Pacific (APAC) holds the largest market share, predominantly fueled by high urbanization, early adoption of super-apps (like Meituan and Grab), and massive transaction volumes in high-density markets like China and India. North America and Europe, while having higher average order values (AOV), are characterized by intense competition between a smaller number of large, consolidated players, focusing on service differentiation and loyalty programs to maintain market control.
In the North American context, particularly the United States, the market is characterized by a duopoly or triopoly (DoorDash, Uber Eats, Grubhub), necessitating aggressive pricing strategies, rapid geographic expansion into suburban areas, and extensive investment in non-food delivery services (e.g., groceries, convenience stores) to diversify revenue. Strict labor laws and ongoing litigation concerning worker classification pose continuous challenges, compelling platforms to refine their independent contractor models while facing political and regulatory scrutiny. The European market, similarly competitive, is distinguished by high cross-border consolidation efforts, exemplified by the strategies of Just Eat Takeaway.com and Delivery Hero, focusing on deep market penetration in key Western European nations while expanding into high-growth Central and Eastern European economies.
Asia Pacific's dominance is structural, supported by younger populations, advanced mobile payment ecosystems (bypassing traditional banking infrastructure), and highly effective logistics solutions tailored for dense urban traffic. Countries like India and Indonesia showcase explosive growth, driven by substantial venture capital investment, localized technology development (including two-wheeler delivery optimization), and cultural preferences for frequent small orders. Conversely, the Middle East and Africa (MEA) and Latin America (LATAM) markets, while smaller, exhibit extremely high growth potential. These regions benefit from late-mover advantages, adopting the most efficient operating models rapidly, with major players like Rappi and Talabat heavily investing in expanding beyond major capital cities and integrating innovative payment solutions due to lower credit card penetration.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Market leader by volume; driven by China (Meituan, Ele.me) and India (Zomato, Swiggy). Characterized by high mobile penetration, super-app integration, and two-wheeler logistics optimization.
- North America: High average order value; market maturity with intense competition among top three platforms. Focus on suburban expansion and quick commerce integration (non-food).
- Europe: Consolidation strategy prevalent; strong presence of global players like Just Eat Takeaway.com and Deliveroo. Increasing regulatory focus on driver welfare and environmental sustainability.
- Latin America (LATAM): High growth potential; driven by rapid urbanization and young, digitally savvy populations (e.g., Brazil, Mexico). Rappi is a dominant regional player focusing on hyperlocal services.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): Emerging markets with accelerating digitalization; significant investment in logistics infrastructure in the GCC countries (e.g., Talabat).
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Online Food Delivery Market.- Uber Eats
- DoorDash
- Deliveroo
- Meituan
- Just Eat Takeaway.com
- Delivery Hero
- Zomato
- GrabFood
- Swiggy
- Rappi
- Takeaway.com
- Foodpanda
- Postmates
- Grubhub
- Talabat
- Wolt
- Ele.me
- Glovo
- SkipTheDishes
- Oda
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Online Food Delivery market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary growth driver for the Online Food Delivery Market?
The primary growth driver is accelerated consumer demand for convenience, fueled by increasing urbanization and high penetration of mobile technology, which makes ordering and real-time tracking seamless and efficient. Additionally, the proliferation of ghost kitchens allows for rapid menu diversification and market scalability.
How is Artificial Intelligence (AI) being used to optimize delivery services?
AI is crucial for operational efficiency, primarily through predictive demand forecasting (anticipating peak hours and locations), dynamic pricing adjustments based on real-time traffic and driver availability, and sophisticated route optimization algorithms that minimize delivery time and mileage for the fleet.
What is the difference between P2C and R2C models in the market?
The Platform-to-Consumer (P2C) model involves third-party aggregators providing both the ordering platform and the logistics/delivery service. The Restaurant-to-Consumer (R2C) model involves restaurants (typically large chains) managing their own delivery fleet and ordering system entirely in-house.
What are the main geographical constraints affecting market profitability?
High urban density is typically favorable, but profitability is often constrained by high operational costs stemming from intense competition requiring heavy subsidies, regulatory uncertainty regarding the classification and benefits of gig workers, and the necessity of maintaining robust technological infrastructure.
How are ghost kitchens impacting the future of the Online Food Delivery industry?
Ghost kitchens (virtual restaurants without customer-facing premises) are transformative, allowing restaurant operators to bypass high real estate costs, rapidly launch multiple brands, and optimize food preparation solely for delivery efficiency, significantly boosting scalability and lowering operational barriers to entry.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager