Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 433881 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 246 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market Size
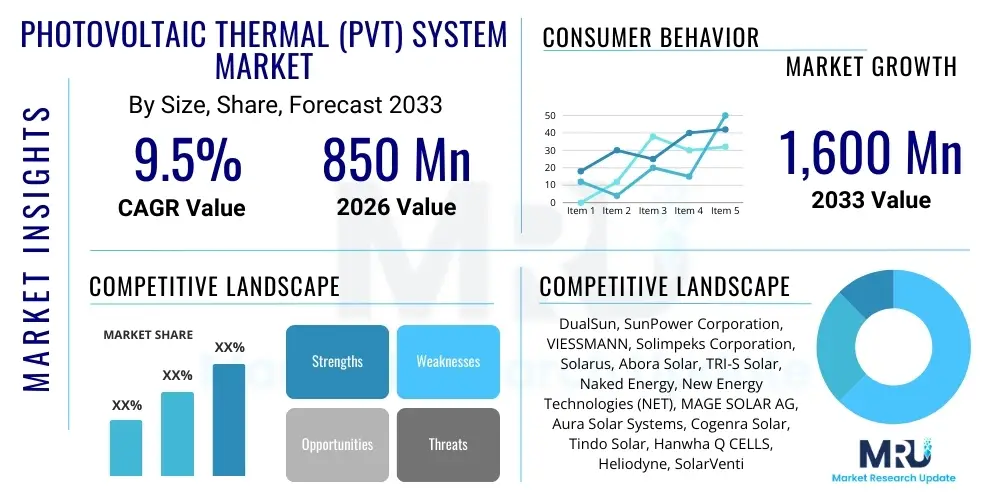
The Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 850 Million in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 1,600 Million by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market introduction
The Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market encompasses innovative technology that integrates conventional photovoltaic (PV) modules, designed to generate electricity, with thermal energy collectors, designed to generate heat. This synergy allows the system to produce both electrical and thermal energy from the same surface area, significantly increasing overall energy conversion efficiency compared to separate PV panels and solar thermal collectors. PVT systems are critical components in the global shift towards high-efficiency, multi-utility renewable energy sources, addressing the increasing demand for sustainable heating, cooling, and power generation solutions across various sectors.
Key applications of PVT systems span residential heating and domestic hot water supply, commercial building climate control, and industrial process heating. The unique benefit of PVT technology lies in its ability to simultaneously utilize incident solar radiation for dual energy output. Furthermore, by actively cooling the PV cells, thermal management improves the electrical efficiency of the PV component, as excessive heat is a primary factor degrading standard PV performance. This dual output capability positions PVT as a crucial enabler for Zero Energy Buildings (ZEBs) and decentralized energy production initiatives, promoting energy independence and reduced carbon footprints globally.
The primary driving factors accelerating market expansion include stringent government regulations promoting renewable energy adoption, escalating energy costs globally, and growing consumer awareness regarding the advantages of highly efficient, space-saving renewable systems. Technological advancements, particularly in collector design, fluid dynamics, and hybrid integration systems, are further enhancing the commercial viability and performance of PVT solutions. The market is also heavily influenced by subsidies and tax credits provided in key regions like Europe and North America to incentivize the installation of these highly efficient solar technologies.
Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market Executive Summary
The Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System market demonstrates robust expansion, underpinned by converging trends in energy efficiency and decarbonization. Business trends show a strong shift towards liquid-based PVT collectors due to their superior thermal transfer capabilities, driving innovation in heat exchange materials and design. Regionally, Europe currently dominates the market share, driven by ambitious renewable energy targets and established regulatory frameworks supporting high-efficiency building standards, particularly in Germany and Scandinavia. However, the Asia Pacific region, led by China and India, is projected to exhibit the highest growth rate, fueled by massive infrastructure development and urgent needs for sustainable power generation to meet rapid urbanization demands. Segmentation trends highlight the residential sector as the largest consumer segment, primarily using PVT for domestic hot water and space heating, while the industrial sector is increasingly adopting concentrating PVT (CPVT) solutions for process heat applications requiring higher temperatures.
Key strategic activities among market participants focus on vertical integration, enhancing manufacturing efficiencies, and forging strategic partnerships with HVAC providers and building developers to streamline installation and adoption. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of specialized PVT manufacturers and large diversified solar energy companies integrating PVT into their product portfolio. Financial performance of key players is increasingly tied to effective supply chain management, particularly regarding copper and aluminum component costs, and successful navigation of regional certification standards. Furthermore, the development of smart PVT systems integrated with AI-driven energy management platforms represents a crucial area for future investment and differentiation, promising optimized energy harvesting and distribution based on real-time climate and demand data.
Regulatory support remains pivotal to market success. Policies such as feed-in tariffs, renewable heat incentives, and performance-based grants significantly lower the initial investment barrier for end-users, accelerating market penetration. The inherent resilience and long operational lifespan of PVT systems contribute to a favorable total cost of ownership (TCO) calculation, making them increasingly attractive compared to separate PV and thermal installations. The market’s future trajectory is contingent upon continued material innovation, standardization of system integration protocols, and sustained governmental commitment to transitioning away from fossil fuel-based heating and cooling solutions.
AI Impact Analysis on Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market
User inquiries regarding the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the PVT market predominantly center on system optimization, predictive maintenance, and smart grid integration. Common user concerns include how AI can manage the dual output (electricity and heat) effectively, ensuring optimal performance under varying weather conditions, and whether AI integration increases system complexity or cost. Expectations are high regarding AI’s capability to maximize energy yield, predict component failures, and seamlessly integrate PVT systems into broader smart home or smart grid ecosystems, ultimately making PVT systems more reliable, efficient, and user-friendly by automating complex control strategies.
AI algorithms are being deployed to dynamically adjust the flow rate of the thermal fluid, ensuring that the solar cells maintain their optimal operational temperature, thereby maximizing both electrical and thermal output throughout the day and across seasonal changes. Machine learning models use historical weather data, current irradiance levels, and internal temperature readings to predict future performance and preemptively adjust system parameters. This level of optimization drastically reduces energy wastage and increases the overall system Coefficient of Performance (COP). The implementation of digital twin technology, driven by AI, further aids in complex urban planning scenarios, simulating the integration of PVT arrays onto diverse building architectures to forecast optimal design specifications before physical installation.
Furthermore, AI facilitates advanced fault detection and diagnostics (FDD). By analyzing sensor data streams from pressure gauges, temperature probes, and power meters, AI can instantly detect anomalies indicative of potential issues like pump failure, leakage, or fouling in heat exchangers. This predictive capability shifts maintenance schedules from reactive to preventive, extending system lifespan and minimizing downtime, which is a major factor in improving the TCO for large-scale commercial and industrial PVT installations. The seamless integration of these systems into demand-side management programs via AI ensures that the energy generated aligns efficiently with fluctuating user demand and utility grid requirements.
- AI optimizes PVT performance by controlling fluid circulation rates to maintain peak electrical and thermal efficiency regardless of weather conditions.
- Machine learning models enable highly accurate predictive maintenance, identifying component wear or failure signs (e.g., pump issues or thermal degradation) before critical breakdown occurs.
- AI facilitates seamless integration into smart grids, managing dual energy outputs for effective load balancing and participation in demand response programs.
- Advanced analytics provide real-time feedback on system efficiency, assisting homeowners and facility managers in maximizing energy self-consumption.
- Generative AI tools are streamlining the design phase, offering optimized PVT configurations based on specific geographical and architectural constraints.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market
The Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System market is propelled by key drivers such as escalating global commitments to renewable energy and significant improvements in energy conversion efficiency offered by hybrid systems. However, the market faces restraints, primarily high initial installation costs compared to conventional separate PV and thermal systems, and complexity in system integration and plumbing, requiring specialized labor. Opportunities are abundant, centered on expanding applications in industrial process heat, and developing low-cost, modular PVT collectors suitable for mass production and easier installation. The market is subject to intense impact forces from environmental regulations pushing for building energy efficiency and the sustained volatility of conventional energy prices, making PVT an increasingly cost-competitive long-term solution.
Drivers prominently include regulatory mandates, such as the EU’s Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD), which necessitate superior energy performance in new constructions and renovations, thereby favoring integrated, high-efficiency technologies like PVT. The technological driver stems from the recognized performance advantage: cooling the PV cells significantly boosts electrical output while simultaneously producing useful thermal energy. This combined efficiency addresses the critical need for space optimization in densely populated urban environments where roof space is limited. Furthermore, subsidies and fiscal incentives offered by governments globally act as a powerful accelerator, reducing the financial burden associated with the higher upfront capital expenditure of PVT systems.
Restraints are primarily focused on market penetration challenges. The lack of standardized installation procedures and the relatively high specialization required for maintenance currently limit widespread adoption, especially in emerging economies. Moreover, the long payback period for some commercial PVT installations, despite lower operational costs, can deter immediate investment decisions. Opportunities for market expansion exist in the development of lightweight, aesthetically pleasing PVT facade integration systems, opening up non-roof applications, and the strategic focus on concentrated PVT (CPVT) for industrial applications that require medium-to-high temperature thermal outputs (e.g., textile, food processing, and chemical industries). Impact forces, such as the ongoing global emphasis on sustainability and the fluctuating cost of natural gas, continuously enhance the value proposition of reliable, decentralized solar solutions.
Segmentation Analysis
The Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System market segmentation offers a detailed view of market structure based on technological configuration, application suitability, and geographical deployment. Primary segmentation revolves around the type of heat transfer medium (liquid or air), which significantly impacts the system’s design complexity and typical applications. Liquid-based systems are dominant, used extensively in residential and commercial settings for hot water, while air-based systems are often used for pre-heating ventilation air and space heating. Application segmentation reveals residential use as the foundational market, but commercial and industrial applications are exhibiting faster growth due to the scale and intensity of their heating and cooling demands.
Technology segmentation distinguishes between Flat Plate PVT and Concentrating PVT (CPVT). Flat Plate PVT systems are the most common due to their simplicity and ability to function effectively with diffuse radiation, making them ideal for standard building integration. Conversely, CPVT systems utilize optics to focus solar radiation, achieving much higher temperatures necessary for industrial processes or large-scale utility operations, although they require sun-tracking mechanisms. Geographic segmentation is crucial, with distinct regulatory environments and climate patterns dictating market dominance, highlighting Europe's technological leadership and Asia Pacific's massive volume potential.
Further analysis of the end-user base confirms that while residential uptake is driven by consumer desire for energy independence and lower utility bills, commercial segment growth is fueled by regulatory pressures (e.g., mandatory renewable energy deployment in new public buildings) and the need for significant operational cost reductions in large facilities like hospitals and hotels. This structural diversity necessitates highly customized product offerings and segmented marketing strategies by market players to address specific regional and application requirements effectively, driving continued product diversification across all major segments.
- By Type
- Liquid-Based PVT Collectors (Dominant for hot water and space heating)
- Air-Based PVT Collectors (Used primarily for pre-heating ventilation)
- Hybrid (Glazed and Unglazed) PVT Systems
- By Technology
- Flat Plate PVT (Most common, versatile for building integration)
- Concentrating PVT (CPVT) (High-temperature output for industrial use)
- By Application
- Residential (Domestic hot water, space heating)
- Commercial (Hotels, hospitals, offices, schools)
- Industrial (Process heat, specialized climate control)
- Utility-Scale (District heating and cooling networks)
- By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific (APAC)
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
Value Chain Analysis For Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market
The value chain for the Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System market begins with upstream material suppliers, focusing on key components like silicon wafers for PV cells, specialized thermal absorber materials (e.g., copper, aluminum), heat transfer fluids (glycol or water mixtures), and high-grade glazing materials. Efficient sourcing and quality control at this stage are paramount, as material costs constitute a significant portion of the total system expenditure. Manufacturers then integrate these components, requiring specialized assembly processes that combine electrical wiring, fluid tubing, and insulation. The complexity of integrating these two distinct technologies demands high precision engineering and specialized manufacturing facilities capable of producing integrated hybrid collectors efficiently and at scale.
The midstream involves system integrators and distributors. Due to the hybrid nature of PVT, distribution channels often overlap between electrical component suppliers and HVAC specialists. Direct channels are prevalent for large commercial and utility projects, where manufacturers handle sales, design, and installation oversight directly to ensure optimal system performance and adherence to specifications. Indirect channels, utilizing specialized wholesalers and authorized dealers, dominate the residential segment, leveraging established networks of plumbers, electricians, and certified solar installers. Training and certification of these installation professionals are critical components of maintaining product quality and safety downstream.
Downstream activities center on installation, commissioning, operation, and maintenance (O&M). Unlike standard PV panels, PVT systems require expertise in both electrical and hydraulic systems, elevating the complexity and cost of installation. End-users receive support through long-term performance monitoring services, often facilitated by IoT sensors and remote diagnostic platforms. The effective management of the thermal fluid, pump functionality, and heat exchanger efficiency are primary focuses of O&M. Strong partnerships with local installation firms and sustained efforts in professional training are essential for manufacturers to reduce installation risks and ensure customer satisfaction, thereby strengthening the overall value chain and fostering long-term market growth.
Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market Potential Customers
The primary customers for Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) systems are highly diverse, spanning residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, all unified by the objective of reducing energy expenditures and enhancing sustainability profiles. Residential homeowners, particularly those in high-cost energy regions or those building custom, energy-efficient homes, represent a critical segment, valuing PVT’s ability to provide both electricity and abundant hot water using minimal roof space. This customer group is primarily interested in return on investment (ROI) through utility bill savings and governmental incentives, often favoring simpler, liquid-based flat plate systems.
The commercial sector constitutes a rapidly expanding customer base, encompassing institutions such as hotels, hospitals, universities, and large office complexes, all of which have substantial, simultaneous demands for electricity (lighting, IT infrastructure) and thermal energy (hot water for sanitation, space heating/cooling). These commercial entities seek high-efficiency solutions that comply with corporate sustainability mandates and reduce large operational overheads. The decision-making process here involves facilities managers and CFOs, who prioritize long-term reliability, low maintenance, and scalability of the PVT deployment.
Industrial users, particularly those requiring medium-to-high temperature process heat (e.g., food processing, brewing, chemical manufacturing), are emerging as major potential buyers, especially for Concentrating PVT (CPVT) technology. For these customers, PVT systems offer a clean, stable source of thermal energy that can replace fossil fuels in specific manufacturing steps. Utility-scale customers, including municipalities developing district heating and cooling networks, represent a highly strategic segment, utilizing large arrays of PVT collectors to provide centralized, efficient thermal energy distribution to entire urban zones, driven by city-level decarbonization targets and energy security considerations.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 850 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 1,600 Million |
| Growth Rate | 9.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | DualSun, SunPower Corporation, VIESSMANN, Solimpeks Corporation, Solarus, Abora Solar, TRI-S Solar, Naked Energy, New Energy Technologies (NET), MAGE SOLAR AG, Aura Solar Systems, Cogenra Solar, Tindo Solar, Hanwha Q CELLS, Heliodyne, SolarVenti, Sunroof, SolaX Power, PV-T.eu. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market Key Technology Landscape
The technological landscape of the Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) market is characterized by ongoing innovation aimed at improving thermal extraction efficiency, reducing heat losses, and enhancing system aesthetics for better building integration. A central focus is on optimizing the absorber design, moving beyond simple copper tubes to microchannel heat exchangers and advanced fluid dynamics that maximize contact between the thermal fluid and the photovoltaic cells. Modern PVT systems utilize specialized selective coatings on the absorber plate to maximize solar absorption while minimizing thermal re-radiation, thereby increasing the useful heat collected. Furthermore, advances in insulation materials, particularly vacuum insulation panels (VIPs), are being incorporated into glazed PVT collectors to drastically reduce heat loss, making them effective even in colder climates or high-temperature applications.
Another significant area of development is the integration of advanced control systems. These electronic controllers, often utilizing microprocessors and sophisticated sensors, manage the synchronization of electricity generation and heat extraction. Modern controllers employ variable speed pumps and advanced algorithms to prioritize either electrical or thermal output based on real-time household or facility demand, meteorological data, and energy storage levels. This "smart" control capability is crucial for maximizing the economic returns of the system. In the concentrating PVT (CPVT) segment, the technology focuses on high-precision optics (mirrors or lenses) and effective tracking systems to concentrate sunlight onto small, high-efficiency multijunction PV cells, while the excess heat is simultaneously captured for thermal output, pushing the envelope of total energy conversion efficiency above 80%.
Moreover, Building Integrated Photovoltaic Thermal (BIPV/T) systems represent a growing technological segment, where the PVT collector serves not only as an energy generator but also as an integral part of the building envelope (e.g., facade, roofing material). This blending of functions offers aesthetic appeal and reduces material costs associated with traditional mounting systems. Material science breakthroughs are introducing lighter, more durable polymers and composite materials for collector construction, reducing weight and simplifying installation. The adoption of Phase Change Materials (PCMs) for integrated thermal energy storage within the PVT panel is also a burgeoning technology, allowing for delayed use of thermal energy, further enhancing the system's overall utility and matching supply more closely with peak demand periods.
Regional Highlights
Geographically, the Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market exhibits highly segmented growth patterns driven by regional climate conditions, energy policies, and construction industry maturity. Europe maintains a leading position, anchored by stringent regulatory frameworks promoting energy efficiency in buildings (e.g., nearly Zero Energy Buildings mandates) and substantial government subsidies for renewable heating solutions in countries like Germany, Austria, and the Netherlands. The region benefits from established supply chains and high awareness among consumers and developers regarding hybrid solar technologies, focusing heavily on residential and commercial building applications.
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region is projected to register the fastest growth rate during the forecast period. This rapid expansion is primarily attributable to massive infrastructure investments in China and India, coupled with critical public policy initiatives aimed at combating air pollution and enhancing rural electrification. Although current adoption levels are lower than in Europe, the sheer scale of energy demand and the push for decentralized renewable solutions present enormous market potential, particularly in urban residential complexes and new industrial zones seeking stable, clean energy inputs. Japan and South Korea also contribute significantly, focusing on technological leadership and high-efficiency product deployment.
North America, led by the US and Canada, represents a mature market with high growth potential, driven by state-level incentives (especially in California and Northeastern states) and increasing consumer interest in energy resilience. The focus in North America is shifting toward high-performance PVT systems that can efficiently handle extreme temperature variations common across the continent. Meanwhile, Latin America and the Middle East & Africa (MEA) are emerging regions. MEA holds long-term promise due to high solar irradiance levels, although market penetration is currently hampered by lack of robust government incentives and infrastructural constraints. Adoption in these regions is typically restricted to high-end commercial projects, specialized agriculture, and remote power generation applications.
- Europe: Market leader due to advanced regulation (ZEB mandates) and strong subsidy programs; high concentration of specialized PVT manufacturers; strong residential and commercial uptake.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Fastest growing market driven by population density, rapid urbanization, large-scale clean energy targets, and government focus on rural and urban energy security (especially China and India).
- North America: Stable growth driven by state-level tax credits and incentives; emphasis on integrating PVT with smart home energy management systems and dealing with diverse climatic challenges.
- Middle East & Africa (MEA): Emerging market with immense solar resource potential; current adoption focused on high-end commercial, industrial process heat, and desalting applications.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market.- DualSun
- SunPower Corporation
- VIESSMANN
- Solimpeks Corporation
- Solarus
- Abora Solar
- TRI-S Solar
- Naked Energy
- New Energy Technologies (NET)
- MAGE SOLAR AG
- Aura Solar Systems
- Cogenra Solar
- Tindo Solar
- Hanwha Q CELLS (Hybrid Offerings)
- Heliodyne
- SolarVenti
- Sunroof
- SolaX Power
- PV-T.eu
- AET (Advanced Energy Technologies)
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary advantage of a PVT system over separate PV and solar thermal collectors?
The primary advantage of a PVT system is its superior overall energy conversion efficiency, often exceeding 80%, compared to conventional systems. It generates both electricity and thermal energy from the same footprint, saving significant space and improving electrical output by actively cooling the PV cells, which otherwise lose efficiency due to heat.
Are PVT systems cost-effective for residential installations?
While the initial cost of PVT systems is generally higher than separate PV installations, they are cost-effective in the long term, particularly in regions with high energy costs or strong governmental renewable heating incentives. The dual output reduces reliance on conventional heating sources, leading to a favorable total cost of ownership and accelerated payback period.
What types of applications are best suited for Concentrating PVT (CPVT) technology?
Concentrating PVT (CPVT) technology is best suited for applications requiring medium to high-temperature thermal energy (above 80 degrees Celsius), such as industrial process heat in manufacturing, large-scale district heating networks, or commercial cooling systems (solar thermal cooling).
How does the performance of PVT systems vary across different climates?
PVT systems perform effectively across diverse climates. In cold climates, high-efficiency glazed PVT collectors with superior insulation minimize heat loss. In hot climates, the active cooling of the PV cells by the thermal fluid ensures that the electrical output remains high, preventing the efficiency drop experienced by standard PV panels.
What are the main segments driving future growth in the PVT market?
Future growth in the PVT market is primarily driven by the Commercial segment (hotels, hospitals) due to large and simultaneous energy needs, and the Industrial segment, where CPVT solutions are increasingly adopted for sustainable process heat, alongside continuous strong residential demand for integrated energy solutions.
The Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by global sustainability goals and the demand for higher energy conversion efficiency in solar technology. Market dynamics are heavily influenced by the interplay between regulatory support, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences towards holistic energy solutions. The European market, characterized by mature regulatory frameworks and a focus on nearly Zero Energy Buildings (nZEB), continues to set the standard for PVT adoption, particularly in residential and small commercial applications where space efficiency is paramount. Liquid-based PVT collectors, which efficiently produce hot water and electricity, dominate this segment. However, the future trajectory points towards rapid acceleration in the Asia Pacific region, fueled by unprecedented urbanization and massive infrastructure projects, notably in China and India, where large-scale deployment of PVT systems is crucial for meeting rapidly escalating energy demands and addressing localized pollution concerns. The competitive landscape features specialized firms and diversified energy giants, all vying to improve thermal extraction mechanisms and system integration aesthetics. Key challenges remain centered on reducing the initial capital investment and standardizing installation practices to broaden market accessibility. Innovation in materials, specifically the use of advanced heat transfer fluids and microchannel absorbers, is critical to further enhance performance metrics and drive down the overall cost of energy delivered. The integration of smart technologies, particularly AI and IoT, is redefining the operational efficiency and management of PVT installations. AI algorithms enable predictive control over fluid flow and temperature management, maximizing the synergistic benefits of the hybrid system under variable solar irradiance and load conditions. This technological sophistication facilitates seamless integration into smart grids and demand response programs, enhancing the value proposition for large commercial and utility customers. The focus on Building Integrated Photovoltaic Thermal (BIPV/T) systems underscores a growing trend toward aesthetic and multi-functional building materials, moving PVT from a simple rooftop fixture to an essential architectural component. Regulatory stability, especially the continuation of feed-in tariffs and renewable heat incentives, remains a vital external factor influencing market growth rates and investor confidence globally. Market segmentation highlights the strategic importance of the industrial sector, where Concentrating PVT (CPVT) technology offers a viable, clean alternative for medium-to-high temperature process heat, replacing fossil fuel dependency in sectors like food and beverage, and textiles. The value chain complexity, integrating both electrical and hydraulic expertise, requires strong cross-industry partnerships between solar installers and HVAC professionals. This interdependence ensures quality installations and robust long-term maintenance, critical for realizing the high lifetime savings promised by PVT systems. The overall market outlook is overwhelmingly positive, driven by the dual imperative of energy security and climate change mitigation, positioning PVT technology as a cornerstone of the next generation of decentralized renewable energy infrastructure. Continuous research into polymer-based collectors, designed for lower weight and cheaper manufacturing, promises to unlock mass market appeal, further democratizing access to high-efficiency solar energy across developing and mature economies alike, cementing the PVT market's place in the transition to net-zero energy systems. The global push for hydrogen production, utilizing high-efficiency solar thermal energy, also presents a future opportunity for high-temperature PVT solutions.
Further detailed analysis indicates that the liquid-based PVT collectors segment holds the largest market share, predominantly due to its established use in domestic hot water applications, which represents the most common thermal energy requirement in residential and commercial settings. These systems, utilizing water or glycol mixtures, are straightforward in design and integrate easily with existing plumbing and heating infrastructure. The market penetration of glazed collectors, which offer superior thermal performance by reducing convective and radiative heat losses, is higher in regions characterized by colder winters, ensuring year-round efficiency. Conversely, unglazed PVT collectors, while having lower thermal output, are cost-effective and often used for applications requiring lower temperatures, such as swimming pool heating or air pre-heating. The trend toward modular and aesthetically appealing designs is strongly influencing product development, as manufacturers aim to minimize visual impact and streamline the installation process, targeting the high-end residential and architectural design markets. The industrial application segment, while smaller in volume today, is experiencing the highest proportional growth, primarily driven by the adoption of CPVT systems. These concentrating technologies are crucial for reaching the high temperatures (up to 150°C) needed for industrial drying, sterilization, and steam generation processes, offering a critical pathway for heavy industry decarbonization. Government policies emphasizing industrial energy audits and mandating the use of best available technologies (BAT) are accelerating this shift.
The competitive strategy among key market players is diversifying, with some companies focusing exclusively on premium, high-efficiency PVT panels targeting the European and North American niche markets, emphasizing certifications and long warranties. Other larger players, such as established PV manufacturers, are integrating PVT into broader energy management packages, leveraging their existing distribution channels and brand recognition to scale market penetration in APAC. Strategic alliances with construction and HVAC firms are becoming commonplace to address the system integration complexities inherent in PVT technology. For instance, partnerships that bundle PVT installation with heat pump technology or advanced insulation are driving complete, energy-efficient building solutions. The supply chain resilience remains a key vulnerability, particularly concerning the sourcing of high-purity silicon and specialized metals like copper, which have faced price volatility. To mitigate this, manufacturers are exploring alternative materials and streamlined manufacturing techniques, including the use of thin-film PV cells integrated with thermal exchangers, which promise lighter weight and lower material consumption. The long-term success of the market relies heavily on reducing the perception of PVT as a niche or overly complex solution, focusing instead on quantifiable metrics of efficiency gain and reduced lifetime operating costs, supported by strong performance data and standardized product testing protocols across all major regions.
The robust growth projection for the Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market, particularly the anticipated climb to $1.6 billion by 2033, underscores its fundamental role in the global energy transition. This forecast is not merely based on general renewable energy trends but on the specific technological advantages PVT offers—namely, its exceptional energy density per square meter and its superior total efficiency. This density makes PVT particularly attractive for high-density urban areas where roof space is at a premium. The market expansion is intrinsically linked to the parallel growth of the smart home technology sector, as PVT systems are increasingly being packaged with smart inverters, thermal storage tanks, and centralized energy monitoring platforms. These integrated solutions offer homeowners and facility managers unprecedented control and optimization capabilities, allowing them to balance instantaneous energy needs with long-term storage objectives, whether electrical or thermal. Furthermore, the regulatory environment continues to evolve in favor of such integrated technologies. Policymakers are recognizing that single-source energy systems (like stand-alone PV) often fail to address the critical need for heating and cooling efficiently, pushing standards that favor hybrid solutions that comprehensively tackle a building’s entire energy load. The sustained investment in research and development is also pivotal; current R&D focuses on creating PVT collectors that are more durable, aesthetically versatile (e.g., colored or transparent PVT options for architectural integration), and less reliant on high-cost materials. This focus on durability and visual appeal is crucial for breaking into the high-end architectural design market and accelerating the adoption of BIPV/T solutions. The global energy storage market, both electrical (batteries) and thermal (water tanks, PCM), serves as a critical complementary segment to the PVT market. Effective storage mechanisms enable PVT systems to decouple energy generation from immediate consumption, substantially increasing the self-consumption rate and maximizing the economic benefits for the end-user. As the cost of both battery storage and advanced thermal storage solutions decreases, the overall economic viability and market attractiveness of integrated PVT systems will continue to rise exponentially, ensuring the projected CAGR of 9.5% remains achievable throughout the forecast period.
The geopolitical landscape also indirectly influences the PVT market. Energy crises and supply chain disruptions affecting natural gas and other fossil fuels heighten the perceived value and necessity of energy independence, which PVT systems strongly promote. This enhanced energy security is a compelling driver for governments and large corporations. Additionally, the development of standardized testing procedures and performance reporting methodologies, spearheaded by international bodies like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Energy Agency (IEA), is instrumental in building customer confidence and streamlining global trade of PVT products. These standards ensure comparability and verified performance claims, mitigating risks associated with new and complex hybrid technologies. Overall, the PVT market is transitioning from a niche technology to a mainstream solution for efficient, decentralized renewable energy generation, supported by a convergence of technological innovation, regulatory tailwinds, and compelling economic fundamentals that prioritize total system efficiency and long-term sustainability over simple low-cost solutions.
The Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) System Market is strategically positioned to capitalize on global energy transition efforts. The market size estimation reflects a trajectory driven by mandatory building efficiency codes and incentives promoting solar thermal contributions. Key market players are investing heavily in R&D to improve collector design, particularly focusing on micro-channel heat exchangers for enhanced thermal transfer and reduced pumping power requirements. The segment analysis confirms that Liquid-Based PVT Collectors will retain dominance, primarily serving residential and light commercial sectors for domestic hot water and space heating. However, the higher growth rate projected for Concentrating PVT (CPVT) highlights the industrial sector's increasing need for high-temperature solar solutions to replace natural gas in process heat applications. Regional growth is polarized, with Europe emphasizing regulatory compliance and quality, while APAC focuses on volume and affordability to address mass market needs. The integration of AI for predictive diagnostics and dynamic energy management is becoming a standard feature, moving PVT from a passive energy collector to an intelligent energy generator. The high initial cost remains the primary restraint, necessitating sustained government subsidies and technological innovation to lower component costs and simplify installation procedures, thereby achieving mass market penetration and fulfilling the ambitious growth projections towards USD 1,600 Million by 2033. The long-term profitability of PVT systems is strongly linked to their ability to integrate seamlessly with existing HVAC infrastructure and contribute meaningfully to zero-energy building goals. This transition requires significant investment in workforce training to ensure the availability of skilled labor capable of managing both the electrical and hydraulic aspects of these complex hybrid systems, ensuring reliable operation and effective maintenance across all segments.
Market research indicates a strong trend towards aesthetic integration, driven by the Building Integrated Photovoltaic Thermal (BIPV/T) segment. This segment aims to make PVT systems visually appealing, acting as roofing or facade materials, thereby eliminating the separate cost of conventional roofing materials and improving overall project economics. The continuous evolution of polymer-based PVT collectors offers significant potential for reducing system weight and manufacturing costs compared to traditional metallic designs, though performance longevity remains an area of focus. Furthermore, the role of PVT in district heating and cooling networks is gaining traction in dense urban areas, particularly in Scandinavia and Central Europe, where large centralized PVT arrays contribute to utility-scale thermal energy supply. This expansion into utility applications signals the technology’s maturation beyond standalone residential systems. The competitive advantage is increasingly shifting toward manufacturers who can offer complete, pre-engineered system solutions that include advanced controllers, heat pumps, and thermal storage tanks, minimizing the complexity for installers and end-users. The interplay of high energy prices and robust climate policy ensures a sustained favorable environment for PVT market expansion globally.
