Poliomycetes Vaccine Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 434900 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 241 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Poliomycetes Vaccine Market Size
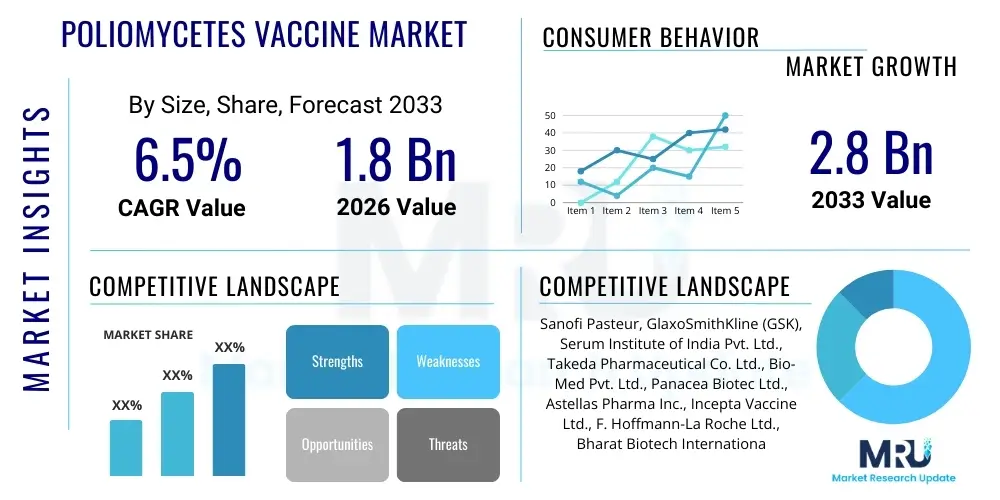
The Poliomycetes Vaccine Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 1.8 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 2.8 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033. This consistent growth is primarily driven by sustained global immunization efforts, particularly the ongoing commitment of international organizations like the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) to eliminate the remaining endemic poliovirus strains, demanding continuous large-scale vaccine procurement and distribution worldwide.
Poliomycetes Vaccine Market introduction
The Poliomycetes Vaccine Market encompasses the development, manufacturing, and distribution of biological preparations designed to provide immunity against the poliomyelitis virus (Poliomycetes). These vaccines are critical tools in public health strategies, aimed at the global eradication of polio. The market historically features two main product types: Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV), administered via injection, and Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV), administered orally. Both vaccines play distinct yet complementary roles in the eradication effort, with IPV being utilized extensively in routine immunization schedules in high-income countries and increasingly adopted globally due to its non-reversion risk, while OPV remains crucial for outbreak response in endemic and high-risk regions due to its ability to induce mucosal immunity and cost-effectiveness in mass campaigns.
Major applications of Poliomycetes Vaccines include national routine immunization programs, targeted supplementary immunization activities (SIAs) in areas with low vaccination coverage, and rapid response campaigns following detected outbreaks of wild poliovirus (WPV) or circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV). The immediate benefits of these vaccines are measured in the reduced incidence of paralytic poliomyelitis and the eventual achievement of disease-free status globally, contributing significantly to public health infrastructure and lowering the long-term healthcare burden associated with lifelong paralysis and disability. The market dynamic is heavily influenced by governmental purchasing power and the centralized procurement strategies employed by international bodies like UNICEF and WHO, ensuring vaccine accessibility in low- and middle-income countries.
Driving factors for market expansion include mandatory childhood immunization policies implemented across most developed and developing nations, guaranteeing a steady baseline demand. Furthermore, the strategic shift recommended by the WHO to transition from trivalent OPV (tOPV) to bivalent OPV (bOPV) and the phased introduction of IPV into all routine programs worldwide (the Polio Eradication Endgame Strategy) necessitates large-scale production and supply chain adaptation for manufacturers. Ongoing surveillance and the necessity of maintaining high immunization coverage, even in polio-free regions, to prevent reintroduction of the virus, sustain the long-term demand curve for both IPV and novel polio vaccines, such as novel Oral Polio Vaccine type 2 (nOPV2), designed to mitigate cVDPV risks.
Poliomycetes Vaccine Market Executive Summary
The Poliomycetes Vaccine Market is characterized by intense regulatory scrutiny and significant reliance on public sector procurement, forming a highly specialized business ecosystem where long-term contracts and adherence to global health standards dictate success. Current business trends show a strategic migration towards Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) technology due to the successful reduction of wild poliovirus transmission and the need to mitigate the risks associated with circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV) strains inherent in traditional OPV use. This transition is driving innovation in production capacity and cold-chain logistics, especially for combination vaccines that include IPV components. Manufacturers are investing heavily in ensuring compliance with the stringent quality standards required by prequalification bodies like the WHO, which is essential for participation in global tenders. The market structure remains oligopolistic, dominated by a few large pharmaceutical entities capable of high-volume, cost-effective manufacturing, coupled with specialized local producers catering to regional demands.
Regional trends indicate that Asia Pacific (APAC) and Africa remain the primary regions driving volumetric demand, fuelled by large birth cohorts and continued supplementary immunization activities, particularly in countries designated as high-risk or those facing cVDPV outbreaks. North America and Europe, which have achieved polio elimination decades ago, focus primarily on ensuring continuous IPV supply for routine childhood schedules and maintaining strict surveillance, representing high-value, stable markets. Conversely, the market in Latin America and the Middle East is marked by periodic procurement cycles dictated by national vaccination policies and occasionally volatile geopolitical landscapes affecting vaccine distribution continuity. Investment in localized production capacity, particularly in India and China, is a significant emerging regional trend impacting global supply dynamics and pricing stability.
Segmentation trends reflect the sustained dominance of the Injectable (IPV) segment in terms of market value, driven by its higher production complexity and mandated use in many global vaccination schedules post-eradication certification. However, the Oral (OPV) segment, specifically the bOPV and the novel nOPV formulations, continues to lead in terms of volume due to its necessity in mass campaigns and outbreak response, particularly in low-income settings. By end-user, Governmental Immunization Programs represent the overwhelming segment share, dwarfing institutional buyers like hospitals and private clinics, underscoring the public health focus of this market. Technological advancements are concentrating on developing enhanced stability formulations and combination vaccines (e.g., DTP-HepB-Hib-IPV) to simplify immunization schedules and improve compliance globally, thus influencing segment growth profiles.
AI Impact Analysis on Poliomycetes Vaccine Market
User inquiries regarding AI's influence on the Poliomycetes Vaccine Market frequently revolve around three core themes: enhancing outbreak predictability, optimizing the complex global supply chain, and accelerating next-generation vaccine development. Users are specifically concerned about how AI can integrate vast epidemiological datasets, including surveillance results, population movement patterns, and environmental factors, to provide predictive analytics capable of forecasting potential cVDPV outbreaks with higher precision than traditional modeling. Furthermore, there is strong interest in utilizing machine learning algorithms to fine-tune the highly sensitive cold chain logistics required for IPV distribution across challenging geographies, minimizing wastage and ensuring prompt availability. Finally, stakeholders seek to understand AI's role in accelerating the discovery of novel vaccine formulations or improving the manufacturing yields of current vaccines, reducing dependence on large-scale cell culture methods and potentially lowering costs associated with global eradication efforts.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (ML) platforms is poised to revolutionize the operational efficiency and strategic direction of the Poliomycetes Vaccine Market. In manufacturing, AI can optimize fermentation processes and quality control, ensuring batch consistency and maximizing output while minimizing contamination risks, thereby enhancing the reliability of the global vaccine supply. From a public health perspective, AI tools enable dynamic risk mapping, allowing global health organizations and national governments to allocate scarce resources, such as emergency vaccine stockpiles (like nOPV), more effectively to areas presenting the highest immediate risk of transmission or outbreak escalation. This shift from reactive response to predictive, preemptive intervention represents a monumental transformation in polio eradication strategy.
Moreover, AI algorithms are instrumental in the complex task of sequencing and analyzing poliovirus strains isolated through environmental surveillance or patient samples. By rapidly identifying genetic drift or mutation patterns, AI facilitates faster decisions regarding vaccine composition updates and surveillance sensitivity adjustments. The potential for AI in clinical trial design, particularly for new formulations aimed at improved immunogenicity or thermal stability, cannot be overstated, streamlining R&D pathways and accelerating the deployment of next-generation tools required to tackle the final stages of eradication, especially in fragile or conflict-affected settings where timely intervention is paramount.
- AI-powered predictive modeling for cVDPV outbreak forecasting and spatial risk assessment.
- Optimization of vaccine cold chain logistics and inventory management through ML algorithms.
- Acceleration of novel vaccine research (e.g., enhanced thermal stability, mucosal immunity boosters) using in-silico drug discovery and lead compound prioritization.
- Enhancement of manufacturing yield and consistency through automated process control and predictive maintenance in bioreactors.
- Real-time analysis of genomic surveillance data for rapid identification of emerging viral strains and appropriate public health response mobilization.
- Personalization of immunization schedules based on regional epidemiological data and individual risk factors, improving coverage efficiency.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Poliomycetes Vaccine Market
The Poliomycetes Vaccine Market is significantly shaped by a unique combination of sustained governmental commitment, inherent biological constraints, and pervasive sociopolitical dynamics. The primary drivers include the universally mandated nature of polio vaccination in childhood immunization schedules and the substantial financial backing provided by the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) and donor nations, ensuring predictable, high-volume demand. Restraints predominantly center around logistical challenges, specifically the stringent cold chain requirements for IPV, particularly in remote or tropical environments, and the rising global issue of vaccine hesitancy, which complicates efforts to achieve and maintain herd immunity thresholds necessary for eradication. Opportunities lie in the accelerated development and deployment of thermally stable vaccines and novel oral vaccines (nOPV) that minimize the risk of vaccine-derived poliovirus, offering manufacturers pathways for product differentiation and market expansion in high-risk zones. These forces collectively create a highly regulated and mission-driven market environment where geopolitical stability and philanthropic funding exert profound influence over market dynamics and growth trajectories.
A major driving force is the success of the Polio Endgame Strategy, which mandates the global withdrawal of OPV Type 2 components and the strategic introduction of at least one dose of IPV into all national programs. This policy directive guarantees robust demand for IPV production capacity through the forecast period, especially in developing regions transitioning their immunization protocols. Furthermore, the commitment to eliminate the last remaining endemic poliovirus in countries like Afghanistan and Pakistan necessitates continuous mass vaccination campaigns using OPV, sustained by international aid. This dual demand structure—IPV for long-term routine programs and OPV for short-term outbreak response—bolsters the overall market stability and growth prospects for core manufacturers engaged in the eradication mission.
However, the market faces acute restraints related to operational complexity. The necessity of maintaining temperatures between 2°C and 8°C throughout the distribution channel is expensive and prone to failure, leading to significant vaccine wastage, especially in regions with unreliable infrastructure. Furthermore, political instability, conflict, and restricted access due to security concerns in high-risk areas severely impede immunization campaigns, creating pockets of vulnerability where the virus can resurge. These geographical challenges are compounded by growing anti-vaccination sentiments fueled by misinformation, which necessitate substantial investment in public health communication and community engagement strategies, indirectly impacting the operational costs and coverage success metrics for vaccine manufacturers and distributors.
Opportunities for growth are concentrated in pharmaceutical innovation targeting enhanced vaccine delivery and stability. Developing poliomyelitis vaccines with greater thermal tolerance would drastically reduce cold chain reliance and associated costs, opening up previously inaccessible markets. Moreover, the focus on combination vaccines integrating IPV with other mandatory childhood antigens (like Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) offers manufacturers an opportunity to capture market share by simplifying national immunization schedules, improving compliance, and increasing per-dose value. The potential for developing novel vaccine technologies that induce superior mucosal immunity without reversion risk (e.g., genetic vaccines or virus-like particle vaccines) represents a significant long-term market opportunity that could redefine global eradication strategies beyond the 2033 forecast horizon.
Segmentation Analysis
The Poliomycetes Vaccine Market segmentation provides a detailed structural view of the commercial landscape, categorized predominantly by Vaccine Type, End-User, and Route of Administration. This delineation is critical for understanding the varied demand profiles driven by differing national health policies, epidemiological needs, and affordability constraints globally. The key driver shaping this segmentation is the strategic policy shift mandated by the WHO's Polio Endgame Strategy, which is prioritizing the gradual transition from Live Attenuated Oral Polio Vaccines (OPV) towards the safer, non-reverting Inactivated Polio Vaccines (IPV). This transition significantly impacts the revenue share distribution across segments, favoring the higher-cost IPV segment in established markets and pushing innovation within the OPV segment (e.g., nOPV) for specific outbreak control applications.
Segmentation by Vaccine Type clearly distinguishes between IPV and OPV, each possessing unique benefits and limitations that determine their deployment context. IPV, typically produced using the Salk method, dominates the market value segment due to its mandatory use in non-endemic countries and its superiority in preventing paralytic polio without the risk of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP) or cVDPV. Conversely, OPV, while inexpensive and easier to administer, is primarily used in mass campaigns and outbreak settings due to its capacity to induce intestinal immunity and its ease of transport and administration, particularly in low-resource environments. The emergence of novel Oral Polio Vaccines (nOPV), designed to be genetically more stable than the traditional Sabin strains, is creating a high-growth niche within the OPV segment, specifically targeting Type 2 circulating vaccine-derived outbreaks.
Analysis by End-User reveals the overwhelming dependence of the market on Governmental Programs and National Immunization Schemes, which account for the vast majority of vaccine procurement volume and value through centralized tenders managed by international agencies. Private sector buyers, including private hospitals, specialized pediatric clinics, and pharmacies, represent a much smaller, albeit stable, secondary market, generally catering to niche travel immunization requirements or supplementary doses for specific high-income demographics. Furthermore, segmentation by Route of Administration underscores the technical differences between injectable vaccines (IPV) and oral vaccines (OPV), impacting cold chain logistics, administrator training requirements, and overall costs of delivery, which are pivotal considerations for health ministries worldwide.
- By Vaccine Type:
- Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV)
- Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV)
- Novel Oral Polio Vaccine (nOPV)
- By Antigen Type:
- Monovalent (mOPV)
- Bivalent (bOPV)
- Trivalent (tOPV - phasing out)
- By End-User:
- Governmental Immunization Programs
- Hospitals and Clinics (Private Sector)
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
- By Route of Administration:
- Injectable (Intramuscular/Subcutaneous)
- Oral
- By Distribution Channel:
- Direct Tenders
- Distributors and Wholesalers
- Retail Pharmacies
Value Chain Analysis For Poliomycetes Vaccine Market
The value chain for the Poliomycetes Vaccine Market is intricate, highly regulated, and dominated by upstream R&D and manufacturing processes, followed by a centralized, public health-centric distribution network. The upstream segment involves the critical steps of selecting suitable seed viruses (for both IPV and OPV), growing these viruses in large-scale cell cultures, inactivation (for IPV), purification, and formulation. This stage is capital-intensive, requiring specialized biosafety level facilities and strict regulatory adherence, limiting the number of global players. Key challenges upstream include ensuring reliable raw material supply, maintaining high viral yields, and achieving high potency while adhering to the complex requirements of WHO prequalification, which dictates access to the largest procurement tenders globally.
The midstream phase focuses on manufacturing, which includes sterile filling, finishing, and packaging, often involving the complex task of integrating the poliomyelitis component into multi-antigen combination vaccines (e.g., Hexavalent vaccines). Quality assurance and control checks throughout this process are paramount. The downstream segment is defined almost exclusively by centralized procurement and logistics. Direct and indirect distribution channels are utilized, but governmental bodies and international organizations (like UNICEF and PAHO) act as the primary purchasers, often negotiating volume discounts through direct tenders. These centralized entities then manage the complex secondary distribution, relying on national cold chain infrastructure to move vaccines to regional and local immunization centers. Direct distribution channels are thus characterized by large, infrequent shipments governed by long-term contracts.
Indirect distribution occurs mainly via established third-party logistics (3PL) providers specializing in cold chain transport, particularly in fragmented markets or for smaller private sector sales. However, the volume channeled through indirect distributors remains marginal compared to the massive governmental purchases. Efficient distribution is critically dependent on maintaining the cold chain (2-8°C), making logistics the most significant operational hurdle in the downstream segment. Failures in cold chain management can lead to significant wastage and compromise the efficacy of immunization programs. Continuous investment in surveillance, inventory management systems, and improved cold chain equipment is essential for optimizing this end of the value chain and ensuring the vaccines reach the target populations intact and on schedule.
Poliomycetes Vaccine Market Potential Customers
The end-user profile for Poliomycetes Vaccines is heavily skewed towards institutional and governmental entities, reflecting the global commitment to eradication as a public health good rather than a commoditized treatment. The overwhelming majority of the demand originates from National Public Health Ministries and Departments of Health across all regions. These governmental bodies act as the primary buyers, responsible for funding, procuring, and implementing universal immunization programs for infants and children, ensuring national compliance with international health regulations and WHO recommendations. Their purchasing power and schedule adherence determine the scale and timing of large-scale market transactions, often consolidated through international procurement mechanisms.
Secondary, yet highly critical, potential customers include global humanitarian and procurement organizations, such as UNICEF, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), and the Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance. These entities act as intermediaries, pooling demand from numerous developing countries to negotiate better pricing and managing the logistics of delivering vaccines to low-income and conflict-affected regions. They represent crucial bulk buyers who enable market accessibility in environments where individual nations lack the financial or logistical capacity to procure necessary supplies directly. This segment is especially important for the distribution of OPV during high-priority outbreak responses.
A smaller, but commercially relevant, segment comprises private healthcare networks, including large hospital systems and specialized pediatric clinics in high-income countries. These customers procure vaccines for routine private immunization services, often catering to patients who prefer private care or those requiring travel-related booster doses. Furthermore, pharmaceutical wholesalers and distributors specializing in vaccine supply constitute potential indirect customers, bridging the gap between manufacturers and the fragmented private clinical market, although their role is secondary to the dominant governmental procurement channel.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 1.8 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 2.8 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 6.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Bio-Med Pvt. Ltd., Panacea Biotec Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Incepta Vaccine Ltd., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Bharat Biotech International Ltd., Zydus Cadila, Johnson & Johnson, Emergent BioSolutions, Pfizer Inc., Merck & Co. Inc., Haffkine Bio-Pharmaceutical Corporation Ltd., Sinovac Biotech Ltd., Chongqing Zhifei Biological Products Co. Ltd., CSL Limited, Indian Immunologicals Limited |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Poliomycetes Vaccine Market Key Technology Landscape
The technological landscape of the Poliomycetes Vaccine Market is characterized by a mature manufacturing base undergoing modernization to meet evolving global health standards and strategic shifts. The established technology relies on classical virology techniques, specifically the large-scale propagation of poliovirus strains (either Salk-type inactivated or Sabin-type attenuated) in mammalian cell culture systems, typically Vero cells. Key technological focus areas involve upstream improvements aimed at enhancing viral yield per batch and ensuring robust biosafety containment, especially crucial for handling large volumes of live poliovirus in OPV production facilities, necessitating sophisticated filtration and purification techniques to ensure product purity and potency according to WHO prequalification guidelines.
A significant technological advancement influencing the market is the development and scaling of novel Oral Polio Vaccines (nOPV), particularly nOPV2. This technology utilizes advanced molecular virology techniques to genetically engineer the Sabin strain to increase its genetic stability, thereby minimizing the risk of reversion to neurovirulence—the key drawback of traditional OPV. This engineering requires precise manipulation and rigorous testing protocols, representing a major step forward in viral vaccine safety technology. Manufacturers capable of rapid scale-up and mass production of nOPV are positioned advantageously, especially for global outbreak response programs managed by agencies like the WHO.
Furthermore, technology is heavily focused on improving product delivery and stability. This includes R&D into developing thermostable IPV formulations that can withstand higher temperatures for longer periods, potentially eliminating the stringent cold chain requirements that currently hinder distribution in remote areas. Other areas include the refinement of conjugation and formulation techniques for multi-antigen combination vaccines (e.g., DTaP-IPV-HepB-Hib) to maintain the stability and immunogenicity of all components within a single dose. The market is also exploring non-traditional delivery systems, such as microneedle patches for IPV, which could simplify administration, reduce needle-stick injury risks, and potentially lower logistics costs associated with trained medical personnel.
Regional Highlights
Regional dynamics are critical in defining the Poliomycetes Vaccine Market due to varying epidemiological statuses, disparate economic resources, and differing national immunization policies. The market is fundamentally segmented into two categories: developed regions which rely almost exclusively on high-cost IPV for routine immunization post-eradication, and developing regions, primarily in APAC and Africa, which utilize a mix of IPV and high-volume, lower-cost OPV for mass campaigns and containment strategies.
North America and Europe: These regions represent mature, stable markets characterized by universal IPV use in routine childhood immunization schedules. Demand is highly predictable, driven by consistent birth rates and mandatory vaccination policies. The focus here is on securing high-quality IPV supply, often through combination vaccines, and maintaining rigorous surveillance systems to prevent importation. Market growth is stable but moderate, relying on pricing stability and the premium valuation of multi-antigen products. The high standard of cold chain infrastructure ensures reliable distribution, but manufacturers must meet stringent regulatory standards imposed by the FDA and EMA.
Asia Pacific (APAC): APAC is the largest volumetric market and the fastest-growing region, driven by its vast population size, high birth rates, and ongoing commitment to bolstering immunization coverage across populous nations like India, China, and Indonesia. While some advanced APAC countries utilize IPV, the region as a whole still relies heavily on bulk procurement of bOPV for supplementary activities, especially in South Asia where cVDPV risks persist. The presence of major local manufacturers (e.g., in India and China) creates a highly competitive environment, significantly impacting global pricing and supply. Infrastructure development and cold chain expansion remain key investment areas.
Middle East and Africa (MEA): This region is crucial for the global polio eradication mission as it contains the remaining endemic foci (e.g., Pakistan, Afghanistan, parts of Africa still grappling with cVDPV outbreaks). The MEA market is highly dependent on international aid and emergency procurement of OPV (including novel nOPV) for mass campaigns. Demand is volatile, peaking during outbreak responses, and is frequently challenged by political instability, security issues, and weak cold chain infrastructure. The focus of manufacturers and health agencies here is on rapid deployment, cultural sensitivity in delivery, and ensuring high coverage rates in high-risk zones.
Latin America (LATAM): The LATAM region, having achieved polio elimination status, maintains high immunization coverage through robust national programs, primarily utilizing IPV within combination vaccines, similar to Western markets. Demand is stable, reflecting standardized public procurement cycles. Challenges include economic volatility in some countries, which can affect the budget allocated for expensive combination vaccines, occasionally leading to shifts in procurement strategy, though the commitment to maintaining IPV coverage remains strong.
- North America: Stable demand for premium IPV combination vaccines; focus on maintenance of elimination status.
- Europe: Universal IPV adoption in routine schedules; strong reliance on centralized purchasing power.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Highest volumetric demand driven by high birth cohorts; significant local manufacturing presence; mixed use of IPV and bOPV/nOPV.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): Critical market for eradication efforts; demand highly volatile and reliant on humanitarian funding and outbreak response strategies (primarily OPV/nOPV).
- Latin America: Mature, stable market transitioning fully to IPV use in routine programs; centralized governmental procurement systems.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Poliomycetes Vaccine Market.- Sanofi Pasteur
- GlaxoSmithKline (GSK)
- Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd.
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
- Bio-Med Pvt. Ltd.
- Panacea Biotec Ltd.
- Astellas Pharma Inc.
- Incepta Vaccine Ltd.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Bharat Biotech International Ltd.
- Zydus Cadila
- Johnson & Johnson
- Emergent BioSolutions
- Pfizer Inc.
- Merck & Co. Inc.
- Haffkine Bio-Pharmaceutical Corporation Ltd.
- Sinovac Biotech Ltd.
- Chongqing Zhifei Biological Products Co. Ltd.
- CSL Limited
- Indian Immunologicals Limited
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Poliomycetes Vaccine market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary difference between IPV and OPV, and how does this affect market deployment?
IPV (Inactivated Polio Vaccine) is injectable, safer as it carries zero risk of reversion to active virus, and primarily used in routine immunization in polio-free regions. OPV (Oral Polio Vaccine) is oral, cheaper, induces better mucosal immunity, and is essential for mass campaigns and outbreak response in endemic or high-risk areas, despite a slight risk of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV).
Why are novel oral polio vaccines (nOPV) critical to the market's future?
Novel OPVs (nOPV) are genetically engineered to be more stable than traditional OPV strains, significantly reducing the likelihood of reversion to a neurovirulent form that can cause cVDPV outbreaks. Their deployment is crucial for accelerating the final stages of global polio eradication and safely transitioning away from older OPV formulations.
Which geopolitical factors most significantly restrain the Poliomycetes Vaccine Market growth?
Geopolitical instability, particularly in remaining endemic areas like Afghanistan and Pakistan, creates security challenges that prevent vaccinators from reaching target populations. This instability, coupled with misinformation and vaccine hesitancy amplified by local conflicts, forms significant barriers to achieving necessary immunization coverage rates.
How does the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) influence vaccine demand and market dynamics?
The GPEI, supported by international donors, is the single largest driver of demand, funding the vast majority of vaccine procurement in developing nations through bulk tenders managed by organizations like UNICEF. GPEI policy decisions, such as the strategic shift towards IPV use, directly mandate manufacturing requirements and global supply changes.
What technological advancements are expected to improve the IPV cold chain challenge?
Key advancements focus on developing thermostable IPV formulations through advanced lyophilization or stabilization techniques, aiming to extend the vaccine’s viability outside the strict 2°C to 8°C range. The introduction of non-traditional delivery systems, such as microneedle patches, also seeks to simplify distribution logistics and reduce cold chain failures in challenging environments.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
