RF Resistor Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 433968 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 257 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
RF Resistor Market Size
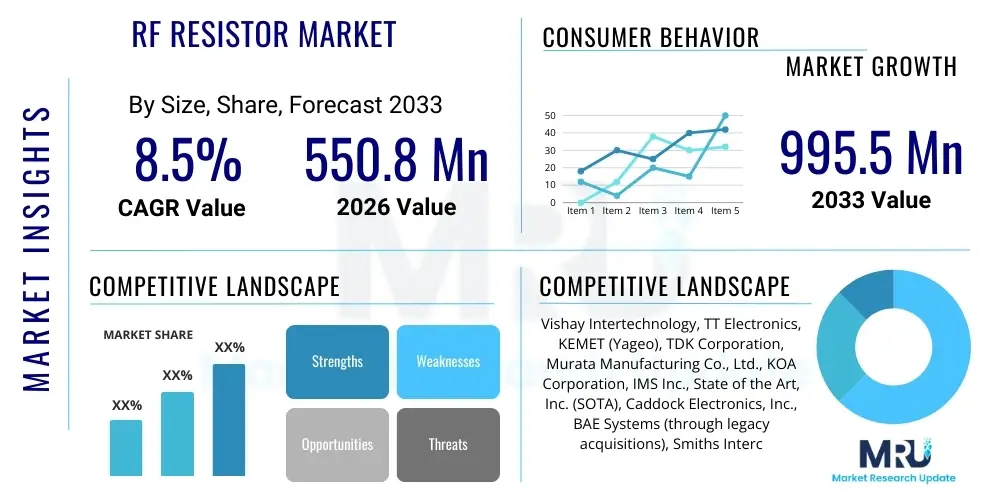
The RF Resistor Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 550.8 Million in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 995.5 Million by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
RF Resistor Market introduction
The RF Resistor Market encompasses specialized passive electronic components designed to operate effectively at high frequencies, typically above 300 MHz, maintaining stable resistance values and minimal parasitic inductance/capacitance. These components are critical for impedance matching, power termination, voltage division, and attenuation in high-frequency circuits. The performance characteristics of RF resistors, such as low noise, tight tolerance, and superior thermal management, make them indispensable in sophisticated communication and radar systems where signal integrity is paramount. They are manufactured using advanced techniques like thin-film, thick-film, and wirewound technologies, tailored specifically for high-frequency environments.
Major applications driving the demand for RF resistors include the expanding telecommunications sector, particularly the deployment of 5G and 6G infrastructure, which requires high-performance, compact components capable of handling millimeter-wave frequencies. Furthermore, the defense and aerospace industries utilize these resistors extensively in electronic warfare systems, radar modules, and high-reliability communication links. The ongoing miniaturization of electronic devices and the increasing complexity of wireless communication standards necessitate continuous innovation in RF resistor design to meet stringent power handling and frequency stability requirements across broad bandwidths.
Key driving factors supporting market expansion include global investment in satellite communication networks, the growing adoption of IoT devices requiring robust wireless connectivity, and the rapid expansion of automotive radar systems (ADAS). The inherent benefits of specialized RF resistors—including their ability to ensure signal clarity, reduce power consumption through efficient impedance control, and operate reliably in extreme environmental conditions—cement their essential role in modern electronic ecosystems. Manufacturers are continuously focused on developing materials and structures that reduce self-heating effects and improve stability at elevated operational frequencies.
RF Resistor Market Executive Summary
The RF Resistor Market is experiencing robust growth fueled primarily by global investments in high-speed data transmission technologies and modernization programs within the defense sector. Business trends indicate a strong shift towards thin-film and thick-film surface-mount device (SMD) components, favored for their compact size, excellent stability, and suitability for automated assembly processes utilized in high-volume manufacturing of consumer and enterprise networking equipment. Regional trends confirm Asia Pacific's dominance, driven by massive manufacturing capacities in electronics and aggressive 5G infrastructure rollout, while North America and Europe maintain strong demand stemming from high-end defense, aerospace, and satellite applications demanding ultra-precision components. Segment trends highlight that fixed attenuators and terminations within the power handling segment are seeing significant uptake, necessitated by the proliferation of high-power RF amplifiers used in base stations and military systems, simultaneously pushing advancements in material science for improved heat dissipation capabilities.
AI Impact Analysis on RF Resistor Market
User inquiries regarding the impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on the RF Resistor Market primarily center on two themes: how AI is accelerating the design and testing cycles of these components, and how the massive data processing required by AI-driven systems (like data centers and autonomous vehicles) influences demand for high-performance RF components. Users express interest in AI's role in optimizing material selection and geometric structures for next-generation, high-frequency resistors, aiming for unprecedented stability and minimal parasitic effects. Furthermore, the reliance of machine learning and large language models on cutting-edge cloud infrastructure, which utilizes dense RF communication architectures, is expected to be a major demand driver, raising concerns about component reliability, thermal management, and ultra-low latency requirements in AI-enabled networking environments.
- AI algorithms optimize RF circuit design, reducing development time for specialized resistor parameters (e.g., thermal resistance and frequency response).
- Increased data center bandwidth demands, driven by AI processing, necessitate higher volumes of ultra-stable RF termination resistors and attenuators.
- AI-enabled automated testing systems enhance quality control and precision measurement of RF resistor characteristics during manufacturing.
- Autonomous vehicle proliferation, reliant on AI and high-frequency sensors (radar, LiDAR), drives demand for highly reliable, automotive-grade RF resistors.
- Predictive maintenance models utilizing AI analyze operational data to anticipate potential failures in RF systems, indirectly requiring more robust initial component specifications.
DRO & Impact Forces Of RF Resistor Market
The RF Resistor Market dynamics are shaped by powerful Drivers, structural Restraints, and evolving Opportunities, which collectively define the overall Impact Forces within the industry. Key drivers include the relentless global expansion of wireless connectivity technologies, specifically 5G and future 6G networks, necessitating high-frequency, precision components for signal conditioning and impedance matching in base stations and user equipment. The escalating demand for high-reliability components in mission-critical applications across defense, space, and medical sectors further cements market expansion. Conversely, the market faces restraints such as the inherent complexity and high cost associated with manufacturing ultra-precise, low-tolerance thin-film resistors, coupled with volatility in the supply chain for specialized substrate materials like alumina and beryllium oxide, which are essential for high-power applications.
Opportunities for growth lie significantly in the burgeoning Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, where billions of connected devices require miniature, low-power RF resistors, alongside emerging applications in quantum computing and high-frequency medical imaging equipment. Moreover, the push toward electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving features is creating a new segment for high-reliability, thermally stable RF components within vehicular communication and sensing systems. Impact forces, such as advancements in material science enabling operation at higher temperatures and frequencies, coupled with intense competitive pricing pressure from Asian manufacturers, continuously influence strategic decisions regarding production localization and technological investment. The shift towards higher frequency bands (e.g., millimeter wave) also acts as a profound impact force, rendering older resistor technologies obsolete and necessitating investment in new manufacturing techniques suitable for precise patterning and minimal parasitic effects.
Segmentation Analysis
The RF Resistor market is primarily segmented based on the component type, power handling capabilities, application vertical, and geographic region. Understanding these divisions is crucial for manufacturers to tailor their product offerings to specific operational requirements, whether they involve high-power termination in military radar systems or highly stable attenuation in consumer wireless devices. The technological basis, particularly the manufacturing method (thin film vs. thick film), dictates the frequency limits and precision achievable, thus separating products for high-end versus mass-market applications. Detailed segmentation allows for a precise analysis of demand patterns and technological maturity across diverse industry sectors.
- By Product Type: Fixed Resistors, Variable Resistors/Trimmers, Chip Resistors, Flange Resistors, Wirewound Resistors.
- By Manufacturing Technology: Thick Film, Thin Film, Foil Resistors.
- By Power Handling Capacity: Low Power (<1W), Medium Power (1W–100W), High Power (>100W).
- By Application: Telecommunication (5G/6G Base Stations, Repeaters), Defense and Aerospace (Radar, Electronic Warfare), Consumer Electronics (Smartphones, Wi-Fi Routers), Medical Devices, Automotive Radar (ADAS).
- By Frequency Range: Sub-6 GHz, Millimeter Wave (mmWave) (24 GHz – 100 GHz).
Detailed Segmentation by Manufacturing Technology: Thin Film
Thin film resistors are characterized by depositing a resistive material, often Nichrome, onto a ceramic substrate using sputtering or vacuum deposition techniques, resulting in film thicknesses typically less than 0.1 micrometers. This precise control over the film geometry yields components with extremely tight tolerances (down to 0.01%), excellent temperature coefficients of resistance (TCR), and superior frequency stability. Their low parasitic characteristics, particularly low inductance, make thin film RF resistors ideal for high-precision applications in test and measurement equipment, satellite communication systems, and high-frequency filters where signal integrity is paramount.
The primary advantage of thin film technology in the RF domain is its ability to minimize noise and drift across wide temperature variations. As RF circuits become more complex and operate at higher frequencies, the demand for thin film resistors increases due to their inherent reliability and performance stability in dense circuit board layouts. However, the manufacturing process is complex and relatively costly, often limiting their use to premium or mission-critical applications where cost is secondary to performance metrics.
Continuous technological advancements in thin film processing are focusing on increasing the power handling capabilities without compromising the precision characteristics. This includes developing advanced substrate materials, such as aluminum nitride, which offer better thermal conductivity than traditional alumina, allowing these miniature, high-precision resistors to dissipate heat more effectively in power amplifiers and active antenna systems necessary for 5G deployment.
Detailed Segmentation by Manufacturing Technology: Thick Film
Thick film resistors are fabricated by screen-printing a specialized paste, containing glass and resistive materials (like ruthenium oxide), onto a ceramic substrate, which is then fired at high temperatures. The resulting film layer is significantly thicker than the thin film counterpart. While thick film resistors generally offer slightly lower precision and higher noise characteristics compared to thin film, they excel in handling higher power loads and offer a more cost-effective manufacturing process, making them suitable for high-volume consumer and industrial applications.
In the RF sector, thick film technology is predominantly used in power attenuation and termination applications where high heat dissipation is required, such as dummy loads, high-power attenuators, and termination resistors in transmitter systems. Their robust structure allows them to withstand greater thermal and mechanical stresses, making them favored in industrial telecommunication equipment and certain defense systems where durability is prioritized alongside moderate RF performance requirements.
Market trends show thick film technology rapidly improving to bridge the performance gap with thin film, particularly through advancements in paste formulations and laser trimming techniques that enhance tolerance control. The cost-effectiveness and ruggedness of thick film technology ensure its sustained dominance in segments requiring moderate precision combined with high power and thermal resilience, especially in automotive electronics and standard Wi-Fi communication infrastructure.
Detailed Segmentation by Application: Telecommunication
The telecommunication segment represents the largest consumer of RF resistors, driven overwhelmingly by global infrastructure upgrades related to 5G, and preparatory work for 6G networks. RF resistors are fundamental components in base station power amplifiers, tower-mounted amplifiers (TMAs), filters, and network backhaul equipment, where they perform crucial functions such as signal attenuation, high-frequency termination, and impedance matching across complex multi-band architectures. The transition to higher frequency bands, particularly mmWave, demands RF resistors with exceptional frequency response flatness and minimal reflection losses.
The deployment of massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology in 5G requires an unprecedented density of RF components within active antenna systems. Each antenna element requires reliable, high-power handling RF resistors to manage signal termination and control linearity. This necessity places intense pressure on manufacturers to deliver physically compact SMD resistors that can operate reliably under high thermal stress caused by concentrated power delivery in a small footprint.
Furthermore, the growth of small cell technology, designed to densify networks and improve coverage in urban areas, relies heavily on miniature, low-power RF resistors. This segment demands cost-efficient, yet high-performance, thick and thin film chip resistors that can be easily integrated into compact repeater units and indoor wireless access points, ensuring seamless high-speed data delivery.
Detailed Segmentation by Application: Defense and Aerospace
The defense and aerospace sector utilizes RF resistors in mission-critical applications such as radar systems (AESA and traditional), electronic warfare (EW) modules, high-frequency satellite communication (SATCOM) transceivers, and secure data links. This sector requires components that meet extremely rigorous specifications regarding shock resistance, temperature stability across harsh environments (e.g., high altitude or extreme cold), and radiation tolerance. RF resistors used here are typically high-precision, thin film, or advanced thick film types, often built on specialized substrates like Beryllium Oxide (BeO) for superior thermal management in high-power radar transmitters.
The continuous modernization of defense systems, shifting towards software-defined radio (SDR) and phased array technologies, increases the complexity and channel density of RF front-ends. Consequently, there is an escalating need for high-power, flange-mount resistors and terminations capable of dissipating significant amounts of power generated by military-grade amplifiers. Reliability and longevity are non-negotiable requirements, leading to stringent qualification processes and a preference for resistors with established track records in severe operational environments.
Investment in space-based assets, including low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations for global communication and surveillance, further propels demand. Space-grade RF resistors must survive launch vibrations and the vacuum of space while maintaining precise electrical characteristics over a decade or more. This subset of the market commands premium pricing due to the extreme reliability and low outgassing requirements inherent in space qualification standards.
Detailed Segmentation by Power Handling Capacity: High Power (>100W)
The high-power segment, defined by RF resistors rated for power dissipation exceeding 100 Watts, is crucial for applications involving signal amplification prior to transmission, such as in high-output broadcast transmitters, industrial heating equipment (RF welding), and advanced military radar installations. These components are predominantly built using thick film technology on highly thermally conductive substrates and feature flange mounting for efficient coupling to external heat sinks or cold plates, ensuring component temperature remains within safe operational limits.
Managing thermal stress is the central challenge in this segment. The effectiveness of a high-power RF resistor is measured not only by its primary resistance value but critically by its thermal resistance and its ability to maintain stable performance as internal temperature rises due to high current flow. Innovation focuses on improving the thermal interface materials and optimizing the physical layout (e.g., using larger footprints or specialized package designs) to maximize heat transfer away from the resistive element.
Demand in this category is strongly influenced by the growth of sophisticated active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar systems used in maritime and airborne defense applications, where thousands of individual transmit/receive modules require robust, high-power terminations. Furthermore, the expansion of cellular networks into rural and remote areas often utilizes higher power base stations to maximize coverage, ensuring sustained demand for high-power dummy loads and attenuators for system testing and termination.
Value Chain Analysis For RF Resistor Market
The RF Resistor market value chain commences with upstream activities involving the sourcing and processing of specialized raw materials, primarily high-purity ceramic substrates (like alumina, aluminum nitride, or beryllium oxide), and resistive metals (such as Nichrome, tantalum nitride, or ruthenium oxide). Material quality and consistency are paramount, as they directly dictate the component's stability and frequency response. Manufacturers then focus on fabrication, utilizing highly technical processes like vacuum sputtering (for thin film) or precise screen-printing and firing (for thick film). Quality assurance, involving rigorous testing for parameters like VSWR, TCR, and power linearity, adds significant value before the components are packaged and prepared for distribution.
Downstream activities involve the distribution channel, which utilizes both direct sales models and an extensive network of specialized electronic component distributors. Direct sales are common for highly customized, high-reliability components destined for large defense contractors or Tier 1 telecom equipment manufacturers, where technical support and deep collaboration are required. Conversely, smaller customers and standard commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components are typically channeled through global distributors (e.g., Avnet, Digi-Key, Mouser), who provide inventory management and logistical support across various geographic regions.
The end-user application determines the final value delivery. For instance, an RF resistor utilized in a high-frequency medical MRI machine carries a higher value and requires a dedicated, traceable supply chain compared to a standard resistor used in a Wi-Fi router. The complexity of modern RF systems, particularly in 5G and aerospace, means that value is increasingly tied to the manufacturer's ability to provide design assistance and deliver components with certified performance guarantees across extreme operating conditions.
RF Resistor Market Potential Customers
Potential customers for RF resistors span various high-technology sectors, ranging from Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) specializing in telecommunications infrastructure to defense prime contractors and medical device manufacturers. The largest volume buyers are telecom infrastructure providers (e.g., Ericsson, Huawei, Nokia, and Samsung) and wireless equipment manufacturers, which require vast quantities of highly stable components for base stations, repeaters, and mobile devices supporting 5G and fiber optic backhaul systems. These customers seek components offering optimal size-to-power ratios and highly competitive pricing due to the immense scale of deployment.
Another critical group of buyers includes defense and aerospace contractors (e.g., Lockheed Martin, Raytheon, Northrop Grumman) who procure specialized, high-reliability, and often custom-designed RF resistors for radar, electronic warfare, and missile guidance systems. These contracts prioritize absolute reliability, adherence to military standards (MIL-SPEC), and performance under extreme environmental conditions over cost sensitivity. Additionally, the growing automotive sector, particularly manufacturers focused on Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, represents a rapidly expanding customer base seeking automotive-grade RF resistors with robust thermal stability for radar sensor modules.
Finally, the test and measurement industry (e.g., Keysight, Rohde & Schwarz) remains a consistent buyer of ultra-high-precision RF resistors, crucial for calibrating sensitive high-frequency instruments such as spectrum analyzers and network analyzers. These customers demand the highest possible tolerance and lowest noise levels to ensure the accuracy of their sophisticated equipment, representing the pinnacle of performance requirements within the market.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 550.8 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 995.5 Million |
| Growth Rate | 8.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Vishay Intertechnology, TT Electronics, KEMET (Yageo), TDK Corporation, Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd., KOA Corporation, IMS Inc., State of the Art, Inc. (SOTA), Caddock Electronics, Inc., BAE Systems (through legacy acquisitions), Smiths Interconnect, Barry Industries, EMC Technology, M-A/Com Technology Solutions (Ampleon), SemiGen, API Technologies, RCD Components, Inc., UltraSource, Inc., Knowles Precision Devices, Passive Plus, Inc. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
RF Resistor Market Key Technology Landscape
The RF Resistor Market is heavily influenced by advancements in thin-film deposition techniques and specialized substrate materials designed to handle high frequencies and manage thermal loads efficiently. Sputtering technology, essential for thin-film precision resistors, has evolved to allow for deposition of highly stable resistive alloys (like Tantalum Nitride) with improved uniformity over large substrate areas, leading to enhanced quality and reduced manufacturing costs. Furthermore, laser trimming techniques have become indispensable, providing ultra-fine adjustments to the resistance value post-deposition, ensuring extremely tight tolerances required for calibration standards and high-end communication filters.
Material innovation remains a core technological focus, particularly the shift towards substrates with superior thermal conductivity. While alumina is standard, high-power applications increasingly utilize aluminum nitride (AlN) or, in highly demanding military contexts, Beryllium Oxide (BeO), to effectively dissipate heat from the resistive element, preventing resistance shift and catastrophic failure under high-power conditions. This is critical for 5G power amplifiers operating at high duty cycles. The integration of resistor networks directly into monolithic microwave integrated circuits (MMICs) using semiconductor fabrication processes (CMOS and GaAs) also represents a significant technological trend, leading to highly integrated, compact RF front-ends.
A key area of development is reducing parasitic elements—specifically stray capacitance and inductance—which become significant signal distortion factors at millimeter-wave frequencies. Resistor designs are moving towards complex geometric shapes (like serpentines or specialized planar configurations) optimized through electromagnetic simulation tools, ensuring near-perfect resistance characteristics across ultra-broad bandwidths. Packaging technology is also crucial, with growing adoption of flip-chip and specialized surface-mount device (SMD) packages that minimize bond wire length and maximize thermal transfer efficiency for operational stability above 30 GHz.
Regional Highlights
- Asia Pacific (APAC) Dominance: APAC commands the largest market share, driven by its status as the global manufacturing hub for consumer electronics and telecommunication equipment. Countries like China, South Korea, and Japan are at the forefront of 5G deployment, demanding high volumes of cost-effective, high-performance RF chip resistors for smartphones, base stations, and IoT devices. Substantial government investment in domestic semiconductor fabrication capabilities further reinforces regional growth.
- North America (NA) Innovation and Defense Spending: North America holds a significant share, characterized by high demand for specialized, high-reliability RF resistors, particularly in the defense, aerospace, and advanced test & measurement sectors. The region benefits from leading research institutions and key players driving innovation in mmWave technology and satellite communication, focusing on stringent performance standards and custom components rather than volume mass production.
- Europe (EU) Automotive and Industrial Applications: Europe represents a mature market with strong demand stemming from the automotive industry (ADAS radar systems), industrial IoT, and advanced military electronics. Regulatory pushes toward electric vehicle adoption and associated V2X communication standards mandate highly stable and reliable automotive-grade RF components, leading to steady growth in specialized segments.
- Latin America (LATAM) Infrastructure Growth: The LATAM market is poised for growth driven by ongoing network modernization and the phased rollout of 5G infrastructure in key economies like Brazil and Mexico. Demand is concentrated on standard and medium-power RF resistors required for cellular network expansion and consumer wireless connectivity devices.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA) Strategic Investment: MEA growth is primarily fueled by large-scale defense modernization projects, particularly in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, requiring advanced RF components for radar and secure communication systems. Furthermore, investment in smart city projects and satellite communication initiatives contributes to increasing market uptake, often relying on imports from established global suppliers.
The Asia Pacific region maintains its pivotal role due to the sheer volume of production and consumption associated with the rapid expansion of wireless communications. Nations in this region are rapidly moving beyond 5G and beginning research into 6G standards, which requires continuous technological refresh cycles for RF components. This cycle of accelerated adoption and high-volume production creates a competitive landscape focused on cost optimization and component miniaturization, particularly in the low and medium power segments used in consumer-facing technologies.
North America’s market focus is distinct, centered on high-margin, ultra-precision applications where performance guarantees outweigh price considerations. The robust presence of major defense prime contractors and global leaders in specialized test equipment ensures sustained demand for thin-film and custom-designed resistors capable of operating reliably in extreme conditions or complex multi-channel systems. This region often dictates the technological frontier in terms of frequency capability and reliability metrics for the global market.
In Europe, the market is characterized by stringent quality controls, particularly driven by automotive and industrial automation standards. The transition to higher levels of autonomous driving necessitates sophisticated 77 GHz and 79 GHz radar systems, each relying on high-stability, temperature-resistant RF resistors. European component manufacturers often specialize in niche, high-specification products catering to these specific industrial and safety-critical applications, ensuring stability despite lower volume demand compared to APAC consumer markets.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the RF Resistor Market.- Vishay Intertechnology
- TT Electronics
- KEMET (Yageo)
- TDK Corporation
- Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- KOA Corporation
- IMS Inc.
- State of the Art, Inc. (SOTA)
- Caddock Electronics, Inc.
- Smiths Interconnect
- Barry Industries
- EMC Technology
- SemiGen
- API Technologies
- RCD Components, Inc.
- UltraSource, Inc.
- Knowles Precision Devices
- Passive Plus, Inc.
- Micro-Ohm Corp.
- Riedon, Inc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the RF Resistor market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary difference between thin film and thick film RF resistors?
The primary difference lies in manufacturing precision and power handling. Thin film RF resistors offer superior precision (tighter tolerances), better thermal coefficient of resistance (TCR), and lower noise, making them ideal for high-frequency precision instrumentation. Thick film resistors are more cost-effective, offer higher power handling capabilities, and are preferred for applications requiring thermal resilience in high-volume, general RF termination.
How is the global deployment of 5G infrastructure affecting the demand for RF resistors?
5G deployment is drastically increasing demand, particularly for millimeter-wave (mmWave) capable resistors. The transition to massive MIMO and active antenna systems requires high densities of miniature, high-frequency, and thermally stable chip resistors for signal attenuation, termination, and impedance matching in base station power amplifiers and filters. This drives innovation in heat dissipation and size reduction.
Which application segment holds the largest market share for RF resistors?
The telecommunication segment, encompassing 5G, 4G LTE, and related networking equipment, currently holds the largest market share. This dominance is due to the sheer volume of components required globally for base stations, repeaters, network densification, and consumer wireless devices, all of which require reliable RF signal conditioning and termination.
What are the key technological challenges currently facing RF resistor manufacturers?
Key challenges include managing heat dissipation in increasingly miniaturized components operating at higher power levels, minimizing parasitic inductance and capacitance to maintain performance at millimeter-wave frequencies (above 30 GHz), and securing a stable, cost-effective supply chain for specialized high-thermal conductivity substrate materials like aluminum nitride (AlN).
What role do RF resistors play in modern automotive radar systems (ADAS)?
RF resistors are essential in automotive radar (77 GHz and 79 GHz) systems for crucial functions such as precise signal termination, impedance matching within the transmitter and receiver chains, and acting as elements in power dividers and attenuators. Their high reliability and stability under automotive temperature extremes are critical for the consistent performance of Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS).
How do operating frequency and power handling requirements impact material choice?
Higher operating frequencies necessitate materials and geometric structures that minimize parasitic effects; thin film on high-purity ceramic is common. Increased power handling demands materials with superior thermal conductivity, such as aluminum nitride or specialized BeO substitutes, often used in conjunction with robust thick film technology and flange-mount packaging to efficiently transfer heat away from the resistive element.
Which region is expected to demonstrate the highest growth rate during the forecast period?
Asia Pacific (APAC) is projected to exhibit the highest Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). This acceleration is driven by aggressive investment in 5G and 6G infrastructure deployment, continuous growth in electronics manufacturing capacity, and the rapid adoption of IoT devices across key economies within the region.
What are the main types of specialized RF resistor packaging?
Common specialized packaging types include Surface Mount Devices (SMD) for high-volume integration, Flange Mount resistors designed for attachment to heat sinks for high-power dissipation, and chip resistors which are small, unencapsulated devices used directly on substrates where size is severely constrained, such as in active antenna arrays.
How does the defense sector's demand for RF resistors differ from the consumer electronics sector?
The defense sector demands ultra-high reliability, compliance with military standards (MIL-SPEC), extreme environmental tolerance (shock, vibration, radiation), and often custom-designed high-power components for radar and electronic warfare, prioritizing performance and ruggedness over cost. Consumer electronics demand high volume, miniaturization, and aggressive cost reduction for use in smartphones and networking gear.
What is the typical tolerance range for high-precision thin-film RF resistors?
High-precision thin-film RF resistors commonly achieve tolerances ranging from ±0.1% down to as low as ±0.01%. This tight tolerance is crucial for maintaining the accuracy of complex RF filters, precision attenuators, and calibration standards used in highly sensitive test and measurement applications.
How are advancements in AI influencing the future design of RF components?
AI is increasingly used in optimizing the design process, specifically leveraging machine learning algorithms to model complex electromagnetic fields and thermal behavior. This allows manufacturers to simulate and optimize resistor geometries and material compositions faster, resulting in components with superior frequency stability and thermal management characteristics for next-generation wireless systems.
Why is Beryllium Oxide (BeO) sometimes preferred as a substrate despite safety concerns?
BeO is preferred in certain legacy or specialized high-power applications, particularly in defense, due to its exceptionally high thermal conductivity, which is several times greater than that of alumina or aluminum nitride. This property is crucial for the survival and stability of ultra-high-power RF terminations and attenuators, although its use is heavily regulated due to potential toxicity risks during fabrication and handling.
What is the significance of the Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) in RF resistor performance?
VSWR is a critical metric indicating the quality of impedance matching. An ideal RF resistor termination should have a VSWR close to 1:1, meaning nearly all signal power is absorbed without reflection. Poor VSWR results in signal loss, increased noise, and reduced efficiency, making it a primary performance indicator for high-frequency applications.
What are the primary restraints on market growth?
The key restraints include the high capital expenditure required for advanced cleanroom manufacturing processes for thin film technology, volatility in the pricing and supply chain of specialized ceramic substrates, and the need for complex, highly controlled testing environments to verify component performance at millimeter-wave frequencies.
What is the role of RF resistors in IoT devices?
In IoT devices, RF resistors are essential for impedance matching circuits connected to antennas and transceivers (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee). They are predominantly miniature, low-power chip resistors that ensure efficient power transfer and minimal signal reflection, critical for maintaining reliable, low-power wireless connectivity over long battery life cycles.
How does the transition to higher frequency bands (e.g., 6G research) affect resistor requirements?
The move towards extremely high frequencies (terahertz range in 6G research) necessitates resistors with virtually zero parasitic inductance or capacitance. This demands radically new fabrication techniques, highly specialized substrate materials, and innovative planar geometries optimized using advanced electromagnetic simulation tools to maintain stable resistance characteristics at unprecedented bandwidths.
What is the difference between a fixed resistor and an attenuator in the RF context?
A fixed resistor provides a specific resistance value (typically 50 or 75 Ohms for termination) or is used as a standard circuit element. An attenuator is a specialized network built using precise RF resistors (often in pi or tee configurations) designed specifically to reduce (attenuate) the signal power level by a fixed, calibrated amount without introducing distortion or reflections.
Who are the typical upstream suppliers in the RF resistor value chain?
Upstream suppliers are primarily manufacturers of high-purity ceramic substrates (like Kyocera or Coorstek), specialized metallic resistive alloys (Nichrome, Tantalum), and various thin-film deposition and printing equipment providers. Their ability to deliver consistent, high-specification materials is foundational to the final component quality.
What defines an RF resistor as 'automotive grade'?
An automotive-grade RF resistor adheres to stringent qualification standards, primarily AEC-Q200. This designation certifies that the component is highly reliable, capable of performing over extended temperature ranges (-55°C to 150°C), resistant to thermal shock, and robust enough to withstand the mechanical stress and vibrations inherent in vehicle operation, particularly for radar and V2X communication modules.
What emerging opportunities exist in the medical device sector for RF resistors?
Opportunities exist in high-frequency medical imaging equipment, such as MRI and advanced diagnostic devices, which require precise RF components for signal generation and detection. Furthermore, RF ablation therapies and remote patient monitoring systems, utilizing wireless communication, demand highly reliable, stable, and miniature RF resistors.
How critical is the Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR) for RF applications?
TCR is highly critical because temperature fluctuations are common in operational environments (e.g., base stations, aircraft). A low TCR ensures that the resistor’s nominal resistance value remains stable despite temperature changes. Instability in resistance leads to impedance mismatches, signal reflections, and performance degradation in sensitive RF circuits.
What is the role of the Middle East and Africa (MEA) region in this market?
The MEA market is primarily driven by strategic national defense spending, necessitating high-performance RF components for modernizing surveillance and communication systems. Additionally, large-scale smart city initiatives and expanding cellular networks contribute to the demand for infrastructure-grade RF resistors, often sourced via international distribution channels.
What differentiates a flange resistor from a standard chip resistor?
Flange resistors are typically high-power components designed with an integrated mounting flange, usually metallic, specifically engineered to be bolted or soldered onto a substantial heat sink or chassis. This design maximizes thermal transfer for high-power dissipation, which is necessary for transmitters and high-output amplifiers, unlike smaller chip resistors used for low-to-medium power signal processing.
How do manufacturers ensure the reliability of RF resistors for space applications?
Space-grade RF resistors undergo highly rigorous testing, including thermal vacuum bake-out to prevent outgassing, extensive screening for radiation hardness, and adherence to specific space component standards (like MIL-PRF-55342). Traceability of materials, minimal mass, and proven long-term stability are paramount requirements for satellite and launch vehicle usage.
What technological segment within RF resistors is growing the fastest?
The Thin Film technology segment is experiencing the fastest growth, particularly in ultra-miniature surface-mount packages. This growth is driven by the performance requirements of 5G mmWave equipment and advanced military systems that require extremely high precision, low noise, and minimal parasitic effects at elevated frequencies.
What is the key impact of supply chain constraints on the market?
Supply chain constraints, particularly involving specialized substrates (AlN, BeO alternatives) and niche resistive metals, can lead to extended lead times, increased manufacturing costs, and potential delays in rolling out high-end telecom and defense projects. This forces OEMs to dual-source components and manage higher inventory levels.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
