Saw Wire Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 434602 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 246 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Saw Wire Market Size
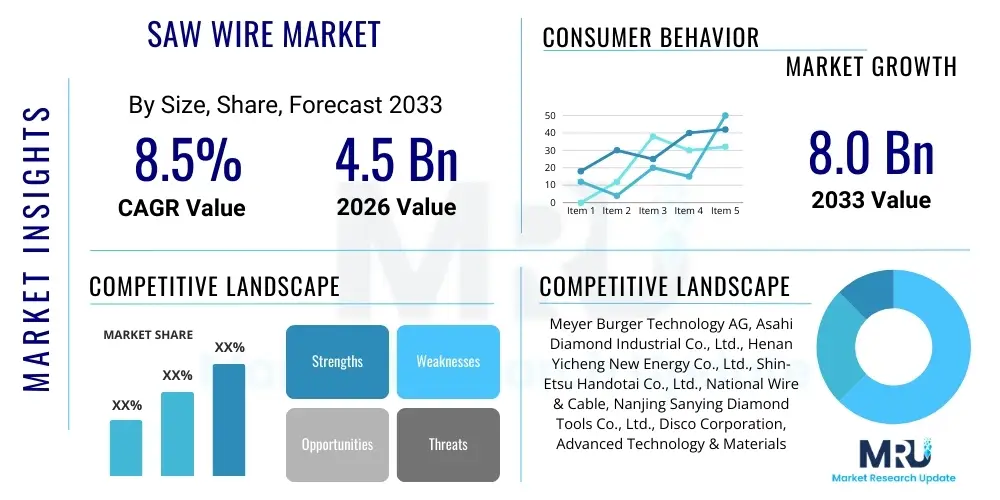
The Saw Wire Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 4.5 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 8.0 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Saw Wire Market introduction
The Saw Wire Market encompasses the global production and distribution of high-strength wires used primarily for slicing hard, brittle materials such as silicon, sapphire, and quartz, critical components in the solar and semiconductor industries. Saw wires, increasingly dominated by advanced diamond wire technology, offer superior cutting efficiency, reduced material loss (kerf loss), and enhanced surface quality compared to traditional slurry-based sawing methods. The transition towards thinner wafers and larger ingot sizes in photovoltaic (PV) and microelectronics manufacturing is the foundational driver for the escalating demand for high-performance saw wire solutions.
Product sophistication is a key characteristic of this market, involving specialized materials like high-carbon steel core wires coated with diamond abrasives through electrochemical or resin bonding processes. Major applications include the production of silicon wafers for solar cells, crucial for the global transition to renewable energy, and the slicing of sapphire substrates used in LED manufacturing and premium consumer electronics. The precise material removal capabilities and high throughput associated with modern saw wire technology make it indispensable for maximizing yield and minimizing costs in highly competitive high-tech manufacturing environments.
The primary benefits driving market adoption include significantly faster slicing speeds, which improve manufacturing productivity, and the environmental advantage of using fewer consumables and less toxic materials compared to older techniques. Furthermore, the inherent stability and consistent performance of diamond saw wire enable manufacturers to achieve ultra-thin wafers, contributing directly to higher efficiency solar cells and smaller, more powerful electronic components. Geographically, manufacturing clusters in Asia Pacific, particularly in China and Southeast Asia, dictate the majority of the demand and innovation pace within the global saw wire ecosystem.
Saw Wire Market Executive Summary
The Saw Wire Market is characterized by robust growth, primarily fueled by the exponential expansion of the solar PV industry and sustained advancements in semiconductor fabrication technologies. Business trends indicate a strong shift towards ultra-thin diamond wire with smaller diameters (below 80 micrometers) to minimize kerf loss, a critical factor in reducing the cost per watt of solar power. Furthermore, material science innovation focusing on enhancing the adherence and uniformity of diamond particles is driving competitive advantages among leading manufacturers. Strategic mergers, acquisitions, and technological partnerships focused on securing stable supply chains for high-purity core wire materials and enhancing proprietary coating processes remain central to market expansion strategies.
Regional trends are overwhelmingly dominated by the Asia Pacific (APAC) region, which houses the vast majority of the world's silicon ingot and wafer manufacturing capacity, particularly in China, which has heavily invested in large-scale PV production. This concentration makes APAC the most crucial market for saw wire consumption and technological deployment. Conversely, North America and Europe focus heavily on niche applications, advanced material research, and the development of next-generation sawing equipment, often serving as critical hubs for high-performance, specialized saw wire variants used in demanding semiconductor and optoelectronics sectors.
Segmentation trends highlight the supremacy of the Diamond Wire segment over the traditional Slurry Wire segment, a transition largely completed within the silicon wafer sector due to productivity mandates. Application-wise, the Solar segment remains the largest volume consumer, while the Semiconductor segment commands higher value due to stringent quality requirements and demand for extremely fine wire diameters. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on customization, offering tailored diamond distribution profiles and wire tension specifications to optimize slicing performance across different types of ingots (monocrystalline vs. multicrystalline silicon).
AI Impact Analysis on Saw Wire Market
Common user questions regarding AI’s impact on the Saw Wire Market generally revolve around four core themes: predictive maintenance, optimization of the slicing process, automation in manufacturing, and material quality assurance. Users are keen to understand how AI algorithms can monitor saw wire vibration, tension, and wear in real-time to prevent catastrophic wire breaks, thereby maximizing uptime and reducing scrap rates in multi-million dollar slicing operations. They also question the capability of machine learning models to correlate input parameters (e.g., cooling fluid composition, wire speed, ingot hardness) with output quality (wafer flatness, subsurface damage) to establish optimal, adaptive cutting protocols for varied material batches.
In response to these concerns, AI and machine learning are increasingly integrated into next-generation saw wire equipment and manufacturing facilities. AI-driven predictive maintenance utilizes sensors attached to the cutting machinery to analyze operational anomalies, detecting subtle deviations in temperature or acoustic signatures that precede wire failure. This capability shifts maintenance from reactive or scheduled intervention to proactive, condition-based servicing, significantly enhancing the overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Furthermore, image recognition AI is being developed to inspect the surface quality of the diamond coating during the manufacturing phase, ensuring highly uniform particle distribution and minimizing defects that could lead to premature wire failure in the end-use application.
The most profound impact of AI lies in process optimization, particularly in maximizing yield and minimizing kerf loss. Machine learning models analyze historical cutting data across various ingot specifications, dynamically adjusting variables like feed rate and wire oscillation patterns in milliseconds. This adaptive control loop ensures that the maximum possible number of high-quality wafers is extracted from each expensive silicon or sapphire ingot. Consequently, the adoption of AI is not merely an improvement but a prerequisite for maintaining cost competitiveness, especially as wafer thickness continues to shrink toward sub-100 micrometer targets.
- AI enables predictive maintenance systems, reducing downtime from unexpected wire breakage.
- Machine Learning optimizes slicing parameters (speed, tension, feed rate) dynamically to enhance wafer yield.
- Computer vision and AI algorithms perform real-time quality control during saw wire coating manufacturing.
- Data analytics derived from AI models assist end-users in selecting the most suitable wire specifications for specific ingot materials.
- Automation driven by AI reduces human intervention in loading and unloading saw wire spools, improving safety and precision.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Saw Wire Market
The dynamics of the Saw Wire Market are shaped by powerful external and internal forces, encapsulated by Drivers, Restraints, and Opportunities (DRO). Primary drivers include the massive global push for solar energy, demanding high volumes of silicon wafers, and the technological requirement for thinner, higher-quality cuts in semiconductor manufacturing. These demands necessitate continuous innovation in wire material science and diameter reduction. However, the market faces significant restraints, notably the intense price competition driven by the concentration of PV production capacity in one region, leading to pressure on profit margins for saw wire manufacturers. Furthermore, dependence on a limited supply chain for high-quality core steel wire poses a structural vulnerability. Opportunities arise from the emergence of new materials requiring precise slicing, such as SiC (Silicon Carbide) and GaN (Gallium Nitride) for power electronics, alongside the untapped potential of recycling spent saw wire materials.
Impact forces stemming from macro-environmental factors significantly influence market behavior. Regulatory frameworks, such as national energy targets and subsidies for renewable energy (like in the US and EU), directly translate into increased demand for solar wafers and, consequently, saw wire. Economic volatility, particularly concerning raw material costs (e.g., high-carbon steel, diamond abrasives), impacts production expenses and pricing strategies. Technological advancement, particularly in crystallization methods leading to larger and purer ingots, forces corresponding innovations in saw wire length and durability. Competitive rivalry is extremely high, characterized by constant technological leapfrogging between key Asian and European players attempting to achieve the smallest wire diameter and highest cutting speed.
The primary driving force remains the relentless pursuit of cost reduction in solar panel manufacturing. The adoption of diamond wire sawing has already dramatically lowered processing costs compared to slurry sawing, but the industry continually demands lower kerf loss, achieved through ever-finer wires. This drive for efficiency creates a perpetual cycle of R&D and capital expenditure for saw wire producers. Conversely, the high capital investment required for state-of-the-art wire drawing and plating equipment acts as a significant barrier to entry, concentrating market power among established, technologically advanced firms capable of handling the precise manufacturing tolerances required for ultra-fine diamond wires.
Segmentation Analysis
The Saw Wire Market is fundamentally segmented based on the core wire type, the abrasive material, the specific diameter, and, most importantly, the end-user application. Analysis shows a clear bifurcation in product demand: high-volume, cost-sensitive wires dominate the solar sector, while specialized, high-precision wires cater to the lower-volume, higher-margin semiconductor and sapphire segments. The continuous trend toward thinner wafers drives segmentation by diameter, with sub-90 micrometer wire gaining paramount importance, forcing manufacturers to differentiate based on the consistency of the diamond coating and the tensile strength of the core material.
From a material perspective, the market is overwhelmingly shifting towards diamond wire, making the traditional distinction between slurry and diamond wire less relevant for new capital investments. Within the diamond wire segment itself, further differentiation occurs based on the diamond bonding method (electroplated, resin, or sintered), each offering varying levels of durability, cutting speed, and lifetime. Understanding these granular segments allows suppliers to tailor their offerings precisely to the operational needs and machinery specifications of major wafer manufacturers, optimizing for either maximum throughput or ultimate precision.
Geographically, market segmentation reflects the global production landscape of crystalline materials. The dominance of Asian producers in PV manufacturing solidifies the APAC region as the central consumption hub for silicon wafer slicing wire, creating a high-volume, highly price-sensitive segment. In contrast, markets in North America and Europe, while smaller in volume, represent segments focused on next-generation materials like compound semiconductors (SiC, GaN) and premium sapphire applications, requiring ultra-precise wire characteristics and specialized R&D support, thereby constituting a distinct high-value segmentation niche.
- Wire Type:
- Diamond Wire
- Slurry Wire (Decreasing Share)
- Application:
- Solar Photovoltaics (PV)
- Semiconductors (Silicon, Compound Semiconductors)
- Sapphire Slicing (LEDs, Consumer Electronics)
- Others (Quartz, Ceramic Materials)
- Wire Diameter:
- Below 90 Micrometers (Ultra-fine)
- 90 Micrometers to 120 Micrometers (Standard Fine)
- Above 120 Micrometers
- Bonding Type:
- Electroplated Diamond Wire
- Resin-bonded Diamond Wire
- Sintered Diamond Wire
Value Chain Analysis For Saw Wire Market
The value chain of the Saw Wire Market is complex, involving highly specialized material providers upstream and large-scale manufacturing operations downstream. Upstream analysis focuses on two critical inputs: the core wire and the abrasive material. High-quality core wire, typically made from high-carbon steel (such as music wire or piano wire), must possess exceptional tensile strength and uniformity, sourced from specialized metal processing firms. Diamond powder, often synthetic monocrystalline diamond, must be meticulously graded for size and purity. The ability to secure stable, high-quality sourcing for these raw materials is a crucial determinant of the final product's performance and cost structure. Any disruption or fluctuation in the price of high-carbon steel severely impacts the entire chain.
Midstream activities involve the highly technical manufacturing processes of wire drawing, surface preparation, and diamond plating/coating. This phase is capital-intensive, requiring specialized electroplating or sintering machinery to ensure the uniform distribution and strong adhesion of diamond particles onto the ultra-fine wire core. Quality control at this stage is paramount, utilizing high-resolution inspection systems to guarantee precise diameter consistency and diamond particle exposure. Manufacturers often invest heavily in proprietary bonding technologies to gain a competitive edge in durability and cutting efficiency, establishing their position as critical value-added processors.
Downstream analysis concerns distribution channels and end-user engagement. Distribution is predominantly direct or through specialized technical distributors who possess the expertise to handle and service these delicate products, which are often shipped in specialized spools. Direct channels are common for large-volume solar customers, facilitating closer collaboration on product customization and technical support. The end-users—wafer manufacturers in the solar and semiconductor industries—are highly sophisticated buyers whose purchasing decisions are based on performance metrics such as kerf loss rate, wire lifetime, and cutting speed, rather than merely price. Indirect sales channels often involve integration with the sale of the sawing equipment itself, where wire providers partner with machinery OEMs to offer complete slicing solutions.
Saw Wire Market Potential Customers
The primary customers of the Saw Wire Market are organizations engaged in the large-scale production of crystalline wafers for high-technology applications. These include major Photovoltaic (PV) ingot and wafer manufacturers, who constitute the largest demand segment globally. These PV customers require high-speed cutting capability, maximal material efficiency, and highly competitive pricing, as the cost of the wafer directly impacts the final solar module price. The rapid technological shifts in solar cell efficiency, such as the move toward N-type monocrystalline wafers, continuously dictate the required specifications and volumes of saw wire purchased.
Another crucial customer segment involves semiconductor wafer fabrication plants (Fabs) and specialized material processing companies. These customers demand extremely high precision, consistency, and low subsurface damage, especially when slicing silicon ingots for advanced microprocessors or compound semiconductors like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Gallium Nitride (GaN) used in power electronics. For these high-value applications, performance and quality assurance heavily outweigh volume and price considerations. The purchasing cycle involves rigorous testing and certification processes to ensure the wire meets extremely tight tolerances for thickness variation and surface roughness.
A third, specialized segment comprises manufacturers of sapphire substrates used primarily in LED lighting, optical windows, and certain consumer electronics (e.g., watch covers, camera lenses). Sapphire is extremely hard, necessitating specific diamond concentration and wire tension profiles. These buyers are concerned with minimizing chipping and maximizing the aesthetic quality of the final slice. Overall, the potential customer base is concentrated among large, multinational corporations with high capital expenditure budgets and strict quality control standards, making the sales cycle long but ensuring stable, high-volume recurring orders once a supplier is qualified.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 4.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 8.0 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 8.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Meyer Burger Technology AG, Asahi Diamond Industrial Co., Ltd., Henan Yicheng New Energy Co., Ltd., Shin-Etsu Handotai Co., Ltd., National Wire & Cable, Nanjing Sanying Diamond Tools Co., Ltd., Disco Corporation, Advanced Technology & Materials Co., Ltd. (AT&M), Noritake Co., Limited, Zhejiang Shangjing New Material Co., Ltd., ILJIN Diamond Co., Ltd., Lianyungang Wuxin Technology Co., Ltd., Huacang Wire, Saint-Gobain, Applied Materials, Inc. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Saw Wire Market Key Technology Landscape
The technological landscape of the Saw Wire Market is characterized by continuous efforts to reduce the wire diameter while simultaneously increasing its mechanical strength and diamond particle adhesion. The core technological advancement has been the shift from traditional slurry cutting to highly efficient diamond wire sawing (DWS). Current R&D focuses on developing ultra-fine wires, often sub-70 micrometers, achieved through sophisticated cold drawing processes for the core steel wire, ensuring a uniform and ultra-high tensile strength necessary to withstand high-speed tension during slicing. This diameter reduction directly contributes to decreased kerf loss, boosting material utilization efficiency, which is vital for high-cost materials like semiconductor silicon and sapphire.
A second critical area of technological innovation lies in the diamond bonding mechanism. Electroplating remains dominant for solar applications due to its cost-effectiveness, but advanced manufacturers are exploring enhanced resin-bonded and sintered diamond wires. Resin-bonded wires offer better control over diamond protrusion and may result in lower subsurface damage, appealing primarily to the semiconductor industry. Sintering technology, though more expensive, produces exceptionally durable wires with high diamond density, suitable for extremely hard materials. Furthermore, proprietary surface treatments and chemical additives are employed during the plating process to ensure superior uniformity of diamond crystal distribution, preventing micro-chipping and improving overall wire lifetime and consistency.
The ancillary technology landscape, encompassing the machinery and testing protocols, is also rapidly evolving. Advancements in sawing machine design, including enhanced oscillation controls and precision tensioning systems, enable the successful utilization of these ultra-fine wires. Quality control technologies, such as non-contact measurement systems using laser micrometers and advanced image analysis, are employed by wire manufacturers to verify diameter tolerance, straightness, and the integrity of the diamond coating along the entire spool length. The integration of I4.0 concepts, including real-time performance monitoring and data feedback loops, is becoming standard practice to ensure optimal utilization of these high-tech sawing consumables.
Regional Highlights
The geographical consumption and production patterns of saw wire are highly skewed, reflecting the global concentration of silicon and sapphire manufacturing. Asia Pacific (APAC) stands as the undisputed powerhouse of the Saw Wire Market, driven overwhelmingly by the colossal investments made in China and, to a lesser extent, in Taiwan, Korea, and Southeast Asia, in photovoltaic (PV) and semiconductor manufacturing capacity. China's dominance in the solar PV supply chain, controlling over 80% of global wafer production, means it commands the majority of the global saw wire demand by volume. This region is characterized by intense price competition and rapid adoption of the latest fine-wire technologies to reduce manufacturing costs per wafer.
North America and Europe represent mature markets that focus less on high-volume solar slicing and more on high-value, niche applications. In North America, demand is robust in the semiconductor sector, particularly for specialized slicing of compound semiconductors like SiC and GaN, essential for electric vehicle power electronics and 5G infrastructure. European companies, historically strong in precision engineering and equipment manufacturing, often lead in developing the next generation of wire sawing machinery and are critical suppliers of ultra-high-quality core wire and specialized diamond coating technologies.
Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa (MEA) currently hold smaller market shares, but their potential is growing, linked closely to nascent solar manufacturing initiatives and increasing local investments in electronics assembly. While MEA's demand is primarily met through imports from APAC, long-term trends suggest growth as renewable energy infrastructure expands. Investment in high-tech manufacturing, such as specialized materials processing, remains limited in these regions, making their consumption profile reliant on either imported finished wafers or small-scale industrial applications rather than large-scale PV production.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Dominates the global market due to massive silicon wafer production for solar PV; driven by China, representing the largest consumption segment by volume and fastest adopter of sub-90 µm wire technology.
- North America: Focuses on high-value semiconductor applications and R&D for next-generation materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN) slicing.
- Europe: Key region for high-quality core wire production and manufacturing of advanced sawing equipment; specialized demand for precision cuts in optoelectronics and high-performance materials.
- MEA & Latin America: Emerging markets with potential growth tied to increasing utility-scale solar projects, though consumption volumes remain relatively low and dependent on imports.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Saw Wire Market.- Meyer Burger Technology AG
- Asahi Diamond Industrial Co., Ltd.
- Henan Yicheng New Energy Co., Ltd.
- Shin-Etsu Handotai Co., Ltd.
- National Wire & Cable
- Nanjing Sanying Diamond Tools Co., Ltd.
- Disco Corporation
- Advanced Technology & Materials Co., Ltd. (AT&M)
- Noritake Co., Limited
- Zhejiang Shangjing New Material Co., Ltd.
- ILJIN Diamond Co., Ltd.
- Lianyungang Wuxin Technology Co., Ltd.
- Tongwei Co., Ltd. (Integrated Manufacturer)
- Saint-Gobain
- Applied Materials, Inc.
- Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
- Tokyo Seimitsu Co., Ltd.
- Bridgestone Corporation (Specialty Wires)
- Zaozhuang Dazhong Diamond Tools Co., Ltd.
- Shenzhen Yicheng New Energy Co., Ltd.
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Saw Wire market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is driving the market transition from slurry wire to diamond wire?
The shift is driven primarily by superior cost-efficiency and productivity. Diamond wire sawing (DWS) offers significantly faster cutting speeds, drastically reduces kerf loss (material waste), and lowers overall operating expenses compared to slurry-based methods, which require costly abrasive materials and disposal management. This transition is essential for manufacturers aiming to reduce the cost per watt of solar energy.
How does the reduction in saw wire diameter impact wafer manufacturing?
Diameter reduction, particularly moving below 90 micrometers, is critical for minimizing kerf loss, the amount of material turned into dust during slicing. By reducing kerf loss, manufacturers can obtain more usable wafers from a single expensive silicon ingot, thereby boosting material utilization efficiency and significantly lowering the manufacturing cost per wafer, a key competitive advantage in the solar sector.
Which application segment holds the largest share in the Saw Wire Market?
The Solar Photovoltaic (PV) segment holds the largest market share by volume. This dominance is attributed to the high-volume manufacturing of silicon wafers required for global solar cell production, especially concentrated in the Asia Pacific region. While the Semiconductor segment requires high-precision wire, the sheer scale of solar cell manufacturing dictates overall market volume.
What are the primary factors determining the tensile strength of saw wire?
The tensile strength is primarily determined by the quality and metallurgy of the core material, typically high-carbon steel wire (music wire). Advanced manufacturing techniques, including precise cold drawing and heat treatments, are employed to ensure ultra-high strength and uniformity. High tensile strength is crucial as it allows the ultra-fine wire to operate under high tension at high speeds without breaking, maximizing operational stability.
How is the increasing demand for compound semiconductors affecting the saw wire industry?
The rising demand for Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN) wafers, critical for power electronics in EVs and 5G, creates a high-value niche segment. These extremely hard materials require specialized saw wire with tailored diamond concentration and stronger bonding techniques (often sintered or specialized resin) to ensure minimal subsurface damage and high-quality slicing, pushing innovation toward durable, high-precision products.
Detailed Technical Market Dynamics and Future Outlook
The future trajectory of the Saw Wire Market is intrinsically linked to material science breakthroughs and the economic viability of ultra-thin wafer technology. The ongoing battle to reduce wire diameter presents significant engineering challenges related to balancing mechanical integrity with abrasive performance. Manufacturers must continually refine the process of electroplating or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to ensure that the diamond particles are securely bonded and uniformly exposed along the wire surface, even at diameters approaching 60 micrometers. Failure to achieve this uniformity leads directly to inconsistent cutting speed and premature wire rupture, severely impacting downstream profitability. Furthermore, the development of diamond wires specifically optimized for cutting hard, large-diameter monocrystalline silicon ingots, which exhibit higher internal stresses than multicrystalline blocks, requires enhanced elastic properties and fatigue resistance in the core steel material, driving up demand for premium, proprietary steel alloys.
Market saturation in standard PV applications is forcing key players to diversify into specialized industrial and electronic applications where margins are higher and technical barriers to entry are more significant. For example, the precise dicing of quartz and advanced ceramic materials, used in optical and industrial sensing devices, requires saw wires with unique abrasive characteristics tailored to avoid fracturing and micro-cracking in these brittle substrates. This segmentation demands flexibility in manufacturing lines and robust R&D pipelines focused on tailored solutions rather than mass standardization. The long-term stability of the market will thus depend on the ability of manufacturers to transition successfully from being commodity suppliers for the solar industry to precision engineering partners for diverse high-tech sectors, focusing on technical specifications such as diamond grit size distribution, protrusion height, and overall wire lifespan consistency under varying operational loads.
Regulatory and environmental pressures also play a growing role in shaping the market's technological evolution. While diamond wire already represents an environmental improvement over slurry, manufacturers are exploring recyclable or biodegradable core materials and less resource-intensive bonding techniques. Furthermore, the push for circular economy practices means that the efficient recovery and reuse of diamond particles from spent wire is becoming a significant competitive factor. Companies that can demonstrate a closed-loop system or significantly reduce the overall environmental footprint of their product life cycle will gain a competitive advantage, particularly in environmentally conscious markets in Europe and North America. Investment in advanced manufacturing analytics, leveraging IoT sensors across production lines, is crucial for optimizing energy consumption and minimizing waste generation during the wire coating process.
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Positioning
The competitive landscape of the Saw Wire Market is characterized by intense technological rivalry between established European and Japanese precision manufacturers and high-volume, cost-effective Chinese producers. Key strategic positioning revolves around two main axes: cost leadership for the solar segment and technological differentiation for the semiconductor and specialized material segments. Companies pursuing cost leadership focus on massive production scale, optimizing supply chain logistics for core materials, and automating manufacturing processes to drive down the per-meter cost of diamond wire. This strategy is highly effective in securing large-volume contracts from major solar wafer producers, but often results in thin profit margins and vulnerability to raw material price fluctuations.
In contrast, firms focusing on technological differentiation invest heavily in R&D to develop patented bonding chemistries and proprietary core wire alloys. These innovations enable them to manufacture ultra-fine wire (e.g., <60 µm) with unparalleled tensile strength and superior cutting quality, crucial for high-value substrates like Silicon Carbide. Their strategy involves securing premium pricing by demonstrating superior performance metrics, such as lower total thickness variation (TTV) in sliced wafers and extended wire longevity. Successfully navigating this competitive environment requires global operational capabilities, robust intellectual property protection, and deep technical partnerships with equipment manufacturers and leading wafer producers to co-develop products tailored to emerging sawing challenges.
A crucial factor influencing market competition is the vertical integration adopted by several large silicon and solar manufacturers who have internalized saw wire production. While this reduces external market size, it also forces independent wire suppliers to become more specialized and focus on non-integrated clients or differentiate themselves through technology that is difficult for end-users to replicate internally. To mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on the cyclical solar industry, many firms are actively seeking expansion into niche industrial sawing applications, such as specialized metal cutting or precision machining, thereby broadening their revenue streams and stabilizing overall business performance against inherent volatility in the high-tech materials markets.
Future Technology Trends: SiC and Large Ingot Processing
The burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) market and the rapid deployment of advanced power grid infrastructure are driving substantial demand for Silicon Carbide (SiC) wafers, which represents one of the most significant future growth opportunities for the saw wire industry. SiC is significantly harder and more brittle than silicon, posing unique slicing challenges. Future saw wire technology must address these difficulties by incorporating specialized diamond treatments and potentially moving beyond traditional electroplating to advanced sintering or brazing techniques that offer maximum diamond retention and durability under extreme stress. Furthermore, the development of dedicated SiC-optimized sawing fluid and machine design is occurring concurrently, creating an interconnected technological ecosystem.
Another major trend is the ongoing increase in the size and weight of silicon ingots (both monocrystalline and multicrystalline) in solar manufacturing to achieve economies of scale. Handling these massive ingots requires saw wires of exceptional length and consistency, often exceeding 500 kilometers per spool. This places immense pressure on wire manufacturers to ensure flawless quality control across massive production runs, demanding highly sophisticated, automated inspection systems. The physical stress exerted on the wire during the slicing of these larger ingots necessitates material science advancements that enhance core wire ductility and resistance to fatigue failure over extended cutting periods, driving up the specifications for high-grade steel inputs.
The evolution towards reusable or segmented saw wire systems is also being explored. While currently cost-prohibitive for high-volume solar applications, research into modular wire segments that can be replaced individually or systems designed for automated diamond replenishment aims to reduce consumable waste and extend the effective service life of the cutting medium. If implemented successfully, such innovations could dramatically alter the current consumption model, shifting the focus from high-volume disposable wire towards long-life, high-performance cutting systems, thereby demanding greater R&D investment and a fundamental shift in supply chain management and service offerings within the saw wire manufacturing sector.
Technical Specifications and Quality Assurance Benchmarks
The technical specifications of modern saw wire are becoming increasingly stringent, moving far beyond simple diameter measurement. End-users now prioritize parameters such as Total Thickness Variation (TTV) control, surface roughness (Ra), and sub-surface damage (SSD) minimization, all directly traceable to the saw wire’s quality. High-precision sawing demands TTV values below 5 micrometers for semiconductor applications and consistent performance for achieving <100 µm wafer thickness in solar. Achieving these benchmarks requires saw wire manufacturers to control the homogeneity of the diamond layer down to the nanoscale, often involving plasma etching or chemical treatment of the core wire surface prior to plating to optimize diamond crystal nucleation and adherence. The diamond concentration, which is the density of abrasive particles, must be precisely optimized: too high, and the wire wears prematurely; too low, and the cutting rate suffers, demonstrating the fine balance required in proprietary coating recipes.
Quality assurance processes are robust and integrated, encompassing both in-line monitoring during manufacturing and comprehensive spool-level certification before shipment. In-line monitoring utilizes advanced laser and optical sensors to continuously check the wire diameter and ovality, ensuring deviations are minimized to less than 1 micrometer. Post-production certification involves rigorous tensile strength tests, fatigue testing under simulated high-tension cutting cycles, and even microscopic analysis of diamond particle protrusion uniformity. Since defects in a single section of a kilometer-long spool can lead to failure during the critical slicing process, the reliability and consistency across the entire length are paramount. The stringent quality demands from the semiconductor industry, driven by zero-tolerance policies for material defects, set the global benchmark for saw wire manufacturing excellence.
Furthermore, the development of specialized lubricants and coolants specifically designed for diamond wire sawing also forms a critical part of the overall technology landscape. These fluids not only reduce friction and heat generation during high-speed cutting but also facilitate the effective removal of silicon kerf sludge from the cutting zone. The interaction between the saw wire's diamond surface, the material being cut, and the cutting fluid is a complex tribological system. Saw wire manufacturers often collaborate with chemical companies to formulate optimized fluid compositions that enhance wire lubrication without compromising diamond particle stability or leaving residues on the finished wafer surface, thereby increasing yield and reducing post-slicing cleaning complexity.
Detailed Analysis of Market Restraints and Mitigation Strategies
One of the foremost restraints impacting the Saw Wire Market is the inherent volatility and consolidation within the downstream solar industry. Large solar wafer manufacturers possess significant bargaining power, driving down the unit price of saw wire through aggressive procurement strategies, which severely compresses the operating margins of wire suppliers, particularly those focused solely on high-volume electroplated wire. This price pressure necessitates continuous efficiency gains in the wire manufacturing process, potentially limiting investment in long-term, high-risk R&D projects. Mitigation strategies often involve adopting hedging mechanisms for core raw material procurement (especially high-carbon steel) and diversifying the customer base geographically to avoid over-reliance on a single high-volume, low-margin region, while simultaneously seeking premium pricing for specialized, high-performance wire variants used in demanding applications.
A second major restraint is the significant capital expenditure required to establish and upgrade high-precision wire drawing and coating facilities. The technical expertise and specialized machinery needed for producing ultra-fine, highly uniform diamond wire constitute a high barrier to entry, limiting the number of competitive players and hindering rapid market supply adjustments in response to sudden surges in demand. Furthermore, the proprietary nature of the best diamond bonding technologies means that intellectual property disputes and the leakage of trade secrets pose ongoing business risks. Companies must invest heavily not only in R&D but also in robust IP protection measures globally to safeguard their competitive advantage derived from patented coating processes and material recipes.
Finally, the challenge of managing kerf sludge and spent wire disposal poses an environmental and economic restraint. Although diamond wire is cleaner than slurry, the resulting silicon dust and metal core must be managed. While some firms are developing sophisticated methods to reclaim silicon from the kerf waste for secondary uses, the sheer volume of spent wire requiring disposal remains a challenge. Innovations in wire design focusing on reduced core weight or materials that are easier to recycle will be necessary to overcome this long-term constraint. The implementation of circular economy principles remains a significant long-term challenge that requires collaborative efforts between wire producers, sawing machine OEMs, and environmental regulatory bodies to establish viable industrial recycling pathways for the composite materials involved.
Global Supply Chain Optimization and Resilience
The global supply chain for saw wire is highly interdependent and susceptible to geopolitical and logistical disruptions. The reliance on specialized high-purity, high-carbon steel from a limited number of global suppliers, primarily based in Asia and Europe, creates a significant vulnerability. Disruptions in steel production or international shipping can severely bottleneck saw wire manufacturing globally, affecting PV production timelines. To build supply chain resilience, major saw wire producers are implementing multi-sourcing strategies, securing long-term contracts with secondary and tertiary suppliers, and, in some cases, exploring localized or regionalized production hubs to mitigate risks associated with long-distance maritime transport and cross-border tariffs.
Furthermore, the procurement of monocrystalline diamond powder, another key input, also presents complexities related to ethical sourcing and consistency of grade. Synthetic diamond manufacturers must meet stringent standards for particle size distribution and crystal morphology, as any variation directly impacts the wire's abrasive performance. Strategic alliances and qualification agreements with leading diamond synthesis labs are essential to ensure a steady supply of high-quality abrasive material, particularly for the precision semiconductor segment where quality variance is unacceptable. The trend towards vertical integration in the core wire production by some players suggests a desire to control the quality and cost of this critical input directly, thereby enhancing supply chain stability.
Logistical optimization is another critical area. Saw wire is a highly sensitive, precision tool; its handling and packaging require specialized spools and climate-controlled transport to prevent damage or degradation of the diamond coating before reaching the end-user's cutting facility. Optimization efforts focus on minimizing transit times, enhancing traceability using digital supply chain tools (e.g., blockchain), and partnering with specialized logistics providers who understand the requirements for transporting high-value, sensitive consumables. Effective supply chain management is not just about cost reduction but fundamentally about ensuring the reliability and quality of the final product delivered to time-sensitive manufacturing lines globally.
Market Opportunities in Advanced Material Slicing
The global push towards electrification and energy efficiency is generating significant market opportunities for saw wire manufacturers outside of traditional silicon PV. The advent of Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN) power devices, crucial for high-voltage and high-frequency applications like electric vehicle battery chargers and 5G communication systems, necessitates extremely precise and damage-free slicing of these challenging materials. Current mechanical slicing methods often result in excessive material waste and time-consuming processes. Advanced diamond wire, particularly those featuring modified bonding matrices and optimized diamond grit sizes, offers a viable pathway to increase yield and reduce the cost of SiC wafer production, positioning this segment as a premium growth area with higher profit margins than the standard PV market.
Additionally, the burgeoning medical and optical sectors provide specialized niches. High-purity quartz and various crystalline glasses used in medical devices (e.g., optical sensors, imaging systems) require ultra-low subsurface damage during slicing to maintain optical clarity and structural integrity. Saw wire tailored for these applications often focuses on low cutting force and resin-bonded diamond surfaces rather than maximum speed. Similarly, the growing use of synthetic sapphire in military and specialized consumer electronics, demanding thin, robust, scratch-resistant cover materials, sustains a niche market for specialized sapphire slicing wire, which typically requires a higher diamond concentration compared to standard silicon wire to effectively manage sapphire's extreme hardness.
Exploiting these advanced material opportunities requires a consultative sales approach, where saw wire suppliers work closely with material researchers and equipment manufacturers to co-develop sawing processes. This involves providing technical support, conducting joint testing programs, and offering custom wire specifications that precisely match the material's crystallographic orientation and hardness characteristics. Firms that successfully transition their expertise from high-volume silicon to high-value compound semiconductors and other exotic materials will secure market leadership and hedge against the cyclical nature of the solar industry, ensuring sustained profitability in the forecast period.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
