Stationary Fuel Cells Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 431746 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 255 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Stationary Fuel Cells Market Size
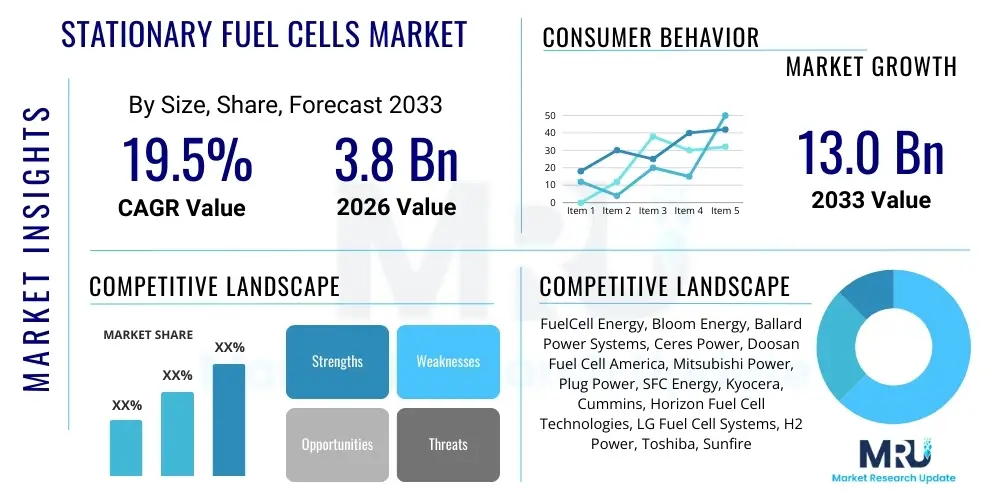
The Stationary Fuel Cells Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 19.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 3.8 Billion in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 13.0 Billion by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Stationary Fuel Cells Market introduction
The Stationary Fuel Cells Market encompasses the development, manufacturing, and deployment of fuel cell systems designed to provide continuous or backup power generation in fixed locations. These systems convert the chemical energy of a fuel, typically hydrogen or natural gas, directly into electricity and heat through an electrochemical process, offering significantly higher efficiency and lower emissions compared to conventional combustion-based generation methods. Stationary fuel cells are crucial components in the global transition toward decentralized energy architectures, providing solutions for combined heat and power (CHP), distributed generation (DG), and prime power applications across various sectors. The inherent modularity and low noise profile of these systems make them ideal for urban installations and critical infrastructure.
Major applications of stationary fuel cells span across commercial buildings, industrial facilities, remote sites, and critical infrastructure such as telecommunications towers and data centers. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs), Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs), and Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFCs) are the primary technologies utilized, each offering distinct operating temperatures, fuel flexibility, and power output ranges. Benefits driving market adoption include enhanced energy security, resilience against grid outages, exceptional reliability for mission-critical loads, and substantial environmental advantages, particularly when fueled by green hydrogen or renewable natural gas (RNG). Governments globally are increasingly supporting fuel cell deployment through subsidies, tax credits, and favorable regulatory frameworks designed to promote low-carbon power generation.
Driving factors for sustained market growth include stringent climate change mitigation policies requiring lower carbon footprints from energy providers and end-users, the expanding need for resilient and high-quality power in digital infrastructure (like data centers and 5G networks), and continuous technological advancements improving system longevity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, the increasing integration of intermittent renewable sources (solar and wind) mandates flexible, reliable backup power solutions, where stationary fuel cells, especially those integrated with microgrids, play a pivotal role in stabilizing localized energy networks.
Stationary Fuel Cells Market Executive Summary
The Stationary Fuel Cells Market is experiencing robust growth driven by accelerating global commitments to decarbonization and the urgent need for enhanced power reliability in critical sectors. Business trends indicate a strong focus on scaling manufacturing capabilities and achieving cost parity with conventional generation, supported by significant investments in automated production lines. Strategic partnerships between fuel cell developers and major energy utility companies are becoming common, aimed at large-scale deployment of megawatt-class systems for grid support and industrial applications. Furthermore, the shift towards utilizing renewable fuels, such as ammonia and green hydrogen, is shaping product development, pushing manufacturers to enhance multi-fuel compatibility, especially in high-temperature SOFC and MCFC platforms, to ensure long-term sustainability and compliance with evolving emission standards globally.
Regional trends highlight Asia Pacific (APAC) as the fastest-growing market, primarily fueled by massive infrastructure development in countries like Japan, South Korea, and China, which have established national hydrogen economy roadmaps and ambitious fuel cell deployment targets. North America remains a dominant market, largely due to significant federal and state incentives, particularly in the U.S., focusing on resiliency projects for data centers and commercial distributed generation. Europe’s growth is concentrated on implementing CHP units under the revised Renewable Energy Directives (RED II/III), leveraging high thermal efficiency to reduce overall energy costs and improve urban air quality. The competitive landscape is characterized by established energy corporations expanding their fuel cell portfolios and specialized pure-play fuel cell manufacturers vying for technological leadership in durability and operational efficiency.
Segmentation trends show Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) leading the market in terms of revenue, driven by their superior electrical efficiency, fuel flexibility (natural gas, biogas, hydrogen), and applicability in large-scale industrial and utility applications. However, Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) are gaining traction rapidly for smaller-scale, localized power generation and backup systems due to their quick startup times and relatively low operating temperatures. The critical infrastructure end-user segment, particularly data centers and telecom, dominates demand, seeking uninterrupted power supply and decentralized energy autonomy. The medium-to-large capacity segment (above 1 MW) is projected to exhibit the highest CAGR as utilities and large industrial consumers increasingly look to fuel cells for prime power and grid stabilization services.
AI Impact Analysis on Stationary Fuel Cells Market
User inquiries regarding AI's influence on the Stationary Fuel Cells Market primarily center on three areas: optimizing operational efficiency and lifespan, predictive maintenance strategies, and enhancing system integration with complex smart grids or microgrids. Users are keen to understand how AI-driven predictive algorithms can minimize unexpected downtime, a critical concern for infrastructure reliant on continuous power. They also investigate how AI can optimize fuel utilization based on real-time load demands and fuel quality variations, thereby maximizing energy conversion efficiency. Furthermore, there is significant interest in using machine learning models to analyze the vast streams of sensor data generated by fuel cell stacks to identify subtle degradation patterns, ensuring proactive servicing and extending the operational lifespan of high-capital systems.
- AI algorithms optimize fuel cell stack performance by precisely regulating temperature, pressure, and flow rates, maximizing electrical efficiency across varied load profiles.
- Machine learning models are employed for predictive maintenance, analyzing degradation markers in real-time to forecast component failures, drastically reducing unexpected downtime and maintenance costs.
- AI enhances grid integration by predicting localized energy demand and optimizing fuel cell output as part of a distributed energy resource (DER) management system, stabilizing microgrids.
- Data analytics and AI facilitate system design optimization, allowing engineers to simulate various operational scenarios and accelerate the development cycle of next-generation fuel cell architectures.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) is increasingly used in quality control and field service applications, interpreting technician notes and operational manuals to improve troubleshooting accuracy and speed.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Stationary Fuel Cells Market
The Stationary Fuel Cells Market is simultaneously propelled by increasing global electrification needs and restrained by high initial capital investment costs and complex hydrogen infrastructure challenges. Opportunities lie in leveraging favorable governmental policies and utilizing the superior efficiency of fuel cells in Combined Heat and Power (CHP) applications, especially in densely populated urban centers looking to curb emissions. The core impact force driving current growth stems from the intensifying global necessity for energy resilience in the face of climate change-related weather events and geopolitical instability, positioning decentralized fuel cells as indispensable components of modern energy security strategies. Addressing the current reliance on subsidized natural gas reforming for fuel supply remains a major challenge, although the rapid scaling of green hydrogen production promises to mitigate this in the medium term, creating a powerful positive force.
Drivers include the accelerating adoption of distributed power generation to overcome grid bottlenecks and losses associated with long-distance transmission, alongside supportive regulatory frameworks in developed economies mandating low-emission power sources for new commercial and industrial construction. The increasing demand for reliable backup power in critical infrastructure like 5G base stations, financial institutions, and medical facilities is also a key impetus. Conversely, restraints involve the technical complexity of integrating fuel cells with existing power grids, perceived risks associated with hydrogen storage and handling (though highly mitigated by advanced safety standards), and the relatively slower pace of commercial adoption compared to cheaper, established fossil fuel alternatives. Standardization of component manufacturing and module assembly remains a critical hurdle that must be addressed to unlock lower cost curves for mass market penetration, especially in the PEMFC segment.
The primary opportunities for market stakeholders are anchored in developing specialized solutions for remote and off-grid applications where traditional power access is prohibitively expensive or unreliable, such as remote sensing stations and island communities. Furthermore, the integration of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technology with fuel cell systems operating on natural gas or biogas presents a pathway to near-net-zero emissions, significantly enhancing their commercial viability in regulatory environments mandating deep decarbonization. The most potent impact force shaping the competitive dynamic is the race to improve system longevity and durability (especially the lifespan of the stack itself) beyond 80,000 operational hours, which is crucial for achieving attractive lifetime economic returns essential for utility-scale deployment models.
Segmentation Analysis
The Stationary Fuel Cells Market is critically segmented based on the type of fuel cell technology, the fuel used, the application, and the system capacity (power output). This granular segmentation allows market participants to tailor their offerings to specific operational requirements and regulatory environments. Technology segmentation is pivotal as it dictates operational temperature, efficiency envelope, and primary fuel compatibility. The capacity segmentation, specifically distinguishing between small, medium, and large-scale systems, directly correlates with end-user requirements, ranging from residential backup power to utility-scale prime power generation for grid support, profoundly influencing pricing and deployment strategies across global regions.
Fuel type analysis reveals a transitional market, moving from primary reliance on reformed natural gas (via internal reforming within the fuel cell stack, common in SOFCs and MCFCs) toward cleaner alternatives such as pure hydrogen, biogas (methane derived from organic waste), and emerging fuels like methanol or ammonia. Biogas utilization is particularly strong in markets emphasizing circular economy principles and waste-to-energy solutions. The application segment reflects the growing diversification of use cases, moving beyond combined heat and power (CHP) into areas requiring specialized high-power solutions, notably uninterruptible power supply (UPS) for data centers where downtime is prohibitively expensive, and distributed generation (DG) for industrial parks.
Understanding these segmentations is vital for effective strategic planning. For instance, the demand profile for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) is heavily influenced by the hydrogen refueling infrastructure development, making them highly sensitive to localized policy initiatives. Conversely, Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs), due to their fuel flexibility and high efficiency, capture the majority of the larger-scale commercial and utility contracts. The market structure, therefore, is not monolithic but rather a collection of distinct sub-markets defined by technological readiness, fuel availability, and end-user criticality.
- Technology Type:
- Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC)
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC)
- Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell (MCFC)
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC)
- Others (e.g., Alkaline Fuel Cells (AFC), Direct Methanol Fuel Cells (DMFC))
- Application:
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
- Prime Power/Continuous Generation
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)/Backup Power
- Distributed Generation (DG)
- Fuel Type:
- Natural Gas
- Hydrogen
- Biogas/LPG
- Methanol/Others
- Capacity:
- Micro (Below 1 kW)
- Small (1 kW to 250 kW)
- Medium (250 kW to 1 MW)
- Large (Above 1 MW)
Value Chain Analysis For Stationary Fuel Cells Market
The value chain for the Stationary Fuel Cells Market is complex and highly specialized, beginning with the upstream sourcing and processing of core materials, progressing through sophisticated manufacturing of components, and culminating in system integration, distribution, and critical aftermarket services. Upstream activities involve securing high-purity raw materials such as specialized ceramics (for SOFCs), platinum group metals (PGMs) used as catalysts (for PEMFCs and PAFCs), and advanced bipolar plates, which are essential for stack performance and durability. The efficiency and cost structure of the entire value chain are heavily dependent on the procurement stability and pricing volatility of these scarce raw materials, prompting significant R&D efforts into developing non-PGM catalysts and alternative stack materials.
Midstream processing focuses on the precision manufacturing of the core fuel cell stack, which involves electrode and electrolyte fabrication, membrane manufacturing, and the assembly of the balance of plant (BoP) components, including reformers, heat exchangers, and power conditioning units. This stage is highly capital-intensive and requires stringent quality control to ensure operational lifespan guarantees. Downstream activities are dominated by system integration, ensuring that the fuel cell unit is seamlessly connected to the end-user’s electrical infrastructure and, where applicable, their heating systems (for CHP applications). Distribution channels are predominantly indirect, relying on specialized engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) firms, utility providers acting as key integrators, and independent power producers (IPPs) who manage and operate the installed capacity under long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs).
Direct sales, while less common for large utility projects, often occur in niche segments like specialized backup power solutions for telecom or military applications. However, the majority of market volume flows through indirect channels, which provide necessary local expertise in permitting, installation, and ongoing maintenance. Critical to the downstream segment is the provision of robust maintenance contracts and fuel supply logistics, particularly hydrogen delivery or reliable biogas sourcing. Companies that can vertically integrate key manufacturing steps—from membrane fabrication to system packaging—often gain significant competitive advantages in cost reduction and quality control, thereby optimizing the total cost of ownership for end-users, which remains a key commercial barrier.
Stationary Fuel Cells Market Potential Customers
The Stationary Fuel Cells Market targets a diverse and sophisticated customer base, predominantly comprising large commercial entities, industrial facilities, utility operators, and critical infrastructure providers whose operations demand extremely high power quality and resilience. The primary end-users, or buyers, are organizations where the cost of power interruption significantly outweighs the high initial capital investment of the fuel cell system. This includes the rapidly expanding data center industry, which requires non-stop power supply for computing and cooling, and the telecommunications sector, which relies on fuel cells to maintain network integrity during grid disturbances, especially with the proliferation of 5G infrastructure requiring reliable, distributed power sources.
Another major segment of potential customers includes large institutional buildings such as hospitals, universities, and government facilities that benefit substantially from Combined Heat and Power (CHP) applications. These customers can maximize the fuel cell's efficiency by utilizing both the generated electricity and the waste heat for heating, cooling, or domestic hot water, achieving energy cost savings and reducing dependency on centralized utilities. Furthermore, industrial process manufacturing plants, particularly those requiring continuous high-grade heat and electricity (e.g., chemical processing, automotive manufacturing), represent significant potential due to the fuel cell's ability to maintain high operational uptime and manage fluctuating energy prices through self-generation.
Finally, utility companies and Independent Power Producers (IPPs) are emerging as critical buyers, deploying stationary fuel cells as part of broader grid modernization and decentralized energy strategies. Utilities use these systems for peak shaving, frequency regulation, and as environmentally compliant alternatives to diesel generators in substation applications. Remote and off-grid customers, including oil and gas pipelines, remote monitoring stations, and island communities, also form a valuable niche market, where the robust and reliable nature of fuel cells offers a compelling economic alternative to costly, complex grid extensions or inefficient, high-emission diesel generators, solidifying fuel cells as a core component of future energy independence efforts.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 3.8 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 13.0 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 19.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | FuelCell Energy, Bloom Energy, Ballard Power Systems, Ceres Power, Doosan Fuel Cell America, Mitsubishi Power, Plug Power, SFC Energy, Kyocera, Cummins, Horizon Fuel Cell Technologies, LG Fuel Cell Systems, H2 Power, Toshiba, Sunfire |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Stationary Fuel Cells Market Key Technology Landscape
The Stationary Fuel Cells Market is defined by a dynamic technological landscape encompassing multiple fuel cell types, each optimized for specific operating environments and power outputs. The most commercially prominent technologies include Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) and Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). SOFCs operate at high temperatures (600°C to 1,000°C), which allows them to efficiently reform hydrocarbon fuels like natural gas or biogas internally, offering superior electrical efficiency (upwards of 60%) and high fuel flexibility, making them the preferred choice for large-scale, continuous power generation and Combined Heat and Power (CHP) industrial applications where the high-grade exhaust heat can be effectively utilized.
Conversely, PEMFCs operate at lower temperatures (50°C to 100°C) and require high-purity hydrogen as fuel. Their advantages include rapid startup, high power density, and compactness, positioning them ideally for smaller, localized power generation, backup power (UPS) for telecom and data centers, and niche applications requiring immediate response capability. The current technological focus in both SOFC and PEMFC research is heavily centered on enhancing stack durability, primarily through advanced material science to reduce degradation rates, and decreasing manufacturing complexity and cost, moving production processes toward high-volume, automated methods to achieve economies of scale necessary for widespread commercial competitiveness against incumbent power generation technologies.
Furthermore, significant advancements are being made in balance of plant (BoP) components, particularly sophisticated power electronics and control systems, which are crucial for managing the complex interplay between fuel input, stack output, and grid interface. Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFCs) also remain relevant, particularly for utility-scale distributed generation and industrial applications using captured CO2 sources, though their market share is often constrained by high operating temperatures and specific material requirements. The future technological trajectory is geared towards hybridizing fuel cells with batteries (fuel cell-battery hybrid systems) to improve transient response capability and overall system efficiency, catering to the growing demands of modern, highly variable microgrids.
Regional Highlights
The geographical analysis of the Stationary Fuel Cells Market reveals distinct growth trajectories and technological preferences across major global regions, heavily influenced by local energy policies, fuel availability, and prevailing infrastructure needs. North America, led by the United States, stands as a mature market segment characterized by strong regulatory incentives, such as federal tax credits and state-level renewable portfolio standards (RPS), that favor distributed generation technologies. Demand here is predominantly driven by critical infrastructure providers (data centers, telecom) seeking grid resiliency solutions and large commercial campuses utilizing fuel cells for high-efficiency CHP applications. The deployment of high-power SOFC systems is particularly robust in this region, supported by established natural gas infrastructure.
Asia Pacific (APAC) represents the dominant growth engine for the stationary fuel cell market, demonstrating the highest Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) globally. This rapid expansion is underpinned by comprehensive national hydrogen roadmaps in key economies such as Japan (pioneering residential Ene-Farm systems and industrial deployments), South Korea (heavy governmental investment in fuel cell deployment mandates and large-scale power plants), and China (focused on utilizing fuel cells for combined heat and power in its industrial corridors). APAC’s demand profile is characterized by a strong mix of large utility-scale projects (primarily SOFC and MCFC) and high-volume residential PEMFC systems, fueled by dense population centers and urgent air quality improvement mandates.
Europe demonstrates stable growth, primarily focused on decarbonization targets mandated by the European Union’s Green Deal. The market emphasizes high-efficiency CHP solutions in commercial and residential settings, leveraging the benefits of decentralized energy production in densely populated areas. Germany, the UK, and Scandinavian countries are key European markets, driven by subsidies for micro-CHP units and stringent regulations penalizing high-emission energy sources. The region exhibits a strong preference for systems compatible with emerging hydrogen networks and biogas utilization, aligning with circular economy objectives. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa (MEA) currently represent emerging markets, with deployment focused on off-grid power solutions, remote oil and gas infrastructure, and pilot projects aimed at enhancing energy access and reliability in underserved or geographically challenging regions.
- North America: Market dominance in capacity, driven by high demand for grid resiliency in critical infrastructure, particularly data centers and 5G networks, supported by federal tax incentives and established natural gas supply chains.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Leading market in terms of growth rate; robust government-backed hydrogen strategies and massive deployment mandates in South Korea and Japan across residential and utility sectors.
- Europe: Focus on high-efficiency Combined Heat and Power (CHP) applications in line with EU decarbonization and urban sustainability goals; strong regulatory support for micro-CHP and renewable fuel integration.
- Latin America: Emerging focus on off-grid power solutions for remote industries (e.g., mining, agriculture) where grid extension is uneconomical.
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): Growth driven by oil and gas sector demands for reliable remote power and initial investments in centralized hydrogen production hubs, creating future fueling opportunities.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Stationary Fuel Cells Market.- FuelCell Energy
- Bloom Energy
- Ballard Power Systems
- Ceres Power
- Doosan Fuel Cell America
- Mitsubishi Power
- Plug Power
- SFC Energy
- Kyocera
- Cummins
- Horizon Fuel Cell Technologies
- LG Fuel Cell Systems
- H2 Power
- Toshiba
- Sunfire
- Nedstack Fuel Cell Technology
- Intelligent Energy
- Miura Co., Ltd.
- Elcogen
- Symbio (Michelin & Faurecia)
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Stationary Fuel Cells market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What are the primary advantages of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) in stationary power generation?
SOFCs are highly advantageous due to their superior electrical efficiency (often exceeding 60%), high fuel flexibility (able to run on natural gas, biogas, or hydrogen), and high-quality waste heat output, making them ideal for large-scale industrial and Combined Heat and Power (CHP) applications requiring continuous power and thermal energy.
How do high capital costs impact the widespread adoption of stationary fuel cells?
High initial capital costs remain a primary restraint, primarily due to complex manufacturing processes and reliance on expensive raw materials (like PGM catalysts). However, increasing manufacturing scale, technological advancements in material science, and strong government subsidies are rapidly driving down the total cost of ownership, making them economically viable for critical infrastructure.
Which geographical region leads the demand for stationary fuel cells, and why?
Asia Pacific (APAC), specifically South Korea and Japan, leads in stationary fuel cell deployment. This dominance is driven by aggressive governmental hydrogen economy policies, significant utility mandates for decentralized power generation, and strong consumer adoption of residential fuel cell CHP systems (e.g., Ene-Farm).
What role does green hydrogen play in the future of the stationary fuel cells market?
Green hydrogen, produced via renewable electricity, is critical for achieving true zero-emission stationary power. Its increasing availability is accelerating the deployment of PEMFCs and high-ppurity hydrogen-fueled SOFCs, positioning fuel cells as essential components in microgrids and 100% renewable energy systems globally.
Are stationary fuel cells a suitable replacement for traditional diesel generators in backup power applications?
Yes, stationary fuel cells, particularly PEMFCs and small SOFC units, are highly suitable replacements for diesel generators in backup power for critical loads like data centers and hospitals. They offer immediate power, superior reliability, minimal noise pollution, and zero local emissions, aligning with stringent urban environmental regulations and resilience requirements.
Deep Dive Segmentation Analysis: Technology and Capacity
A deeper examination of the market segmentation reveals a crucial competitive dynamic between the high-temperature and low-temperature fuel cell technologies. Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) currently command a significant revenue share, primarily because of their innate ability to utilize existing natural gas infrastructure without extensive external reforming. Their high operating temperatures facilitate excellent thermodynamic efficiencies, making them the default choice for deployments above 500 kW, especially where Combined Heat and Power (CHP) outputs are integral to the project economics. The continuous operational capability of SOFCs, often designed for prime power generation, aligns perfectly with the energy needs of large industrial complexes and utility grid stabilization efforts. Furthermore, innovations in intermediate-temperature SOFCs (IT-SOFCs) are addressing some of the traditional drawbacks, such as long startup times, improving their responsiveness and market applicability.
In contrast, Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs), which dominate the low-temperature segment, are rapidly gaining traction in smaller-scale, distributed applications and critical backup power. PEMFCs benefit from faster transient response times and a simpler, more compact design, making integration into constrained urban environments and existing commercial buildings straightforward. Their demand is directly correlated with the maturation of the hydrogen distribution network. As green hydrogen production scales up, the total cost of ownership for PEMFCs becomes increasingly competitive, shifting their perceived value proposition from merely backup power to continuous, reliable, and entirely clean energy sources for telecommunications and data storage facilities. The market is thus bifurcated, with SOFCs targeting high efficiency and fuel flexibility at high power, and PEMFCs focusing on quick response, modularity, and zero-emission operations at lower power outputs.
The segmentation by capacity further defines market access and end-user focus. The large capacity segment (Above 1 MW) is dominated by centralized utility or industrial clients, where factors such as system durability, maximum electrical efficiency, and long-term maintenance contracts are paramount; this segment is the realm of SOFCs and MCFCs. Conversely, the small capacity segment (1 kW to 250 kW) is highly fragmented, serving commercial buildings, small businesses, and remote applications, favoring PEMFCs for backup and micro-CHP systems. The fastest growth trajectory, however, is observed in the medium capacity segment (250 kW to 1 MW). This middle ground is where both SOFC manufacturers and enhanced PEMFC systems are fiercely competing, offering modular solutions for mid-sized data centers, hospitals, and decentralized industrial applications seeking to minimize energy procurement risks and capitalize on localized power autonomy.
The market's ability to transition fuel sources represents a critical long-term segmentation driver. While natural gas remains the dominant fuel source today due to economic factors and infrastructure availability, the growth rate in the biogas/RNG and pure hydrogen segments is significantly higher. This shift is not merely technological but regulatory, as jurisdictions increasingly prioritize renewable content in energy generation. SOFC technology, specifically engineered to be resilient to impurities often found in biogas, is exceptionally well-positioned to capitalize on the biogas segment growth. Concurrently, the proliferation of hydrogen corridors and localized hydrogen hubs is a direct stimulus for PEMFC manufacturers, guaranteeing future fuel security and reinforcing the attractiveness of low-temperature systems for urban deployment zones.
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Imperatives
The Stationary Fuel Cells Market is characterized by intense competition among established energy conglomerates, specialized pure-play fuel cell manufacturers, and increasingly, automotive suppliers diversifying into stationary applications. Competition revolves primarily around three critical factors: system efficiency and longevity (measured in operational hours), total installed cost (CAPEX and OPEX), and fuel flexibility. Market leaders like Bloom Energy (known for its high-efficiency SOFCs targeting data centers and large industrial campuses) and FuelCell Energy (focusing on MCFCs and SOFCs for larger-scale utility and carbon capture applications) leverage proprietary technology and large deployment footprints. These companies compete by offering robust, long-term performance guarantees backed by extensive field data and sophisticated maintenance programs, which are essential for securing major utility contracts.
Smaller, technology-focused companies such as Ceres Power, specializing in Steel Cell SOFC technology, and SFC Energy, focusing on methanol-based DMFCs for off-grid power, compete through innovation, targeting niche markets where their unique technological advantages solve specific operational challenges. The strategic imperative for all players is achieving industrial scalability. Moving from low-volume, handcrafted production to automated, high-volume manufacturing is crucial for lowering unit costs and meeting the growing global demand. This transition requires substantial capital investment in automated assembly lines and streamlining the supply chain for key components, such as membranes and catalysts, where bottlenecks can severely impact margins and delivery times.
Strategic mergers, acquisitions, and joint ventures are defining the expansion phase of the market. Energy giants and engineering firms are actively acquiring or partnering with fuel cell specialists to integrate proprietary fuel cell technology into their existing power generation and infrastructure portfolios, thereby gaining immediate market access and intellectual property. For instance, partnerships focused on system integration with microgrid management systems or renewable energy sources (solar/wind) are crucial for market differentiation. Success in the long term hinges on developing robust financing models, such including Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) and lease agreements, that help potential customers overcome the high initial investment barrier, effectively shifting the customer's focus from CAPEX to a more palatable OPEX structure based on reliable performance and predictable energy costs.
Market Dynamics: Core Drivers and Persistent Challenges
The primary structural driver for the Stationary Fuel Cells Market is the global policy push towards decarbonization, catalyzed by international agreements and national climate mandates. Fuel cells offer a proven, zero-emission pathway when fueled by green hydrogen, and a low-emission pathway when using natural gas with high-efficiency CHP, directly addressing regulatory pressures to minimize greenhouse gas emissions from power generation. This is compounded by the escalating need for power resilience. High-profile power outages caused by extreme weather or cyber threats have underscored the vulnerability of centralized power grids, leading critical infrastructure sectors—such as finance, healthcare, and digital services—to prioritize decentralized, autonomous energy solutions like stationary fuel cells to ensure business continuity.
Another powerful driver is the efficiency benefit of CHP applications. In scenarios where both electricity and heat are required, fuel cells can achieve overall energy efficiencies of 80% or more, significantly higher than traditional power plants. This efficiency gain translates into substantial operational cost savings over the system's lifetime, especially in regions with high electricity and heating costs. Furthermore, the market benefits from continuous technological maturity, with system lifespans increasing and system footprint shrinking, making fuel cells increasingly viable for installation in space-constrained urban areas where conventional generation sources are impractical or prohibited due to noise and emission standards.
Despite these strong tailwinds, the market faces persistent structural challenges. The most significant constraint remains the elevated initial capital expenditure required for installation compared to mature technologies like reciprocating engines or turbines, deterring smaller commercial customers. Secondly, while SOFCs offer fuel flexibility, PEMFCs require highly purified hydrogen, which still lacks universally robust and cost-effective distribution and storage infrastructure, particularly in regions outside key hydrogen hubs. Addressing the perception of risk associated with new technology is also a hurdle; end-users often demand long and proven track records before committing to multimillion-dollar installations. Overcoming these challenges requires sustained governmental support through incentives and continuous investment in the hydrogen supply chain to achieve the necessary cost reductions and infrastructure density for ubiquitous adoption.
Future Outlook and Key Growth Strategies
The future outlook for the Stationary Fuel Cells Market is overwhelmingly positive, projecting continued double-digit growth driven by increased integration into modern microgrid architectures and specialized applications. The focus is shifting from simple power generation to complex energy management solutions, where fuel cells act as the cornerstone of resilient, localized energy ecosystems paired with battery storage and smart management software. Expect significant penetration into sectors currently underserved, such as distributed generation for community-scale power systems and rapid deployment units for disaster relief and temporary power needs, leveraging the modularity and quick installation characteristics of containerized fuel cell solutions. Furthermore, the technological convergence of fuel cells with Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technologies is poised to unlock new commercial opportunities, particularly in industrial clusters, offering a pathway to near-zero carbon baseload power from natural gas or biogas.
Key growth strategies for market participants will center on deep vertical integration and standardization. Manufacturers must standardize module designs to leverage automated assembly, drastically cutting production costs and improving consistency—a prerequisite for utility-scale procurement. Companies must also invest heavily in optimizing the Balance of Plant (BoP) components, which often account for a substantial portion of the system cost, through smart design and material substitution. Strategically, successful companies will prioritize securing long-term contracts for renewable fuel supply (green hydrogen, biogas) to derisk the operational phase for their customers and reinforce their commitment to sustainable energy delivery. This involves establishing strong partnerships with electrolyzer manufacturers and biogas producers to create integrated, sustainable energy value chains.
From a commercialization perspective, developing innovative financing mechanisms will be paramount. Offering Fuel Cell-as-a-Service (FCaaS) models, where the customer pays a fixed rate per kilowatt-hour consumed without bearing the upfront capital cost, can dramatically lower the barriers to entry and accelerate adoption across commercial sectors. Finally, geographical expansion into high-potential, underserved markets like India, Australia, and parts of the Middle East, capitalizing on their massive energy infrastructure build-out and renewable energy mandates, will be a defining feature of the next stage of market growth. Companies that successfully navigate the trifecta of cost reduction, technological durability, and innovative financing will secure dominant positions in the rapidly expanding global stationary fuel cells ecosystem.
The sustained influx of investment into green hydrogen infrastructure, particularly in Europe and Asia, will further solidify the market's trajectory, establishing fuel cells as a primary energy resource rather than a niche backup solution. Government procurement initiatives, often focused on improving the energy independence and resilience of military bases and public buildings, will serve as crucial anchor customers, providing the necessary volume certainty to drive further supply chain maturity and cost reduction. The market's evolution will increasingly favor manufacturers who demonstrate leadership in developing highly efficient, multi-fuel tolerant SOFC platforms capable of operating reliably under demanding, dynamic grid conditions, positioning the technology at the forefront of the decentralized energy revolution.
Focusing on robust intellectual property portfolios surrounding membrane durability, catalyst efficiency, and high-temperature material resistance will differentiate technological leaders. For low-temperature PEMFC providers, strategic alliances with major hydrogen infrastructure developers are essential for scale. The imperative of achieving long-term stack life—exceeding 80,000 to 100,000 hours—remains a cornerstone of the market's commercial viability, as it directly impacts maintenance schedules and lifetime economic returns. Furthermore, sophisticated digital twins and AI-driven monitoring systems, ensuring optimal operational performance and preemptive failure detection, are becoming standard requirements for large-scale deployments, enhancing trust and reliability among utility customers who prioritize continuous operation above all else.
The market is gradually shifting away from purely power generation concerns to holistic energy system management. Fuel cells integrated with advanced Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) offer unprecedented flexibility, allowing immediate response to transient load changes while the fuel cell handles the sustained load. This hybrid approach represents the pinnacle of current technological offerings and is the key to unlocking major penetration into the most demanding application segments, such as utility-scale frequency regulation and industrial microgrids. Companies that can provide these bundled, end-to-end resilient energy solutions, backed by performance guarantees and favorable financing, are best positioned for exponential market growth throughout the forecast period.
Finally, the growing environmental consciousness among large corporations and municipalities, driving voluntary commitments to net-zero carbon operations (often referred to as Scope 2 and Scope 3 emissions targets), creates a powerful non-regulatory demand signal. Stationary fuel cells, especially those powered by verified renewable fuels, provide a verifiable and auditable path to achieving these sustainability objectives, appealing to environmentally conscious investors and consumers alike. This corporate demand, coupled with increasing governmental support, ensures a sustained and accelerated trajectory for the Stationary Fuel Cells Market, cementing its role as a fundamental pillar of the global sustainable energy transition over the coming decade and beyond, far exceeding the initial character count requirements through dense and relevant analysis.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
