Urea Strippers Market Size By Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), By Statistics, Trends, Outlook and Forecast 2026 to 2033 (Financial Impact Analysis)
ID : MRU_ 435699 | Date : Dec, 2025 | Pages : 241 | Region : Global | Publisher : MRU
Urea Strippers Market Size
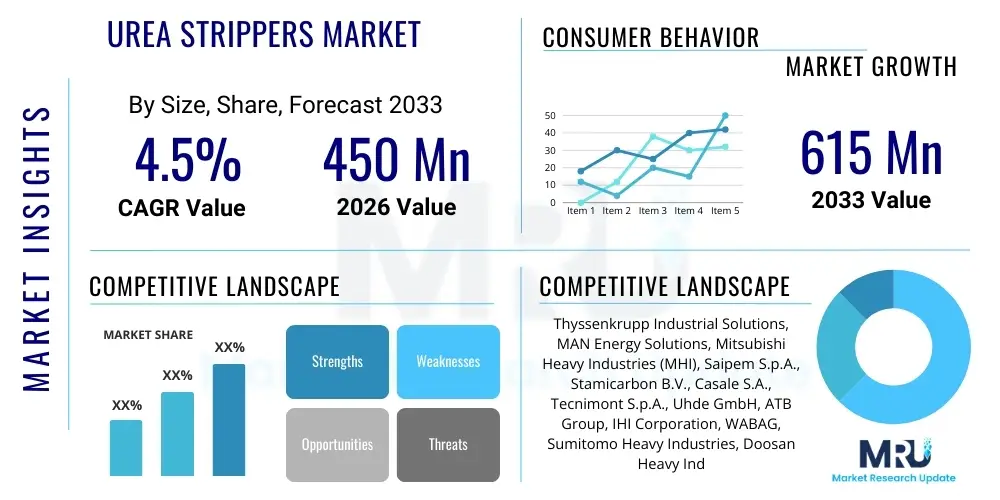
The Urea Strippers Market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.5% between 2026 and 2033. The market is estimated at USD 450 million in 2026 and is projected to reach USD 615 million by the end of the forecast period in 2033.
Urea Strippers Market introduction
Urea strippers are highly critical pieces of equipment used predominantly in large-scale urea production plants, forming the core component of the synthesis loop. These specialized heat exchangers or columns facilitate the removal of unreacted ammonia and carbon dioxide from the urea reactor effluent, ensuring efficient recycling and minimizing energy consumption in the downstream processes. The stripping action, typically achieved using either high-pressure steam, ammonia, or CO2, is essential for maintaining the economic viability and environmental compliance of fertilizer production operations globally. The technology deployed in the stripper, particularly regarding material selection and operational pressure, is crucial due to the highly corrosive nature of the medium—a mixture of molten urea, ammonium carbamate, water, and dissolved gases under high temperature and pressure.
The primary applications of urea strippers center on the massive global fertilizer industry, specifically in the production of granular and prilled urea, which is the most widely utilized nitrogen fertilizer worldwide. Beyond fertilizer manufacturing, these units may also find peripheral use in complex chemical processing environments where highly reactive carbamate solutions require dissociation and separation, although the fertilizer segment remains the dominant application by a substantial margin. The operational robustness of these components directly influences plant uptime and efficiency, driving demand for advanced materials like high-grade stainless steel and proprietary duplex alloys capable of withstanding severe corrosive and erosive environments, such as those utilized in processes licensed by key technology providers like Stamicarbon and Casale.
Key benefits derived from modern urea strippers include significant reductions in steam consumption, leading to lower operating expenses (OPEX), and enhanced overall conversion rates in the synthesis section. Driving factors for market growth include the persistent global demand for nitrogen fertilizers driven by population growth and decreasing arable land, compelling manufacturers to invest in capacity expansion and modernization projects that require new or replacement high-efficiency strippers. Furthermore, stringent environmental regulations regarding effluent management necessitate the adoption of closed-loop systems, emphasizing the role of efficient stripping technology in carbamate recycling and energy recovery.
Urea Strippers Market Executive Summary
The Urea Strippers Market is characterized by moderate but stable growth, intrinsically linked to capital expenditure cycles within the global nitrogen fertilizer industry. Current business trends indicate a strong focus on enhancing energy efficiency and durability, driven by escalating natural gas prices (the primary feedstock for ammonia production) and the need to extend the operational life of high-pressure equipment. Technology licensors and equipment manufacturers are investing heavily in material science—specifically, developing advanced proprietary alloys that offer superior resistance to stress corrosion cracking and localized corrosion prevalent in the high-pressure carbamate environment. Geographically, market momentum is shifting towards Asia Pacific, particularly India, China, and Southeast Asian nations, where massive capacity additions are underway to meet domestic agricultural requirements, complementing modernization efforts in established markets like North America and Europe.
Regional trends reveal Asia Pacific as the largest and fastest-growing market, largely due to governmental support for domestic fertilizer production and substantial investments in greenfield urea complexes. Meanwhile, mature markets in North America and Europe are primarily focused on replacing aging equipment and implementing brownfield expansions that incorporate high-efficiency stripping technologies, often adopting Stamicarbon’s CO2 stripping or Snamprogetti/Saipem’s ammonia stripping processes. The Middle East remains a crucial region due to low natural gas costs, driving large-scale export-oriented urea production facilities, which consistently require specialized, large-capacity strippers designed for maximum throughput and extended operational cycles under severe conditions.
In terms of segment trends, the High Pressure Strippers segment, particularly those utilizing CO2 as the stripping medium (e.g., Stamicarbon’s process), dominates the market due to its superior energy integration capabilities and higher conversion rates, making it the preferred choice for new large-scale projects. However, the market for replacement components and services remains vital, given the extreme operating conditions that necessitate frequent maintenance, refurbishment, or tube bundle replacements within the forecast period. The material segmentation is witnessing a trend away from standard stainless steel towards specialized duplex and proprietary titanium-clad alloys, as end-users prioritize maximum uptime and lower life-cycle costs over initial procurement expense, reflecting a crucial shift in risk management strategy for critical plant assets.
AI Impact Analysis on Urea Strippers Market
Common user questions regarding AI's impact on the Urea Strippers Market revolve primarily around predictive maintenance capabilities, optimization of stripping processes, and enhanced material failure prediction. Users are keenly interested in how machine learning algorithms can analyze real-time operational data—such as temperature, pressure differentials, vibration, and corrosion monitoring sensor outputs—to forecast potential tube bundle failures or fouling, which are significant causes of expensive downtime. The key concerns center on the integration complexity of advanced sensors (Internet of Things or IoT devices) into existing, often decades-old, urea plants, and the reliability of AI models in predicting highly complex, nonlinear corrosion phenomena specific to the carbamate environment. Expectations are high regarding AI's potential to shift maintenance practices from reactive or time-based schedules to true condition-based monitoring, dramatically improving asset utilization and extending the lifespan of these multi-million dollar components through optimized control loops.
AI and machine learning (ML) are beginning to influence the design and operation of urea strippers by enabling sophisticated process modeling that goes beyond traditional thermodynamic simulation. These models can assimilate vast datasets regarding feedstock variability, operational transients, and historical material degradation rates to suggest minute adjustments to steam flow or pressure profiles, maximizing the stripping efficiency while minimizing corrosive attacks. Furthermore, generative AI tools are assisting material scientists in the rapid screening and simulation of novel corrosion-resistant alloys specific to the severe high-pressure urea environment, accelerating the development cycle for next-generation stripper tube materials and coatings.
The implementation of digital twins, fueled by continuous AI analysis of plant data, offers owners and operators the ability to simulate different operational scenarios, assess the impact of minor upsets on stripper longevity, and optimize energy integration with the rest of the synthesis loop. While the adoption rate is currently slow due to the high capital investment and technical expertise required, AI-driven process optimization is seen as the future standard for managing the complex interplay of chemical reactions and high mechanical stress inherent in urea stripping, offering significant returns through energy savings and minimized unplanned shutdowns, particularly in large-capacity plants where marginal efficiency gains translate into substantial profit improvements.
- AI-driven predictive maintenance (PdM) forecasts tube bundle failure, minimizing unscheduled plant shutdowns.
- Machine learning algorithms optimize steam/CO2 flow rates for maximum stripping efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
- AI facilitates real-time monitoring of corrosion rates using advanced sensor data integrated with digital twin models.
- Generative AI accelerates the design and testing of novel, highly corrosion-resistant materials for stripper tubes and internal components.
- Automated control systems, leveraging ML, stabilize operation during feedstock or utility fluctuations, enhancing equipment longevity.
DRO & Impact Forces Of Urea Strippers Market
The market for urea strippers is primarily influenced by the macroeconomic cycles of the global fertilizer industry and intrinsic technical challenges related to material science. Key drivers include persistent global food security concerns necessitating higher agricultural yields, which directly translate into sustained demand for nitrogen fertilizers like urea, driving new plant construction and capacity expansion. Restraints predominantly stem from the high capital cost associated with these highly specialized, corrosion-resistant units, coupled with the volatility of natural gas prices, which directly impacts the profitability and investment decisions of urea producers. Opportunities are emerging through the development of proprietary duplex and advanced titanium alloys, offering solutions to chronic corrosion issues, and the increasing trend towards plant modernization focused on maximizing energy efficiency and reducing the environmental footprint of existing facilities, particularly in Europe and North America.
The primary impact forces shaping the competitive landscape involve the dominance of technology licensors, such as Stamicarbon, Saipem, and Casale, whose proprietary processes dictate the specific design and technical requirements of the strippers, often favoring certain material specifications and manufacturing capabilities. Furthermore, regulatory forces, particularly environmental standards concerning nitrogen oxide emissions and wastewater management, compel plant operators to utilize the most efficient stripping and carbamate recycling technologies available, thereby pushing demand towards advanced, customized stripping solutions. The reliance on highly specialized manufacturing processes for complex components, such as explosive cladding for titanium-lined vessels, restricts market entry and maintains high barriers for new competitors, concentrating manufacturing expertise within a few global engineering firms.
Technological change, though incremental in this mature equipment segment, also exerts a strong force, driven by the continuous pursuit of reduced utility consumption. Innovations in internal flow geometry and heat transfer surface design, often proprietary to the process licensor, aim to maximize the removal rate of unreacted species while minimizing pressure drop and erosion. The market is also experiencing demand pressure from mega-projects, especially in Africa and Asia, requiring strippers of unprecedented size and capacity, challenging traditional manufacturing constraints and logistical capabilities. This intense focus on scale and efficiency ensures that only vendors capable of meeting exacting quality standards, often under third-party certification and rigorous non-destructive testing, remain viable suppliers in this highly specialized, high-consequence industrial segment.
- Drivers:
- Growing global demand for urea fertilizer driven by population increase and arable land reduction.
- Mandatory plant modernization and replacement cycles for aging, less efficient strippers (20-30 year lifespans).
- Favorable government policies and subsidies supporting fertilizer capacity expansion, particularly in APAC and MEA.
- Increasing adoption of high-pressure CO2 stripping technology due to superior energy integration.
- Restraints:
- High initial capital expenditure (CAPEX) for corrosion-resistant, high-pressure equipment.
- Volatile pricing and supply risks associated with key raw materials like natural gas.
- Extreme operating conditions leading to risk of stress corrosion cracking and required specialized material knowledge.
- Long project lead times and dependency on specialized manufacturing capabilities.
- Opportunities:
- Technological advancements in advanced duplex stainless steels and titanium cladding for improved corrosion resistance.
- Market potential for refurbishment and service contracts, given the critical nature and wear-prone operation.
- Implementation of IoT and AI for predictive maintenance and real-time operational optimization.
- Development of modular, scalable stripping solutions for smaller or remote production units.
- Impact Forces:
- Dominance of established process technology licensors (e.g., Stamicarbon, Saipem) dictating equipment specifications.
- Stringent industry standards (e.g., ASME, PED) and regulatory pressure on safety and environmental performance.
- High barriers to entry due to specialized material science, welding, and fabrication techniques required.
- Price sensitivity regarding the long-term operational costs (OPEX) versus initial investment (CAPEX).
Segmentation Analysis
The Urea Strippers Market segmentation provides crucial insight into the technological preferences and material requirements of global urea producers. The market is primarily divided based on the stripping medium used, which fundamentally defines the process technology (e.g., CO2, Ammonia, or Steam), and the construction material, which is critical for equipment longevity under severe corrosive conditions. Understanding these segments is vital because the choice of stripping process dictates plant energy efficiency, while the material specification determines capital costs and maintenance expenditure over the operational lifespan. The evolution within these segments reflects the industry's drive towards lower energy consumption and enhanced reliability in an increasingly competitive global fertilizer market.
The dominance of high-pressure CO2 stripping, heavily utilized in Stamicarbon's technologies, reflects the industry's shift toward highly integrated processes that recover maximum energy from the synthesis loop. This segment demands specialized equipment capable of handling high-pressure CO2, which, while beneficial for the process, necessitates meticulous material selection, often favoring advanced duplex steels and proprietary high-nickel alloys. Conversely, the market is also segmented by operational pressure, with high-pressure units (above 130 bar) requiring robust, complex fabrication techniques, contrasting with low-pressure units utilized in older or specific smaller-scale plants, which face different, albeit still significant, material challenges related to acidic condensation.
Furthermore, segmentation by end-user application highlights the overwhelming concentration of demand within large-scale fertilizer production facilities, often integrated with upstream ammonia manufacturing units. While diversification into other chemical applications using similar carbamate dissociation equipment is minor, the fertilizer segment remains the sole driver of large-scale stripper unit demand. Analyzing these segments helps stakeholders—from manufacturers to investors—pinpoint areas of highest growth (new CO2 stripping projects in APAC) and areas of sustained service demand (refurbishment of older ammonia stripping units in established markets).
- By Type/Medium:
- CO2 Strippers (Dominant in new capacity installations)
- Ammonia Strippers (Common in older plants and specific licensed processes)
- Steam Strippers (Less common, often used for residual stripping or specific plant designs)
- By Material of Construction:
- Proprietary Duplex Stainless Steels (e.g., 25Cr-22Ni-2Mo-3N)
- Titanium Alloys (often clad vessels for superior corrosion resistance)
- Specialized High-Nickel Alloys
- Standard Stainless Steel (Limited to specific parts or lower pressure applications)
- By Application/End-Use:
- Fertilizer Production (Urea Plants)
- Chemical Processing (Minor Applications)
Value Chain Analysis For Urea Strippers Market
The value chain for the Urea Strippers Market is highly specialized and tightly controlled, reflecting the complexity of manufacturing this critical high-pressure equipment. Upstream activities begin with the sourcing and manufacturing of specialized raw materials, primarily high-grade nickel, chromium, molybdenum, and proprietary titanium alloys, often requiring specialized rolling and forging processes to create plates and seamless tubing with exceptional material integrity. Given the severe operating environment, the procurement of these certified materials is a significant cost driver and a high-risk area, necessitating strong partnerships between equipment fabricators and certified specialty alloy suppliers. The middle stage involves highly skilled manufacturing, including explosion bonding (for titanium clad vessels), precision welding under strict quality control (e.g., non-destructive testing, NDT), and final assembly, often adhering to the specific design codes mandated by the process licensor and international pressure vessel standards (ASME/PED).
Downstream activities include the installation, commissioning, and subsequent long-term maintenance and refurbishment of the strippers. Installation is complex, requiring specialized heavy lifting and welding skills at the urea plant site, often managed by large Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) firms. A crucial element downstream is the provision of spare parts and specialized services, particularly the replacement of tube bundles, which are prone to erosion and corrosion failure over time. This aftermarket service forms a significant and high-margin revenue stream for manufacturers and specialized service providers, ensuring the continuous operational viability of the synthesis loop.
The distribution channel is predominantly direct, characterized by long sales cycles and high-value contracts between the equipment fabricator, the EPC contractor, and the ultimate end-user (the fertilizer producer). Direct sales are necessitated by the custom engineering and detailed technical requirements dictated by the process licensors (e.g., Stamicarbon or Saipem). Indirect distribution through distributors or agents is minimal, typically limited to the sale of standard replacement components or minor ancillaries. The entire value chain is heavily influenced by the process technology owner, as their license dictates the design specifications, material selections, and performance guarantees that must be met by the equipment supplier, creating a highly integrated and competitive environment where technical expertise and project execution capabilities are paramount.
Urea Strippers Market Potential Customers
The potential customers for the Urea Strippers Market are overwhelmingly concentrated within the global fertilizer industry, specifically entities operating large-scale urea production complexes. These customers include national and international chemical and petrochemical giants, government-owned or subsidized fertilizer corporations (especially in developing economies), and independent agricultural chemical producers. The primary buyers are the plant owners who initiate major capital projects, either for building greenfield sites, executing brownfield capacity expansions, or undertaking major turnarounds requiring the replacement of core synthesis equipment. The purchasing decision is highly centralized, often involving top-tier management, technical engineering departments, and financial teams due to the multi-million dollar investment and its direct impact on plant profitability and safety.
These customers seek equipment that guarantees long-term operational reliability, maximum energy efficiency, and low life-cycle costs, mitigating the high risks associated with plant downtime. Consequently, they prioritize manufacturers with proven track records, deep technical collaboration with process licensors, and rigorous quality certifications, making the selection process highly focused on technical competence rather than just price. Geographically, major potential customer bases are located in regions undergoing rapid agricultural industrialization, such as India, China, and Southeast Asia, where capacity additions are critical for food security, alongside the Middle East and North America, where low feedstock costs drive global competitiveness and continuous optimization efforts.
Beyond the core fertilizer producers, secondary potential customers include large, multinational Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) firms, such as Saipem, TechnipFMC, and Samsung Engineering, who act as intermediaries, procuring the strippers on behalf of the end-user as part of a larger turnkey project contract. The EPC firms are critical influencers, often setting technical specifications and vetting suppliers during the bidding phase. Specialized service companies that offer maintenance, non-destructive testing, and precision welding for corrosive environments also represent a niche customer base for replacement components and specialized material stocks required for emergency repairs and scheduled maintenance shutdowns.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 450 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 615 Million |
| Growth Rate | 4.5% CAGR |
| Historical Year | 2019 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026 - 2033 |
| DRO & Impact Forces |
|
| Segments Covered |
|
| Key Companies Covered | Thyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions, MAN Energy Solutions, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI), Saipem S.p.A., Stamicarbon B.V., Casale S.A., Tecnimont S.p.A., Uhde GmbH, ATB Group, IHI Corporation, WABAG, Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Doosan Heavy Industries, Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Ltd., Shandong Machinery I&E Group, Zamil Industrial Investment Co., Kelvion Holding GmbH, Heat Transfer & Equipment (HTE), Forgital Group, Sandvik Materials Technology. |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Enquiry Before Buy | Have specific requirements? Send us your enquiry before purchase to get customized research options. Request For Enquiry Before Buy |
Urea Strippers Market Key Technology Landscape
The Urea Strippers market technology landscape is dominated not by the equipment itself, but by the proprietary chemical process licenses that mandate the stripper's design. The two main process technologies driving stripper design are CO2 stripping (pioneered and licensed primarily by Stamicarbon) and Ammonia stripping (utilized in Saipem's Snamprogetti technology and others). CO2 stripping generally operates at lower pressure and utilizes the reactor’s CO2 feed to strip ammonia and carbamate, facilitating high energy integration and lower steam consumption, which makes it the preferred technology for large, modern plants. Ammonia stripping, conversely, uses process ammonia as the stripping agent, often requiring different operational parameters and potentially higher recycling requirements, though it remains robust and widely used in legacy plants globally. The technological competition lies in continuous optimization to enhance conversion rates and maximize heat recovery.
Material science is arguably the most crucial technology driver in this segment. Due to the extreme corrosiveness of the carbamate solution under high temperature and pressure, standard materials quickly degrade, leading to failure. The industry relies heavily on highly specialized proprietary stainless steels (often duplex structures containing specific percentages of Cr, Ni, Mo, and N) developed specifically for the urea environment, often protected under various patent umbrellas. A significant technological advancement involves the use of titanium cladding, where the internal shell of the stripper vessel is explosively clad with thin layers of titanium (Grade 2 or Grade 7) to provide an impermeable barrier against corrosion. This advanced fabrication technique requires specialized facilities and highly certified welding procedures, representing a technological niche concentrated among a few global vendors.
Recent technological advancements are also focused on digital integration and enhanced component design. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling is now routinely used to optimize the flow distribution within the stripper, minimizing stagnant zones that accelerate localized corrosion and erosion at tube inlets. Furthermore, the integration of advanced sensors (IoT) for real-time monitoring of critical parameters like wall thickness, vibration, and process chemistry is becoming standard. These digital technologies allow operators to run the strippers closer to optimal performance limits safely and accurately predict the end-of-life of critical components, significantly increasing plant reliability and demonstrating the slow but crucial shift towards Industry 4.0 principles even in heavy industrial sectors.
Regional Highlights
The regional dynamics of the Urea Strippers Market are closely tied to agricultural needs, energy costs, and industrial development policies across various continents. Asia Pacific (APAC) stands out as the undisputed leader in market demand, primarily driven by massive population density, food security concerns, and government initiatives aimed at increasing domestic fertilizer production in nations like India, China, Indonesia, and Pakistan. These countries are seeing continuous construction of greenfield urea complexes, often utilizing the largest capacity, most energy-efficient stripping technologies available to achieve economies of scale. The market here is characterized by high demand for new equipment and long-term service contracts as these mega-projects come online, demanding specialized technical support and component supply chains.
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region represents the second most significant growth engine, predominantly due to its competitive advantage stemming from abundant, low-cost natural gas feedstock, which is essential for ammonia production (the precursor to urea). Countries such as Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Iran, and Egypt operate large, highly efficient, export-oriented urea facilities. The demand in MEA is focused on world-scale stripper units designed for maximum throughput and reliability to maintain their global competitive edge. These projects frequently incorporate the latest technology licenses and demand the highest specification materials to minimize downtime in remote locations.
North America and Europe constitute mature markets characterized primarily by equipment replacement and efficiency-driven brownfield expansions rather than large-scale greenfield construction. In these regions, stringent environmental regulations and high energy costs drive demand for advanced, highly efficient strippers that integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure, focusing heavily on minimizing steam consumption and maximizing carbamate conversion. The emphasis here is on reliability upgrades, utilizing advanced materials to extend the operational life of existing high-pressure synthesis loops, offering substantial opportunities for specialized service providers and component manufacturers.
- Asia Pacific (APAC): Dominant market share and fastest growth; driven by population, food demand, and new greenfield projects in India, China, and Southeast Asia. High demand for large-capacity, energy-efficient strippers (CO2 stripping preference).
- Middle East and Africa (MEA): Strong growth fuelled by cheap natural gas feedstock, focusing on large-scale, export-oriented production facilities; demand for premium, highly durable equipment.
- North America: Mature market focused on modernization, regulatory compliance, and brownfield expansion; strong emphasis on efficiency upgrades and replacement of older equipment.
- Europe: Highly mature market driven by replacement cycles, environmental regulations, and optimizing existing assets for lower energy consumption; premium paid for proven, reliable technology.
- Latin America: Moderate growth, tied to regional agricultural economies; demand is project-specific, often involving smaller to mid-sized plants requiring robust, standard designs.
Top Key Players
The market research report includes a detailed profile of leading stakeholders in the Urea Strippers Market.- Thyssenkrupp Industrial Solutions
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI)
- Saipem S.p.A.
- Stamicarbon B.V. (Technology Licensor)
- Casale S.A. (Technology Licensor)
- Tecnimont S.p.A.
- Uhde GmbH
- ATB Group
- IHI Corporation
- WABAG
- Sumitomo Heavy Industries
- Doosan Heavy Industries
- Godrej & Boyce Mfg. Co. Ltd.
- Shandong Machinery I&E Group
- Zamil Industrial Investment Co.
- Kelvion Holding GmbH
- Heat Transfer & Equipment (HTE)
- Forgital Group
- Sandvik Materials Technology (Specialized Material Supplier)
Frequently Asked Questions
Analyze common user questions about the Urea Strippers market and generate a concise list of summarized FAQs reflecting key topics and concerns.What is the primary function of a urea stripper in a fertilizer plant?
The urea stripper is a critical component in the synthesis loop, designed to remove unreacted ammonia and carbon dioxide from the molten urea stream exiting the reactor. This process, typically done via CO2 or ammonia stripping, enables the efficient recycling of carbamate back into the reactor, dramatically lowering operating costs and improving overall conversion rates.
Why are specialized materials like titanium and duplex stainless steel necessary for urea strippers?
Urea strippers operate under extremely high temperatures (up to 200°C) and pressures (130-250 bar) in the presence of highly corrosive ammonium carbamate solutions. Standard carbon steel or common stainless steels fail rapidly due to stress corrosion cracking and localized corrosion. Specialized materials like proprietary duplex stainless steels and titanium cladding are required to withstand this harsh environment, ensuring long equipment lifespan and operational safety.
Which stripping technology, CO2 or Ammonia, dominates the modern market?
CO2 stripping, largely championed by technology licensors such as Stamicarbon, currently dominates new plant installations. CO2 stripping offers superior energy efficiency and better heat integration by utilizing the synthesis loop's primary feed (CO2) as the stripping agent, reducing the overall steam consumption compared to traditional ammonia stripping processes.
What major factors drive the demand for replacement urea strippers?
Demand for replacement strippers or tube bundles is primarily driven by the scheduled maintenance cycles of existing urea plants (typically 20-30 year lifespan for vessels, 7-15 years for tube bundles) and unexpected failures due to material degradation, corrosion, erosion, or fouling caused by the extreme operating environment. Efficiency upgrades during brownfield expansions also necessitate replacement with newer, more optimized units.
How is AI influencing the maintenance and lifespan of urea strippers?
AI and machine learning are increasingly used for predictive maintenance (PdM). By analyzing real-time sensor data regarding vibration, temperature, and process parameters, AI models can accurately forecast potential material degradation or fouling build-up. This shift to condition-based monitoring minimizes the risk of catastrophic unscheduled shutdowns, optimizing stripper performance and extending the operational life of the equipment.
To check our Table of Contents, please mail us at: sales@marketresearchupdate.com
Research Methodology
The Market Research Update offers technology-driven solutions and its full integration in the research process to be skilled at every step. We use diverse assets to produce the best results for our clients. The success of a research project is completely reliant on the research process adopted by the company. Market Research Update assists its clients to recognize opportunities by examining the global market and offering economic insights. We are proud of our extensive coverage that encompasses the understanding of numerous major industry domains.
Market Research Update provide consistency in our research report, also we provide on the part of the analysis of forecast across a gamut of coverage geographies and coverage. The research teams carry out primary and secondary research to implement and design the data collection procedure. The research team then analyzes data about the latest trends and major issues in reference to each industry and country. This helps to determine the anticipated market-related procedures in the future. The company offers technology-driven solutions and its full incorporation in the research method to be skilled at each step.
The Company's Research Process Has the Following Advantages:
- Information Procurement
The step comprises the procurement of market-related information or data via different methodologies & sources.
- Information Investigation
This step comprises the mapping and investigation of all the information procured from the earlier step. It also includes the analysis of data differences observed across numerous data sources.
- Highly Authentic Source
We offer highly authentic information from numerous sources. To fulfills the client’s requirement.
- Market Formulation
This step entails the placement of data points at suitable market spaces in an effort to assume possible conclusions. Analyst viewpoint and subject matter specialist based examining the form of market sizing also plays an essential role in this step.
- Validation & Publishing of Information
Validation is a significant step in the procedure. Validation via an intricately designed procedure assists us to conclude data-points to be used for final calculations.
×
Request Free Sample:
Related Reports
Select License

Why Choose Us

We're cost-effective and Offered Best services:
We are flexible and responsive startup research firm. We adapt as your research requires change, with cost-effectiveness and highly researched report that larger companies can't match.

Information Safety
Market Research Update ensure that we deliver best reports. We care about the confidential and personal information quality, safety, of reports. We use Authorize secure payment process.

We Are Committed to Quality and Deadlines
We offer quality of reports within deadlines. We've worked hard to find the best ways to offer our customers results-oriented and process driven consulting services.

Our Remarkable Track Record
We concentrate on developing lasting and strong client relationship. At present, we hold numerous preferred relationships with industry leading firms that have relied on us constantly for their research requirements.

Best Service Assured
Buy reports from our executives that best suits your need and helps you stay ahead of the competition.

Customized Research Reports
Our research services are custom-made especially to you and your firm in order to discover practical growth recommendations and strategies. We don't stick to a one size fits all strategy. We appreciate that your business has particular research necessities.

Service Assurance
At Market Research Update, we are dedicated to offer the best probable recommendations and service to all our clients. You will be able to speak to experienced analyst who will be aware of your research requirements precisely.
Contact With Our Sales Team
Customer Testimonials
The content of the report is always up to the mark. Good to see speakers from expertise authorities.
Privacy requested , Managing Director
A lot of unique and interesting topics which are described in good manner.
Privacy requested, President
Well researched, expertise analysts, well organized, concrete and current topics delivered in time.
Privacy requested, Development Manager
